
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1740886
자동차용 가스 충전식 쇼크 업소버 시장 기회, 성장 촉진요인, 산업 동향 분석 및 예측(2025-2034년)Automotive Gas Charged Shock Absorber Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
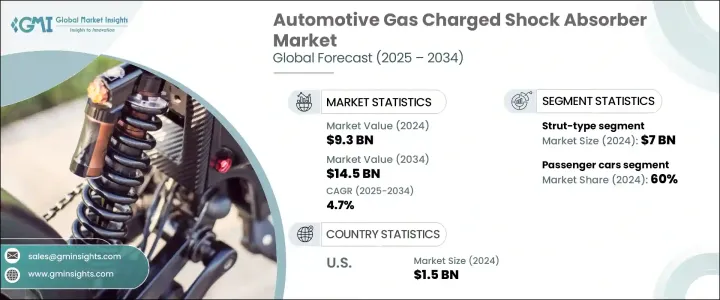
세계의 자동차용 가스 충전식 쇼크 업소버 시장 규모는 2024년에 93억 달러로 평가되었고, 승차감의 향상, 뛰어난 차량 핸들링, 다양한 지형에서의 보다 안전한 운전 체험에 대한 소비자의 기대의 고조에 지지되어, CAGR 4.7%를 나타내 2034년에는 145억 달러에 달할 것으로 전망됩니다.
자동차 제조업체가 선진적인 서스펜션 시스템으로의 시프트를 계속하는 가운데, 가스 충전식 쇼크 업소버와 같은 고성능 부품 수요가 크게 늘고 있습니다. 이러한 업소버는 특히 고속 주행과 오프로드 주행에서 진동을 줄이고 차량의 안정성을 높이고 부드러운 승차감을 실현하는 데 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다.

자동차 기술의 진화에 따라 소비자는 현재 자동차에 편안함과 성능을 모두 요구하고 있으며, 그 결과 선진적인 댐핑 시스템이 자동차 공학의 최전선에 위치하고 있습니다. 급차 부문의 세계 확대, 도시 지역의 교통 체증 증가, 장거리 운전 습관의 급증은 종합적으로 더 뛰어난 충격 관리 시스템의 필요성을 부추기고 있습니다. 통기나 발포에 대한 내성을 제공함으로써 기존의 유압식 쇼크에 비해 중요한 이점을 제공해 연속 운전이나 공격적인 운전에서도 안정된 성능을 보증합니다.
| 시장 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 시작 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 연도 | 2025-2034년 |
| 시작 금액 | 93억 달러 |
| 예측 금액 | 145억 달러 |
| CAGR | 4.7% |
성능에 중점을 둔 차량 플랫폼, 특히 SUV 및 크로스오버의 급속한 보급과 함께, 가스 충전 쇼크 업소버는 승용차와 상용차 모두에서 표준 부품이 되고 있습니다. 효율성을 실현하고 다양한 하중과 조건에서 최적의 균형을 유지하는 능력은 오늘날의 서스펜션 시스템에 필수적입니다. 피치 컨트롤의 개선, 전체적인 부드러운 승차감을 요구하는 소비자 요구의 고조에 대응하기 위해서 설계되고 있습니다. 이러한 기호의 고조는 도로 상황이나 운전에 대한 기대가 크게 다른 도시와 농촌 모두에서 현저하고, 가스 차지드 시스템의 다용도성을 한층 더 실증하고 있습니다.
승용차 부문은 마이커 소유율 상승, 가처분 소득 증가, 중간 소득층 확대로 견인되어 2024년에는 60%의 압도적 점유율을 차지했습니다. 드라이빙 체험을 제공하는 자동차를 구매자가 요구하고 있기 때문에 프리미엄 서스펜션 컴퍼넌트에 대한 주목이 높아지고 있습니다. 가스 충전식 쇼크 업소버는 보다 뛰어난 감쇠 특성을 제공하는 것으로 이 수요에 응해, 쾌적성, 제어성, 안전성을 목적으로 한 최신의 자동차 플랫폼으로 선호되는 선택지가 되고 있습니다.
