
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1797764
궤도간 수송기 시장 기회, 성장 촉진요인, 산업 동향 분석 및 예측(2025-2034년)Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV) Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
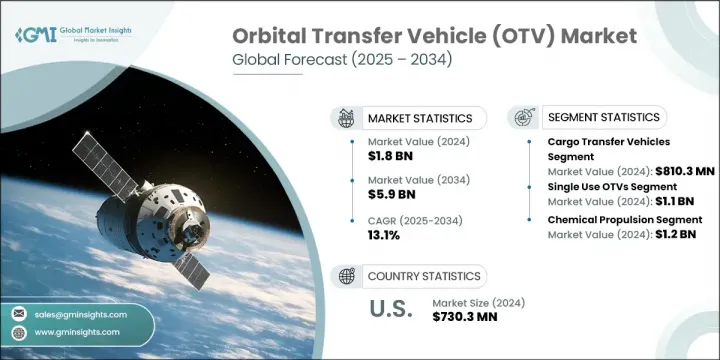
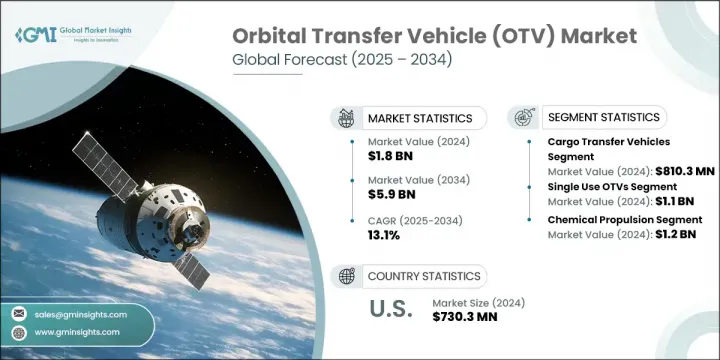
세계의 궤도간 수송기 시장은 2024년에는 18억 달러로 평가되었고 CAGR 13.1%를 나타내 2034년에는 59억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
시장 성장의 원동력이 되는 것은 적응성이 높은 위성 전개 방법에 대한 요구의 높아짐, 소형 위성이나 큐브 싯의 발사 빈도의 상승, 추진 시스템의 급속한 진보, 궤도 인프라에의 자본 유입의 급증, 상업 우주 구상의 꾸준한 증가 등입니다. 산업이 전통적인 발사 시스템에서 이동함에 따라, OTV는 지구 저궤도(LEO), 지구중 궤도(MEO), 정지 궤도(GEO), 그리고 그 앞의 태양계 우주 공간 등 다양한 궤도 목적지로 페이로드를 운반할 수 있는 필수적인 우주 전달 솔루션으로 대두되고 있습니다. 관민 모두 위성 별자리, 우주 서비스 모듈, 궤도 하비탓, 월면 지원 구조물의 개발에 다액의 투자를 하고 있어 시장의 장기적 성장을 더욱 뒷받침하고 있습니다.
유연한 위성 운송에 대한 수요 증가는 OTV 부문의 확대를 뒷받침하는 중요한 요소입니다. 사업자는 현재 경직된 사전 정의된 발사 프로파일에 묶이지 않고 더 높은 응답성과 임무에 따른 궤도 배치를 제공하는 전개 시스템을 요구하고 있습니다. 궤도간 수송기는 우주 물류 솔루션으로서 다양한 궤도 환경에서 온디맨드 위성 운송을 가능하게 함으로써 구식 시스템을 대체하고 있습니다. 이와 병행하여 국방부문에서 민간항공우주신흥기업까지 우주를 전문으로 하는 다양한 사업체가 보다 견고한 궤도 생태계를 구축하기 위한 노력을 강화하고 있습니다.
| 시장 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 시작 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 연도 | 2025-2034년 |
| 시작 금액 | 18억 달러 |
| 예측 금액 | 59억 달러 |
| CAGR | 13.1% |
화물 수송기 부문은 2024년 8억 1,030만 달러를 창출했습니다. 이 부문은 궤도 스테이션을 유지하고 새로운 상업 플랫폼으로 가는 길을 열기 위해 고안된 페이로드 재공급 임무의 빈도가 증가하여 계속 이익을 얻고 있습니다. 위성의 정비나 궤도상의 자산 보수가 중시되게 됨으로써, 미션 크리티컬한 하드웨어의 시기 적절하고 안전한 운송을 보증하는 전용의 화물 수송기에 대한 수요도 가속하고 있습니다. 자율적인 도킹 시스템의 개발과 항공우주 조직 간의 세계 협력 관계의 확대는 재사용 화물 운송 기술의 채택을 촉진하고 있습니다.
