
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1744375
어뢰 시장(2025-2035년)Global Torpedo Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
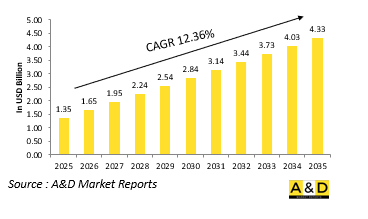
세계의 어뢰 시장 규모는 2025년에 13억 5,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2025-2035년 12.36%의 연간 평균 성장률(CAGR)로 확대될 전망이며, 2035년까지 43억 3,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.

어뢰 시장 서문 :
어뢰는 주로 잠수함, 수상함, 항공기에 의해 사용되며 해군의 위협을 교차하고 무력화하기 위해 불가결한 수중 병기입니다. 이러한 자주식 탄약은 직접 충격 또는 근접 폭발을 통해 적 잠수함이나 수상함을 추적하고 파괴하도록 설계되었습니다. 해군의 기뢰나 폭뢰와는 달리 어뢰는 탑재된 유도 시스템을 사용하여 능동적으로 목표를 찾아낼 수 있기 때문에 해상에서의 공격적이고 방어적인 작전에서 매우 효과적입니다. 그 관련성은 평시의 억제력, 전시의 타격 임무 및 대접근 전략에 이릅니다. 해상영역이 더욱 쟁탈적으로 됨에 따라 어뢰는 스텔스성, 기습성, 살상력을 제공함으로써 해중전에서 중심적인 역할을 하고 있습니다. 현대의 해군 전술은 특히 초크 포인트나 영해에서 수중에서의 우위성과 전략적 억제력을 유지하기 위해 점점 더 이 무기에 의존하고 있습니다. 디젤 전기 잠수함에서 장거리 초계기까지 다양한 플랫폼에 장착되는 어뢰는 해군 능력의 중요한 층을 형성하고 있습니다. 어뢰는 또한 해상 연락선을 확보하고 적대 해군의 수상 침공을 억제하는 데 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다. 세계 방위 커뮤니티는 비대칭적이고 고강도 분쟁 시나리오에서 어뢰의 영구적인 가치를 인식하고 어뢰 개발을 계속 우선시하고 있습니다. 어뢰의 지속적인 진화는 해저 지배와 통합된 해상 전투 준비로의 광범위한 전환을 반영하고 있습니다.
어뢰 시장에서의 기술 영향 :
기술의 진보는 해상 방위에서 현대 어뢰의 능력과 역할을 크게 변화시켰습니다. 추진 시스템의 혁신은 보다 조용하고 빠른 어뢰를 가져오고 공격 정확도를 향상시키면서 탐지 위험을 줄이고 있습니다. 서멀 엔진, 선진적인 전기 모터, 개량된 유체역학에 의해, 이러한 병기는 보다 높은 스텔스성으로 보다 장거리의 운용이 가능하게 되어 있습니다. 유도에 관해서는 신형은 선진적인 소나, 항적호밍 센서, 관성항법 시스템을 통합하고 있어 복잡한 환경에 적응하고 대항책을 능가할 수 있습니다. 인공지능과 자율적인 조준 알고리즘도 등장해 어뢰가 오퍼레이터의 입력을 최소화하면서 미끼와 정당한 위협을 구별할 수 있게 돼 있습니다. 강화된 데이터 링크 기능을 통해 발사 후 코스 중간 업데이트가 가능해지며 운영자는 보다 유연한 제어를 할 수 있습니다. 탄두 설계는 컴팩트함과 안전성을 유지하면서 더 집중적이고 효과적인 데미지를 주도록 진화하고 있습니다. 게다가 모듈러 아키텍처를 통해 신속한 업그레이드와 미션에 특화된 구성이 가능합니다. 이러한 기술적 진보는 살상력을 높일 뿐만 아니라 고도화되는 대잠수함전 시스템에 대한 생존성도 향상시키고 있습니다. 네트워크 중심의 해군 작전으로의 통합과 맞물려 최신 어뢰는 현재 전략적 억제력과 고도로 경합하는 해저 환경에서 정밀 도구 역할을 하며, 기존형과 비대칭형의 해상 전역에서 성공적인 임무 수행을 지원하고 있습니다.
