
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1811816
감시 레이더 시장(2025-2035년)Global Surveillance Radar Market 2025 - 2035 |
||||||
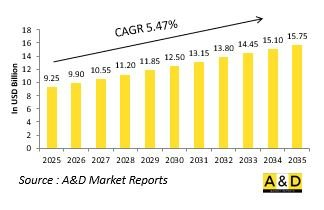
세계의 감시 레이더 시장 규모는 2025년 92억 5,000만 달러로 추정되며, 2035년까지 157억 5,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있으며, 예측 기간인 2025-2035년의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)은 5.47%가 될 것으로 보입니다.

감시 레이더 시장의 소개
방위 감시 레이더 시장은 현대 안보 인프라에 필수적인 부분으로 항공, 해상 및 지상 위협의 감지, 추적 및 모니터링을 지원합니다. 이 시스템은 조기 경계와 상황 인식을 제공하도록 설계되었으며, 군가 방어와 공격 전략 모두에서 정보를 기반으로 결정을 내릴 수 있도록합니다. 기상 및 항공 관제에 주안을 두는 민간 레이더와 달리, 방어 감시 레이더는 탄력성, 정밀도, 적대적 상황 하에서의 운용 능력을 중시하여 설계되어 있습니다. 스텔스 기계와 무인 항공기에서 극초음속 무기 및 저고도 순항 미사일에 이르기까지 군가 점점 복잡해지는 위협에 직면함에 따라 이러한 레이더의 중요성이 커지고 있습니다. 그 역할은 전투에만 그치지 않고, 국경 경비, 연안 감시, 평화 유지 활동에도 빠뜨릴 수 없습니다. 시장은 대규모 고정 설비에서 분쟁 지역으로 신속하게 배치할 수 있는 이동식 유닛에 이르기까지 다양한 시스템을 포함하도록 발전해 왔습니다. 이 다양성은 현대 방어 전략에서 유연성의 필요성을 반영합니다. 통합적인 방공 및 미사일 방어가 중시되는 가운데, 감시 레이더는 감지 네트워크의 요점으로 계속해서, 분쟁 환경에서의 활동을 종합적으로 파악해, 자국의 영공과 영해를 지키는 것을 국가에 보증하고 있습니다.
감시 레이더 시장의 기술 영향
기술의 진보는 방어 감시 레이더의 능력을 재구성하고 감지 범위, 정밀도, 대항 조치에 대한 내성을 향상시키고 있습니다. 가장 획기적인 개발 중 하나는 능동 전자 스캔 어레이 시스템의 광범위한 채택으로 레이더는 가로챌 확률을 낮게 유지하면서 여러 목표를 동시에 추적 할 수 있습니다. 이 기술은 적이 기존의 레이더 신호를 교란하기 위해 전자전을 전개하는 분쟁 공역에서의 응답성과 생존성을 향상시킵니다. 디지털 신호 처리와 인공지능의 발전으로 성능이 더욱 향상되었습니다. 최신 레이더는 백그라운드 크러터를 필터링하고 실제 위협과 디코이를 구별하며 실시간으로 실용적인 통찰력을 제공할 수 있습니다. 또한 이러한 시스템은 지휘 통제 네트워크와도 통합되어 하늘, 육지, 바다 영역에서 데이터를 원활하게 공유할 수 있습니다. 이러한 연결성은 신속한 조정이 임무의 성공을 좌우하는 공동작전이나 연합작전에 있어서 매우 중요합니다. 시장 개척과 소형화 기술도 시장을 형성하고 있어 차량이나 선박, 심지어 무인 플랫폼에 탑재 가능한, 보다 경량으로 기동성이 높은 시스템의 개발을 가능하게 하고 있습니다. 한편, 양자 레이더와 패시브 레이더의 개념에 관한 조사는 스텔스 기술에 대항하는 것을 목적으로 한 미래의 방향성을 부각하고 있습니다. 이러한 기술 혁신이 쌓여 감시 레이더는 현대 차세대 방어 전략에 필수적인 존재로 남아 있습니다.