단일 청소년 궤도간 수송기 부문은 2024년에 11억 달러를 창출했습니다. 이러한 수송기는 구조가 단순화되고, 제조 비용이 절감되고, 일회성 페이로드 배치가 포함된 임무에 적합하기 때문에 점점 더 선호되고 있습니다. 복잡한 회수 시스템이나 재사용 시스템이 필요 없기 때문에 차량 회수가 현실적이지 않은 고위험 또는 장거리 임무에 이상적인 솔루션을 제공합니다. 그 사용은 전략적 배달의 신뢰성이 가장 중요시되는 정부 기관 및 방어 관련 임무에서 특히 널리 퍼져 있습니다. 게다가 신흥기업과 항공우주산업에 대한 신규 진입기업은 검사, 프로토타입의 검증, 경제적으로 실행 가능한 궤도실증실험의 초기 단계에서 싱글유스 플랫폼을 선택하는 경우가 많습니다.
미국의 궤도간 수송기 시장은 2024년 7억 3,030만 달러를 창출했습니다. 이 강력한 지위는 위성 발사능력 강화, 궤도상 보수시스템의 개발, 궤도상 파편 경감전략의 실시 등 정부기관과 민간사업자 모두의 지속적인 노력에 지지되고 있습니다. 이러한 공동 투자는 궤도 운영의 효율성을 높이고 페이로드의 조작성을 향상시키고 우주 자산의 수명을 연장하는 것을 목표로합니다. 궤도의 지속가능성과 임무의 유연성이 점점 더 중요해지고 있으며, 이 부문에서의 일본 리더십은 계속 강화되고 있습니다.
세계의 궤도간 수송기 시장을 적극적으로 형성하고 있는 유명 기업은 Astroscale Holdings Inc., Virgin Galactic, D-Orbit SpA, Relativivity Space, OHB SE, Quantum Space LLC, Northrop Grumman Corporation, ArianeGroup SAS, Space Machines Company Pty Corporation, China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology(CALT), SpaceX, MayaSpace SAS, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Altius Space Machines Inc, Impulse Space Inc., Roscosmos/Energia, Firefly Aerospace, Atomos Space LLC, Gama Space SAS, Rocket LLC, Thales Alenia Space SA, United Launch Alliance LLC(ULA), Orbital Operations Ltd, CASIC/ExPace, Momentus Inc., Starfish Space Inc.가 있습니다. 궤도간 수송기 시장 주요 기업은 경쟁을 강화하기 위해 기술 혁신과 파트너십을 선호합니다. 대부분은 유연한 미션 구성을 지원하기 위해 자체 추진 시스템과 모듈형 차량 설계에 투자하고 있습니다.경계 전략적 협력 관계와 조직 간의 협력 관계는 기업이 보다 광범위한 발사 플랫폼에 액세스하고 로켓을 다양한 임무 아키텍처에 통합하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
목차
제1장 조사 방법과 범위
제2장 주요 요약
제3장 산업 고찰
- 생태계 분석
- 공급자의 상황
- 이익률
- 비용 구조
- 각 단계에서의 부가가치
- 밸류체인에 영향을 주는 요인
- 파괴적 혁신
- 생태계 분석
- 산업에 미치는 영향요인
- 성장 촉진요인
- 위성 전개 유연성에 대한 수요 증가
- 소형 위성과 큐브사트의 발사 증가
- 추진 기술의 진보
- 우주 인프라 투자 증가
- 상업우주활동 확대
- 함정과 과제
- 기술적 신뢰성과 미션 보증
- 규제의 복잡성과 우주 교통 관리
- 성장 촉진요인
- 성장 가능성 분석
- 규제 상황
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- PESTEL 분석
- 기술과 혁신의 상황
- 현재의 기술 동향
- 신흥기술
- 새로운 비즈니스 모델
- 컴플라이언스 요건
- 국방예산 분석
- 세계의 방위비의 동향
- 지역 방위 예산 배분
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 라틴아메리카
- 주요 방위 근대화 프로그램
- 예산 예측(2025-2034년)
- 산업의 성장에 미치는 영향
- 국가별 방위 예산
- 지속가능성에 대한 노력
- 공급 체인의 탄력
- 지정학적 분석
- 인재 분석
- 디지털 변혁
- 합병, 인수, 전략적 제휴의 상황
- 위험 평가 및 관리
- 주요 계약 체결(2021-2024년)
제4장 경쟁 구도
- 서론
- 기업의 시장 점유율 분석
- 지역별
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 시장 집중 분석
- 지역별
- 주요 진출기업의 경쟁 벤치마킹
- 재무실적의 비교
- 수익
- 이익률
- 연구개발
- 제품 포트폴리오 비교
- 제품 라인업의 넓이
- 기술
- 파괴적 혁신
- 지리적 존재의 비교
- 세계 실적 분석
- 서비스 네트워크의 범위
- 지역에 의한 시장 침투율
- 경쟁 포지셔닝 매트릭스
- 리더
- 도전자
- 팔로워
- 틈새 진출기업
- 전략적 전망 매트릭스
- 재무실적의 비교
- 주요 개발(2021-2024년)
- 합병과 인수
- 파트너십 및 협업
- 기술적 진보
- 확대 및 투자 전략
- 지속가능성에 대한 노력
- 디지털 변혁의 대처
- 신흥기업/스타트업기업경쟁 구도
제5장 시장 추정·예측 : 유형별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 화물 수송기
- 승무원 수송기
- 연료 보급기
- 위성 정비 및 파편 제거기
- 기타
제6장 시장 추정·예측 : 차종별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 일회용 OTV
- 재사용형 OTV
제7장 시장 추정·예측 : 추진 시스템별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 화학추진
- 전기추진
- 핵열 추진
- 기타
제8장 시장 추정·예측 : 적재량별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 소형(최대 200kg)
- 중형(200kg-1,000kg)
- 대형(1,000kg 이상)
제9장 시장 추정·예측 : 용도별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 위성 배치
- 우주 탐사
- 궤도상 서비스
- 우주여행
- 우주 정거장 보급 및 승무원 교대
- 기타
제10장 시장 추정·예측 : 최종 용도별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 정부 우주 기관
- 상업 우주 기업
- 관민 파트너십
제11장 시장 추정·예측 : 지역별(2021-2034년)
- 주요 동향
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 스페인
- 이탈리아
- 네덜란드
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 호주
- 한국
- 라틴아메리카
- 브라질