설치 유형별로는 스트럿 유형의 가스 충전식 쇼크 업소버가 2024년의 평가액 70억 달러로 시장을 리드했습니다. 탑재 서스펜션의 레이아웃에 있어서의 공간 효율을 서포트해, 차량 전체의 중량을 경감해 연비와 배출 가스의 저감에 공헌합니다. 또, 설치의 용이함이나 유지관리의 간소화도 실현하고 있어, 스트럿 유형의 쇼크 업소버는 대규모 자동차 제조에 있어서 비용 대비 효과적인 솔루션이 되고 있습니다.
북미의 자동차용 가스 충전식 쇼크 업소버 시장은 2024년에 15억 달러를 차지했고, 2025년부터 2034년에 걸쳐 CAGR 4.9%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 이 성장 배경에는 이 지역의 호조로운 자동차 생산, 주요 OEM의 존재, 고 내구성 서스펜션 시스템이 필요한 픽업 및 크로스 오버와 같은 대형 자동차에 대한 선호도가 높아지고 있으며, 전동화를 추진하는 이 지역은 경량화와 에너지 효율을 지원하면서 최신 드라이브 트레인 요건에 맞는 고급 쇼크 업소버 수요를 밀어 올리고 있습니다.
Hitachi Astemo, HL Mando, Gabriel India, KYB, Showa, ZF Friedrichshafen, Chassis Brakes, Endurance Technologies, Cofap, Tenneco 등 주요 기업은 기술 혁신과 전략적 제휴를 통해 시장에서의 지위를 적극적으로 강화하고 있습니다. 많은 기업들이 노면에서의 피드백과 운전 행동을 바탕으로 실시간 적응성을 제공하는 전자 제어 감쇠 시스템을 개발함으로써 스마트카와 자율주행차의 미래에 맞추어 제공하는 제품을 다양화하고 있습니다.
목차
제1장 조사 방법과 범위
제2장 주요 요약
제3장 업계 인사이트
- 생태계 분석
- 공급자의 상황
- 원재료 공급자
- 부품 공급업체
- 제조업체
- 기술 공급자
- 유통 채널 분석
- 최종 용도
- 이익률 분석
- 공급자의 상황
- 트럼프 정권에 의한 관세에 대한 영향
- 무역에 미치는 영향
- 무역량의 혼란
- 보복 조치
- 업계에 미치는 영향
- 공급측의 영향(원재료)
- 주요 원재료의 가격 변동
- 공급망 재구성
- 생산 비용에 미치는 영향
- 수요측의 영향(판매가격)
- 최종 시장에의 가격 전달
- 시장 점유율 동향
- 소비자의 반응 패턴
- 공급측의 영향(원재료)
- 전략적인 업계 대응
- 공급망 재구성
- 가격 설정 및 제품 전략
- 무역에 미치는 영향
- 기술과 혁신의 상황
- 특허 분석
- 규제 상황
- 코스트 내역 분석
- 가격 동향
- 지역
- 차량
- 주요 뉴스와 대처
- 영향요인
- 성장 촉진요인
- 승차감과 조종 안정성에 대한 수요 증가
- 전기자동차와 하이브리드 자동차의 보급 증가
- 서스펜션 시스템의 기술적 진보
- 세계 자동차 생산 확대
- 업계의 잠재적 위험 및 과제
- 유압 쇼크 업소버에 비해 높은 비용
- 엄격한 환경 및 안전 규제
- 성장 촉진요인
- 성장 가능성 분석
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- PESTEL 분석
제4장 경쟁 구도
- 서론
- 기업의 시장 점유율 분석
- 경쟁 포지셔닝 매트릭스
- 전략적 전망 매트릭스
제5장 시장 추계·예측 : 기술별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 트윈 튜브 가스
- 모노 튜브 가스
제6장 시장 추계·예측 : 최종 용도별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 승용차
- 해치백
- 세단
- SUV
- 상용차
- 소형 상용차(LCV)
- 중형 상용차(MCV)
- 대형 상용차(HCV)
제7장 시장 추계·예측 : 설치별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 스트럿 타입
- 텔레스코픽
제8장 시장 추계·예측 : 판매 채널별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- OEM
- 애프터마켓
제9장 시장 추계·예측 : 지역별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 영국
- 스페인
- 이탈리아
- 러시아
- 북유럽 국가
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 호주 및 뉴질랜드
- 동남아시아
- 라틴아메리카
- 브라질
- 멕시코
- 아르헨티나
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 남아프리카
- 사우디아라비아
제10장 기업 프로파일
- AL-KO Fahrzeugtechnik
- Bilstein
- Chassis Brakes
- Cofap
- Endurance
- Gabriel
- Hitachi Astemo
- ITW
- Jiangsu Huachuan
- KYB
- Liuzhou Shuangfei
- Magneti Marelli
- Mando
- Ride Control
- S&T Motiv
- Showa
- Tenneco
- Tokico
- YSS Suspension
- ZF Friedrichshafen
The Global Automotive Gas Charged Shock Absorber Market was valued at USD 9.3 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 4.7% to reach USD 14.5 billion by 2034, supported by rising consumer expectations for enhanced ride comfort, superior vehicle handling, and safer driving experiences across diverse terrains. As automakers continue to shift toward advanced suspension systems, the demand for high-performance components like gas-charged shock absorbers is gaining significant traction. These absorbers play a key role in reducing vibrations, enhancing vehicle stability, and delivering smoother rides, especially in high-speed and off-road conditions.