감시 레이더 시장의 주요 촉진요인
방위 감시 레이더 시장의 성장은 진화하는 안보 요건과 위협의 고도화에 의해 촉진됩니다. 각국은 영공, 해안선, 중요한 인프라를 지키기 위해서는 조기 발견이 기본임을 인식하고 있습니다. 무인 항공기 시스템, 스텔스 기술, 첨단 미사일 시스템의 보급으로 지금까지보다 작고 빠르고 감지하기 어려운 위협을 식별 할 수있는 레이더에 대한 수요가 탄생했습니다. 또 다른 큰 추진력은 통합 방어 시스템의 중요성입니다. 현대 군은 단순히 감지뿐만 아니라 요격 미사일, 항공기, 사령부와 원활하게 연결하는 레이더를 찾고 있습니다. 이 상호 운용성은 여러 영역의 위협에 대한 협력적인 대응을 가능하게 하고 계층화된 방어 아키텍처를 강화합니다. 탄도 미사일 방어의 중요성이 높아짐에 따라 광대한 거리의 고속 발사체를 추적할 수 있는 장거리 레이더에 대한 의존도가 더욱 높아지고 있습니다. 방위 근대화를 위한 예산 배분도 중요한 역할을 합니다. 각국 정부는 통상전과 비대칭전의 시나리오에 대비하기 위해 레이더 기술에 대한 투자를 우선하고 있습니다. 게다가 재해 감시나 국경 감시 등 비전투적 역할에 대한 방위군의 관여가 증가하고 있는 것도 안정적인 수요를 확보하고 있습니다. 이러한 요인들을 종합하면 탄력적이고 미래에 대비할 수 있는 방어 전략을 형성하는데 감시 레이더가 중심적인 역할을 한다는 것이 분명해집니다.
감시 레이더 시장의 지역 동향
방어 감시 레이더 시장의 지역 동향은 지리적 요구, 안보 과제, 기술 우선순위의 융합을 반영합니다. 해양 국가는 광대한 해로를 감시하고, 잠재적인 침입을 억제하기 위해 해안 및 해군 레이더 시스템을 중시하고, 내륙 지역은 공중으로부터의 침입을 방지하기 위해 국경 감시 및 방공 레이더에 중점을 둡니다. 따라서 지역은 레이더 조달 전략에 큰 영향을 미칩니다. 방위 선진국은 전자 주사식 위상배열와 장거리 조기 경계 레이더와 같은 최첨단 기술의 채택을 주도하고 있습니다. 이들의 초점은 스텔스기나 극초음속의 위협에 대항할 수 있는 통합 방공 및 미사일 방어 시스템의 구축에 있습니다. 이와는 대조적으로, 신흥 경제국은 전장 감시에서 재해 대응에 이르기까지 여러 목적에 대응할 수 있는 기동적이고 비용 효율적인 솔루션을 선호하는 경우가 많습니다. 지역의 긴장과 동맹 관계도 수요를 형성합니다. 영토분쟁이나 대립이 격화하고 있는 지역은 항상 경계와 억지력을 확보하기 위해 레이더 네트워크에 다액의 투자를 실시합니다. 한편, 다국간 작전에 종사하는 국가는 상호운용성을 중시하고 자국의 시스템과 동맹국의 시스템의 무결성을 확보합니다. 수입품에 대한 의존도를 줄이기 위해 레이더의 국산화를 추진하는 국가도 있고, 선진적인 설계에 접근하기 위해 공동 개발에 의존하는 국가도 있습니다. 이러한 동향은 세계의 방위 감시 레이더 시장의 다양성과 활력을 부각하고 있습니다.
주요 감시 레이더 계획
독일 의회의 승인을 받은 Indra는 독일 공군의 국가 조달국(BAAINBw)과 지구 저궤도상의 물체를 감지하도록 설계된 차세대 레이더 시스템을 장비하는 계약을 체결했습니다. 이 레이더는 고속 궤도에서 파편과의 충돌 가능성으로부터 활동 위성을 보호하고 다른 위성이 위성에 접근, 간섭 및 정보 수집을 시도하는 위험에 대항하는 데 도움이 됩니다. Indra는 독일의 자회사를 통해 입찰에 참여하고 입증된 성숙도, 뛰어난 성능, 확장 가능한 기능 업그레이드를 가능하게 하는 모듈식으로 유연한 설계의 우주 레이더가 평가되어 계약을 획득했습니다.