- 멕시코
- 아르헨티나
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 사우디아라비아
- 남아프리카
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
제12장 기업 프로파일
- 세계적 주요 기업
- 지역 주요 기업
- 파괴적 혁신/틈새 진출기업
- Starfish Space Inc.
- Atomos Space LLC
- Astroscale Holdings Inc.
- Virgin Galactic
The Global Orbital Transfer Vehicle Market was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 13.1% to reach USD 5.9 billion by 2034. The market growth is driven by an increasing need for adaptable satellite deployment methods, the rising frequency of small satellite and CubeSat launches, rapid progress in propulsion systems, surging capital flow into orbital infrastructure, and a steady uptick in commercial space initiatives. As the industry shifts away from traditional launch systems, OTVs are emerging as indispensable in-space delivery solutions capable of maneuvering payloads to various orbital destinations-including low Earth orbit (LEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO), geostationary orbit (GEO), and beyond to cislunar space. Both public and private sectors are channeling considerable investments into developing satellite constellations, in-space service modules, orbital habitats, and lunar support structures-further fueling long-term growth in the market.
Heightened demand for flexible satellite transportation is a critical factor powering the expansion of the OTV space. Operators now seek deployment systems that offer greater responsiveness and mission-specific orbital placement, rather than being tied to rigid, predefined launch profiles. Orbital transfer vehicles, acting as in-space logistics solutions, are replacing older systems by enabling on-demand satellite delivery across a diverse range of orbital environments. In tandem, various space-focused entities-from national defense divisions to commercial aerospace startups-are ramping up efforts to construct more robust orbital ecosystems.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $1.8 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $5.9 Billion |
| CAGR | 13.1% |
The cargo transfer vehicles segment generated USD 810.3 million in 2024. This segment continues to benefit from the growing frequency of payload resupply missions designed to sustain orbital stations and pave the way for emerging commercial platforms. The growing emphasis on satellite servicing and orbital asset maintenance is also accelerating demand for dedicated cargo vehicles that ensure the timely, secure transport of mission-critical hardware. Developments in autonomous docking systems and expanding global cooperation between aerospace organizations are driving the adoption of reusable cargo transport technologies.
The single-use orbital transfer vehicles segment generated USD 1.1 billion in 2024. These vehicles are increasingly favored due to their simplified structure, reduced manufacturing costs, and suitability for missions involving one-time payload deployments. By eliminating the need for complex retrieval or reuse systems, they provide an ideal solution for high-risk or long-distance missions where vehicle recovery is impractical. Their utilization is particularly prevalent among government bodies and defense-related missions, where strategic delivery reliability is paramount. Additionally, startups and newer entrants to the aerospace industry often opt for single-use platforms during initial stages of testing, prototype validation, or conducting economically viable orbital demonstrations.