어뢰 시장의 주요 촉진요인 :
몇 가지 중요한 요소가 현대 해군 전략에서 어뢰의 세계 개발과 배포를 추진하고 있습니다. 각국이 전략적 수로와 해양자원을 확보하려고 하고 있는 가운데, 해저 영역에서의 우위를 둘러싼 경쟁의 격화가 큰 영향을 미치고 있습니다. 잠수함의 활동은 감시와 억제의 양면에서 활발해지고 있으며, 효과적인 수중 공격 옵션의 필요성이 강조되고 있습니다. 중층 방어 및 신속한 대응 능력을 선호하는 해군 독트린의 진화는 공격 태세와 방위 태세 모두에서 어뢰의 관련성을 강화하고 있습니다. 무인 플랫폼의 통합과 연안 작전의 확대에는 얕고 좁은 수역에서 활동할 수 있는 컴팩트하고 효율적인 어뢰가 필요합니다. 지역 핫스팟에서 대잠수함의 위협에 대한 우려는 다양한 잠수함과 수상 적을 대항하도록 설계된 어뢰에 대한 투자를 더욱 촉진합니다. 또한 블루워터 작전에 있어서의 전력 투사에 중점을 두는 것으로, 장거리형이나 멀티 롤형의 개발이 촉진되고 있습니다. 현대 해군은 또한 자립을 중시하고 있으며, 국산 어뢰의 설계 및 생산에 관한 연구 증가를 촉진하고 있습니다. 작전 즉각성과 유연한 배포 옵션은 여전히 중요한 목표이며 발사 시스템 및 저장 능력을 강화합니다. 이러한 원동력은 신뢰할 수 있는 억지력을 유지하고, 해상에서의 전술적 선택을 개선하고, 갈등이 격화하는 세계적인 안보 환경에서 해상에서의 우위성을 확보하는 전략적 전환을 반영하고 있습니다.
어뢰 시장의 지역 동향 :
어뢰의 개발과 배치는 지역에 따라 다르며, 명확한 해양 전략 및 위협 인식에 의해 형성되고 있습니다. 인도 태평양 지역에서는 해군 경쟁과 영토 분쟁이 격화되고 있으며, 특히 잠수 함대 확대와 해저 지배 확립을 목표로 하는 국가들에 의해 선진적인 어뢰 시스템에 대한 대규모 투자가 이루어지고 있습니다. 연안국과 군도국은 대잠능력을 강화하고 있으며, 얕은 물이나 혼잡한 해역에 적합한 기민한 어뢰를 중시하고 있습니다. 유럽에서는 상호운용성과 현대화에 초점이 맞춰져 있으며, 방위 프로그램은 종종 NATO 표준에 맞추기 위해 레거시 어뢰를 업그레이드하는 것을 목적으로 하고 있습니다. 이 지역에서는 시레인 보호와 지역 불안정 대응이 중시되고 있기 때문에 중량형과 경량형 모두에 대한 수요가 안정적입니다. 전략적인 해상 교통의 요충지를 안고 있는 중동은 연안 시설의 안전 확보와 수상 침공 억제를 목적으로 하는 광범위한 해군 방위망의 일부로서 어뢰에 의존하고 있습니다. 북미는 고도의 유도 시스템과 멀티 도메인 플랫폼과의 통합을 중시하여 기술적 세련성 면에서 계속해서 선도하고 있습니다. 한편 남미와 아프리카 일부에서는 근대화 노력과 지역 협력으로 어뢰 능력이 점차 확대되고 있습니다. 이러한 지역 전체에서 효과적인 해저 무기가 해상 억제, 함대 방위, 장기적인 전략적 안전 보장 계획의 중심이라는 폭넓은 인식을 반영하고 있습니다.
주요 어뢰 프로그램
인도 국방부는 이 나라의 잠수함 능력을 대폭 강화하는 것을 목적으로 한 2개의 대형 계약에 조인했습니다. 하나는 프랑스 해군그룹과 선진 전자중어뢰(EHWT) 구매에 관한 계약으로 금액은 877크로입니다. 또 하나는, 뭄바이를 거점으로 하는 마자곤 독 조선소와 신형의 공기 독립 추진(AIP) 시스템을 통합하기 위한, 약 1,990억 크로의 대형 계약입니다. AIP 기술은 국방연구개발기구(DRDO)가 독자적으로 개발한 것으로, 'Atmanirbhar Bharat'(자립된 인도) 구상하에 큰 뒷받침이 됩니다. 두 계약을 합하면, 총액 2,867크로가 되어, 인도 잠수 함대의 내구성, 살상력, 자립성을 강화하는데 있어서 큰 전진이 됩니다.