목차
감시 레이더 시장 보고서 정의
감시 레이더 시장 세분화
용도별
플랫폼별
지역별
향후 10년간 감시 레이더 시장 분석
이 장에서는 10년간의 감시 레이더 시장 분석을 통해 감시 레이더 시장의 성장, 변화하는 추세, 기술 채용의 개요 및 전체 시장의 매력에 대한 자세한 개요를 제공합니다.
감시 레이더 시장 시장 기술
이 부문에서는 이 시장에 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상되는 상위 10개 기술과 이러한 기술이 시장 전체에 미칠 수 있는 영향에 대해 설명합니다.
세계 감시 레이더 시장 예측
이 시장의 10년간 예측은 위의 전체 부문에서 자세히 설명합니다.
지역 감시 레이더 시장 동향과 예측
이 부문은 지역별 감시 레이더 시장 동향, 촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제, 그리고 정치, 경제, 사회, 기술 등의 측면을 다룹니다. 또한 지역별 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석도 자세히 다루고 있습니다. 지역 분석의 끝에는 주요 기업 프로파일링, 공급업체 상황, 기업 벤치마킹가 포함됩니다. 현재 시장 규모는 일반적인 시나리오를 기반으로 추정됩니다.
북미
촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제
PEST
시장 예측 및 시나리오 분석
주요 기업
공급자 계층의 상황
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
감시 레이더 시장의 국가별 분석
이 장에서는 이 시장에서 주요 방어 프로그램을 다루며 이 시장에서 신청된 최신 뉴스와 특허에 대해서도 설명합니다. 또한 국가 수준의 10년간 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석에 대해서도 설명합니다.
미국
방어 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장의 현재 기술 성숙도
시장 예측 및 시나리오 분석
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
감시 레이더 시장 기회 행렬
기회 행렬은 독자가 이 시장에서 기회의 높은 부문을 이해하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
감시 레이더 시장 보고서에 대한 전문가의 의견
이 시장에서 가능한 분석에 대한 당사의 전문가의 의견을 제공합니다.
결론
리서치사에 대하여
JHS 25.09.22The Global Surveillance Radar market is estimated at USD 9.25 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 15.75 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.47% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Introduction to Surveillance Radar Market:
The defense surveillance radar market is an integral part of modern security infrastructure, supporting the detection, tracking, and monitoring of aerial, maritime, and ground-based threats. These systems are designed to provide early warning and situational awareness, enabling armed forces to make informed decisions in both defensive and offensive operations. Unlike civilian radars that primarily focus on weather or air traffic control, defense surveillance radars are engineered for resilience, precision, and the ability to operate under hostile conditions. The importance of these radars has grown as militaries face increasingly complex threats ranging from stealth aircraft and drones to hypersonic weapons and low-altitude cruise missiles. Their role extends beyond combat, as they are also vital for border security, coastal monitoring, and peacekeeping operations. The market has evolved to include a wide variety of systems, from large fixed installations to mobile units capable of rapid deployment in conflict zones. This diversity reflects the need for flexibility in modern defense strategies. With the rising emphasis on integrated air and missile defense, surveillance radars remain the cornerstone of detection networks, ensuring that nations maintain a comprehensive picture of activities in contested environments and safeguard their airspace and territorial waters.