With evolving automotive technologies, consumers now expect their vehicles to offer both comfort and performance, which has placed advanced damping systems at the forefront of vehicle engineering. The global expansion of premium vehicle segments, growing urban traffic congestion, and a surge in long-distance driving habits are collectively fueling the need for better shock management systems. Gas-charged shock absorbers provide a crucial advantage over traditional hydraulic shocks by offering resistance to aeration and foaming, which ensures consistent performance under continuous or aggressive driving. As the automotive sector leans more into electrification and smart vehicle systems, these absorbers are being tailored to support dynamic loads without compromising energy efficiency or battery range.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $9.3 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $14.5 Billion |
| CAGR | 4.7% |
With the rapid adoption of performance-focused vehicle platforms, particularly SUVs and crossovers, gas-charged shock absorbers are becoming a standard component in both passenger and commercial vehicle categories. Their ability to deliver advanced damping efficiency and maintain optimal balance under varying loads and conditions makes them indispensable in today's suspension systems. These shock absorbers are engineered to meet the growing consumer need for better handling, reduced body roll, improved pitch control, and overall smoother rides. Automakers are integrating gas-charged absorbers into newer models to differentiate performance features and meet the demand for premium ride quality. This growing preference is evident in both urban and rural settings, where road conditions and driving expectations vary significantly, further validating the versatility of gas-charged systems.
The passenger vehicle segment commanded a dominant 60% share in 2024, driven by the increasing rate of personal car ownership, rising disposable incomes, and an expanding middle-class demographic. Consumers are prioritizing vehicles that offer improved comfort, stability, and handling-particularly for daily commutes and longer journeys. In emerging economies, where car sales are booming, the focus on premium suspension components is intensifying as buyers look for vehicles that deliver a seamless driving experience. Gas-charged shock absorbers meet this demand by providing better damping characteristics, making them a preferred choice in modern vehicle platforms aimed at comfort, control, and safety.
Based on mounting type, strut-type gas charged shock absorbers led the market with a valuation of USD 7 billion in 2024. These components are widely adopted due to their integrated construction, which combines the coil spring and shock absorber into one compact unit. This configuration supports space efficiency in front suspension layouts and helps reduce the vehicle's overall weight, contributing to fuel efficiency and lower emissions. The design also offers ease of installation and simplified maintenance, making strut-type shock absorbers a cost-effective solution for large-scale automotive manufacturing.
The North America Automotive Gas Charged Shock Absorber Market accounted for USD 1.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.9% from 2025 to 2034. This growth is backed by strong regional vehicle production, the presence of major OEMs, and a rising preference for larger vehicles like pickups and crossovers that demand high-durability suspension systems. The region's push toward electrification is also boosting demand for advanced shock absorbers that align with modern drivetrain requirements while supporting weight reduction and energy efficiency.