본 보고서에서는 세계의 어뢰 시장에 대해 조사했으며, 10년간의 부문별 시장 예측, 기술 동향, 기회 분석, 기업 프로파일, 국가별 데이터 등을 정리했습니다.
목차
어뢰 시장 보고서 정의
어뢰 시장 세분화
지역별
시작 플랫폼별
유형별
향후 10년간 어뢰 시장 분석
이 장에서는 10년간의 어뢰 시장 분석을 통해 어뢰 시장의 성장, 변화하는 동향, 기술 채용의 개요 및 시장의 매력에 대한 자세한 개요를 제공합니다.
어뢰 시장에서 시장 기술
이 부문에서는 이 시장에 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상되는 상위 10개 기술과 이러한 기술이 시장 전체에 미칠 수 있는 영향에 대해 설명합니다.
세계 어뢰 시장 예측
이 시장의 10년간의 어뢰 시장 예측은 위의 전체 부문에서 자세히 설명합니다.
지역별 어뢰 시장 동향 및 예측
이 분야에서는 지역별 어뢰 시장 동향, 촉진요인, 과제, 그리고 정치, 경제, 사회, 기술 등의 측면을 망라하고 있습니다. 또, 지역별 시장 예측 및 시나리오 분석도 상세하게 다루고 있습니다. 지역 분석의 최종 단계에서는 주요 기업의 프로파일링, 공급업체의 정세, 기업 벤치마크 등에 대해 분석하고 있습니다. 현재 시장 규모는 일반 시나리오에 따라 추정되고 있습니다.
북미
촉진요인, 억제요인 및 과제
PEST
시장 예측 및 시나리오 분석
주요 기업
공급자 계층의 상황
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
어뢰 시장의 국가별 분석
이 장에서는 이 시장에서 주요 방위 프로그램을 다루며 이 시장에서 신청된 최신 뉴스와 특허에 대해서도 설명하고, 국가 수준의 10년간 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석에 대해서도 설명합니다.
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장의 현재 기술 성숙도
시장 예측 및 시나리오 분석
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
어뢰 시장 기회 행렬
어뢰 시장 보고서에 관한 전문가의 의견
결론
항공 및 방위 시장 보고서에 대해서
AJY 25.06.18The Global Torpedo market is estimated at USD 1.35 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 4.33 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.36% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Introduction to Torpedo Market:
Torpedoes are essential underwater weapons used primarily by submarines, surface ships, and aircraft to engage and neutralize naval threats. These self-propelled munitions are designed to track and destroy enemy submarines and surface vessels through direct impact or proximity detonation. Unlike naval mines or depth charges, torpedoes can actively seek out targets using onboard guidance systems, making them highly effective in both offensive and defensive maritime operations. Their relevance spans peacetime deterrence, wartime strike missions, and anti-access strategies. As maritime domains become more contested, torpedoes play a central role in undersea warfare by offering stealth, surprise, and lethality. Modern naval tactics increasingly depend on these weapons to maintain underwater superiority and strategic deterrence, especially in choke points and territorial waters. Equipped on a variety of platforms-from diesel-electric submarines to long-range patrol aircraft-torpedoes form a critical layer of naval capability. They are also instrumental in securing sea lines of communication and in deterring surface incursions by hostile navies. The global defense community continues to prioritize torpedo development, recognizing their enduring value in asymmetric and high-intensity conflict scenarios. Their continued evolution reflects a broader shift toward undersea dominance and integrated maritime combat readiness.