Technology Impact in Surveillance Radar Market:
Technological advances are reshaping the capabilities of defense surveillance radars, driving improvements in detection range, accuracy, and resilience against countermeasures. One of the most transformative developments has been the widespread adoption of active electronically scanned array systems, which allow radars to track multiple targets simultaneously while maintaining a low probability of interception. This technology enhances responsiveness and survivability in contested airspace, where adversaries deploy electronic warfare to disrupt traditional radar signals. Advances in digital signal processing and artificial intelligence are further enhancing performance. Modern radars can filter through background clutter, distinguish between genuine threats and decoys, and deliver actionable insights in real time. These systems also integrate with command-and-control networks, allowing seamless sharing of data across air, land, and sea domains. Such connectivity is crucial for joint and coalition operations where rapid coordination determines mission success. Materials and miniaturization technologies are also shaping the market, enabling the development of lighter, mobile systems that can be mounted on vehicles, ships, or even unmanned platforms. Meanwhile, research into quantum radar and passive radar concepts highlights future directions aimed at countering stealth technologies. Collectively, these innovations ensure that surveillance radars remain indispensable in modern and next-generation defense strategies.
Key Drivers in Surveillance Radar Market:
The growth of the defense surveillance radar market is fueled by evolving security requirements and the increasing sophistication of threats. Nations recognize that early detection is fundamental to safeguarding airspace, coastlines, and critical infrastructure. The proliferation of unmanned aerial systems, stealth technologies, and advanced missile systems has created demand for radars capable of identifying threats that are smaller, faster, and harder to detect than ever before. Another major driver is the emphasis on integrated defense systems. Modern militaries seek radars that not only detect but also seamlessly connect with interceptors, aircraft, and command centers. This interoperability allows for coordinated responses to multi-domain threats and strengthens layered defense architectures. The rising importance of ballistic missile defense has further increased reliance on long-range radars capable of tracking high-speed projectiles across vast distances. Budgetary allocations for defense modernization also play a key role. Governments are prioritizing investments in radar technology to ensure preparedness for both conventional and asymmetric warfare scenarios. In addition, the increasing involvement of defense forces in non-combat roles, such as disaster monitoring and border surveillance, ensures consistent demand. Collectively, these drivers underline the central role of surveillance radars in shaping resilient and future-ready defense strategies.
Regional Trends in Surveillance Radar Market:
Regional trends in the defense surveillance radar market reflect a blend of geographic needs, security challenges, and technological priorities. Maritime nations emphasize coastal and naval radar systems to monitor expansive sea lanes and deter potential intrusions, while landlocked regions focus on border surveillance and air defense radars to protect against aerial incursions. Geography, therefore, heavily influences radar procurement strategies. Advanced defense powers are leading the adoption of cutting-edge technologies such as electronically scanned arrays and long-range early warning radars. Their focus lies in building integrated air and missile defense systems that can counter stealth aircraft and hypersonic threats. In contrast, emerging economies often prioritize mobile, cost-effective solutions that can serve multiple purposes, from battlefield surveillance to disaster response. Regional tensions and alliances also shape demand. Areas experiencing territorial disputes or heightened rivalries invest heavily in radar networks to ensure constant vigilance and deterrence. Meanwhile, nations engaged in multinational operations emphasize interoperability, ensuring that their systems align with those of allies. Industrial capability further defines regional dynamics, as some countries push for indigenous radar development to reduce dependency on imports, while others rely on collaborations to access advanced designs. These trends together highlight the diversity and vitality of the global defense surveillance radar market.
Key Surveillance Radar Program:
After receiving approval from the German Parliament, Indra has signed a contract with the National Procurement Office (BAAINBw) of the Bundeswehr to equip the Luftwaffe with a next-generation radar system designed to detect objects in low Earth orbit. The radar will safeguard active satellites from potential collisions with high-speed orbital debris and help counter risks posed by other satellites attempting to approach, interfere with, or gather intelligence on them. Indra, through its German subsidiary, was invited to participate in the tender and secured the contract based on the proven maturity, superior performance, and modular, flexible design of its space radar, which allows for scalable capability upgrades.
Table of Contents
Surveillance Radar Market Report Definition
Surveillance Radar Market Segmentation
By Application
By Platform
By Region
Surveillance Radar Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year surveillance radar market analysis would give a detailed overview of surveillance radar market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Surveillance Radar Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Surveillance Radar Market Forecast
The 10-year Surveillance Radar Market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Surveillance Radar Market Trends & Forecast
The regional surveillance radar market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Surveillance Radar Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Surveillance Radar Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Surveillance Radar Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.


