Leading companies such as Hitachi Astemo, HL Mando, Gabriel India, KYB, Showa, ZF Friedrichshafen, Chassis Brakes, Endurance Technologies, Cofap, and Tenneco are actively strengthening their market positions through innovation and strategic collaborations. These players are investing heavily in R&D to enhance shock absorber performance, expand their manufacturing footprint globally, and form key partnerships with OEMs. Many are also diversifying their offerings by developing electronically controlled damping systems that provide real-time adaptability based on road feedback and driving behavior, aligning with the future of smart and autonomous vehicles.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Research design
- 1.1.1 Research approach
- 1.1.2 Data collection methods
- 1.2 Base estimates & calculations
- 1.2.1 Base year calculation
- 1.2.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.3 Forecast model
- 1.4 Primary research and validation
- 1.4.1 Primary sources
- 1.4.2 Data mining sources
- 1.5 Market scope & definition
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis, 2021 - 2034
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.1.1 Raw material providers
- 3.1.1.2 Component providers
- 3.1.1.3 Manufacturers
- 3.1.1.4 Technology providers
- 3.1.1.5 Distribution channel analysis
- 3.1.1.6 End use
- 3.1.2 Profit margin analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.2 Impact of Trump administration tariffs
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.2.1.1 Trade volume disruptions
- 3.2.1.2 Retaliatory measures
- 3.2.2 Impact on industry
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (raw materials)
- 3.2.2.1.1 Price volatility in key materials
- 3.2.2.1.2 Supply chain restructuring
- 3.2.2.1.3 Production cost implications
- 3.2.2.2 Demand-side impact (selling price)
- 3.2.2.2.1 Price transmission to end markets
- 3.2.2.2.2 Market share dynamics
- 3.2.2.2.3 Consumer response patterns
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (raw materials)
- 3.2.3 Strategic industry responses
- 3.2.3.1 Supply chain reconfiguration
- 3.2.3.2 Pricing and product strategies
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.3 Technology & innovation landscape
- 3.4 Patent analysis
- 3.5 Regulatory landscape
- 3.6 Cost breakdown analysis
- 3.7 Price trend
- 3.7.1 Region
- 3.7.2 Vehicle
- 3.8 Key news & initiatives
- 3.9 Impact forces
- 3.9.1 Growth drivers
- 3.9.1.1 Growing demand for ride comfort & handling stability
- 3.9.1.2 Rising adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles
- 3.9.1.3 Technological advancements in suspension systems
- 3.9.1.4 Expansion of global automotive production
- 3.9.2 Industry pitfalls & challenges
- 3.9.2.1 Higher cost compared to hydraulic shock absorbers
- 3.9.2.2 Stringent environmental & safety regulations
- 3.9.1 Growth drivers
- 3.10 Growth potential analysis
- 3.11 Porter's analysis
- 3.12 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.3 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.4 Strategic outlook matrix
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Technology, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Twin-tube gas
- 5.3 Monotube gas
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By End Use, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Passenger cars
- 6.2.1 Hatchback
- 6.2.2 Sedan
- 6.2.3 SUV
- 6.3 Commercial vehicles
- 6.3.1 Light Commercial Vehicles (LCV)
- 6.3.2 Medium Commercial Vehicles (MCV)
- 6.3.3 Heavy Commercial Vehicles (HCV)
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Mount, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Strut-type
- 7.3 Telescopic
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Sales Channel 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 OEM
- 8.3 Aftermarket
Chapter 9 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 U.S.
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 Germany
- 9.3.2 France
- 9.3.3 UK
- 9.3.4 Spain
- 9.3.5 Italy
- 9.3.6 Russia
- 9.3.7 Nordics
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 China
- 9.4.2 India
- 9.4.3 Japan
- 9.4.4 South Korea
- 9.4.5 ANZ
- 9.4.6 Southeast Asia
- 9.5 Latin America
- 9.5.1 Brazil
- 9.5.2 Mexico
- 9.5.3 Argentina
- 9.6 MEA
- 9.6.1 UAE
- 9.6.2 South Africa
- 9.6.3 Saudi Arabia
Chapter 10 Company Profiles
- 10.1 AL-KO Fahrzeugtechnik
- 10.2 Bilstein
- 10.3 Chassis Brakes
- 10.4 Cofap
- 10.5 Endurance
- 10.6 Gabriel
- 10.7 Hitachi Astemo
- 10.8 ITW
- 10.9 Jiangsu Huachuan
- 10.10 KYB
- 10.11 Liuzhou Shuangfei
- 10.12 Magneti Marelli
- 10.13 Mando
- 10.14 Ride Control
- 10.15 S&T Motiv
- 10.16 Showa
- 10.17 Tenneco
- 10.18 Tokico
- 10.19 YSS Suspension
- 10.20 ZF Friedrichshafen



