Technology Impact in Torpedo Market:
Technological advancements have profoundly reshaped the capabilities and roles of modern torpedoes in maritime defense. Innovations in propulsion systems have led to quieter and faster torpedoes, reducing detection risk while improving strike precision. Thermal engines, advanced electric motors, and improved hydrodynamics enable these weapons to operate over longer distances with greater stealth. In terms of guidance, newer models integrate advanced sonar, wake-homing sensors, and inertial navigation systems, allowing them to adapt to complex environments and outmaneuver countermeasures. Artificial intelligence and autonomous targeting algorithms are also emerging, enabling torpedoes to distinguish between decoys and legitimate threats with minimal operator input. Enhanced data-link capabilities provide mid-course updates, giving operators more control and flexibility after launch. Warhead design has evolved to deliver more focused and effective damage while maintaining compactness and safety. Additionally, modular architecture allows for rapid upgrades and mission-specific configurations. These technological gains are not only boosting lethality but also improving survivability against increasingly sophisticated anti-submarine warfare systems. Combined with integration into network-centric naval operations, modern torpedoes now serve as both strategic deterrents and precision tools in highly contested undersea environments, supporting mission success across both conventional and asymmetric maritime theaters.
Key Drivers in Torpedo Market:
Several critical factors are propelling the global development and deployment of torpedoes in contemporary naval strategies. The growing competition for dominance in undersea domains is a major influence, as nations seek to secure strategic waterways and maritime resources. Increased submarine activity-both for surveillance and deterrence-has underscored the need for effective underwater strike options. Evolving naval doctrines that prioritize layered defense and rapid-response capabilities reinforce the relevance of torpedoes in both offensive and defensive postures. The integration of unmanned platforms and the expansion of littoral operations require compact, efficient torpedoes capable of operating in shallow and confined waters. Concerns over anti-submarine threats in regional hotspots further drive investment in torpedoes designed to counter a variety of submersible and surface adversaries. Additionally, a focus on force projection in blue-water operations encourages the development of long-range and multi-role variants. Modern navies are also emphasizing self-reliance, prompting increased research into indigenous torpedo design and production. Operational readiness and flexible deployment options remain key goals, leading to enhancements in launch systems and storage capabilities. These drivers collectively reflect a strategic shift toward maintaining credible deterrence, improving tactical options at sea, and ensuring maritime superiority in an increasingly contested global security environment.
Regional Trends in Torpedo Market:
Torpedo development and deployment vary by region, shaped by distinct maritime strategies and threat perceptions. In the Indo-Pacific, heightened naval competition and territorial disputes have led to significant investments in advanced torpedo systems, particularly by nations aiming to expand their submarine fleets and assert undersea dominance. Coastal and archipelagic states are enhancing their anti-submarine capabilities, emphasizing agile torpedoes suited for shallow and congested waters. In Europe, the focus is on interoperability and modernization, with defense programs often aimed at upgrading legacy torpedoes to align with NATO standards. The region's emphasis on protecting sea lanes and responding to regional instability contributes to steady demand for both heavy and lightweight variants. The Middle East, with its strategic maritime chokepoints, relies on torpedoes as part of broader naval defense networks aimed at securing coastal installations and deterring surface incursions. North America continues to lead in terms of technological sophistication, emphasizing advanced guidance systems and integration with multi-domain platforms. Meanwhile, in South America and parts of Africa, torpedo capabilities are expanding gradually through modernization efforts and regional cooperation. Across these regions, the trajectory reflects a broader recognition that effective undersea weaponry is central to maritime deterrence, fleet defense, and long-term strategic security planning.
Key Torpedo Program:
India's Ministry of Defence has signed two major contracts aimed at significantly strengthening the country's submarine capabilities. One agreement, valued at ₹877 crore, was signed with France's Naval Group for the acquisition of advanced Electronic Heavy Weight Torpedoes (EHWT). The second and larger contract, worth approximately ₹1,990 crore, was signed with Mumbai-based Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders for the integration of a new Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) system. The AIP technology, developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), is a major boost under the 'Atmanirbhar Bharat' (self-reliant India) initiative. Together, the contracts total ₹2,867 crore and mark a significant step forward in enhancing the endurance, lethality, and self-reliance of India's submarine fleet.
Table of Contents
Torpedo Market Report Definition
Torpedo Market Segmentation
By Region
By Launch Platform
By Type
Torpedo Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year torpedo market analysis would give a detailed overview of torpedo market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Torpedo Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Torpedo Market Forecast
The 10-year torpedo market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Torpedo Market Trends & Forecast
The regional torpedo market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Torpedo Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Torpedo Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Torpedo Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.



