United States Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV) Market generated USD 730.3 million in 2024. This strong position is underpinned by sustained efforts from both governmental institutions and commercial operators to enhance satellite launch capabilities, develop in-orbit maintenance systems, and implement orbital debris mitigation strategies. These collaborative investments aim to enhance the efficiency of orbital operations, increase payload maneuverability, and extend the useful life of space assets. The growing emphasis on orbital sustainability and mission flexibility continues to strengthen the country's leadership in the sector.
Prominent players actively shaping the Global Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV) Market include Astroscale Holdings Inc., Virgin Galactic, D-Orbit S.p.A., Relativity Space, OHB SE, Quantum Space LLC, Northrop Grumman Corporation, ArianeGroup SAS, Space Machines Company Pty Ltd, Sierra Space, Moog Inc., ISRO / Antrix Corporation, China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT), SpaceX, MaiaSpace SAS, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Altius Space Machines Inc., Impulse Space Inc., Roscosmos / Energia, Firefly Aerospace, Atomos Space LLC, Gama Space SAS, Rocket Lab USA Inc., Blue Origin LLC, Epic Aerospace LLC, Thales Alenia Space S.A., United Launch Alliance LLC (ULA), Orbital Operations Ltd, CASIC / ExPace, Momentus Inc., and Starfish Space Inc. Leading companies in the orbital transfer vehicle market are prioritizing innovation and partnerships to solidify their competitive edge. Many are investing in proprietary propulsion systems and modular vehicle designs to support flexible mission configurations. Strategic collaborations-both cross-border and inter-organizational-are helping firms access broader launch platforms and integrate their vehicles into diverse mission architectures.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Type trends
- 2.2.2 Vehicle type trends
- 2.2.3 Propulsion system trends
- 2.2.4 Payload capacity trends
- 2.2.5 Application trends
- 2.2.6 End use trends
- 2.2.7 Regional trends
- 2.3 TAM Analysis, 2025-2034 (USD Billion)
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin
- 3.1.3 Cost structure
- 3.1.4 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.5 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.6 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.3 Industry impact forces
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3.1.1 Increasing demand for satellite deployment flexibility
- 3.3.1.2 Rising small satellite and cubesat launches
- 3.3.1.3 Advancements in propulsion technologies
- 3.3.1.4 Increased investments in space infrastructure
- 3.3.1.5 The growing commercial space activities
- 3.3.2 Pitfalls and challenges
- 3.3.2.1 Technical Reliability and Mission Assurance
- 3.3.2.2 Regulatory Complexity and Space Traffic Management
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4 Growth potential analysis
- 3.5 Regulatory landscape
- 3.5.1 North America
- 3.5.2 Europe
- 3.5.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.5.4 Latin America
- 3.5.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.6 Porter's analysis
- 3.7 PESTEL analysis
- 3.8 Technology and Innovation landscape
- 3.8.1 Current technological trends
- 3.8.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.9 Emerging business models
- 3.10 Compliance requirements
- 3.11 Defense budget analysis
- 3.12 Global defense spending trends
- 3.13 Regional defense budget allocation
- 3.13.1 North America
- 3.13.2 Europe
- 3.13.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.13.4 Middle East and Africa
- 3.13.5 Latin America
- 3.14 Key defense modernization programs
- 3.15 Budget forecast (2025-2034)
- 3.15.1 Impact on industry growth
- 3.15.2 Defense budgets by country
- 3.16 Sustainability initiatives
- 3.17 Supply chain resilience
- 3.18 Geopolitical analysis
- 3.19 Workforce analysis
- 3.20 Digital transformation
- 3.21 Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships landscape
- 3.22 Risk assessment and management
- 3.23 Major contract awards (2021-2024)
Chapter 4 Competitive landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 By region
- 4.2.1.1 North America
- 4.2.1.2 Europe
- 4.2.1.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.1.4 Latin America
- 4.2.1.5 Middle East & Africa
- 4.2.2 Market concentration analysis
- 4.2.1 By region
- 4.3 Competitive benchmarking of key players
- 4.3.1 Financial performance comparison
- 4.3.1.1 Revenue
- 4.3.1.2 Profit margin
- 4.3.1.3 R&D
- 4.3.2 Product portfolio comparison
- 4.3.2.1 Product range breadth
- 4.3.2.2 Technology
- 4.3.2.3 Innovation
- 4.3.3 Geographic presence comparison
- 4.3.3.1 Global footprint analysis
- 4.3.3.2 Service network coverage
- 4.3.3.3 Market penetration by region
- 4.3.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.3.4.1 Leaders
- 4.3.4.2 Challengers
- 4.3.4.3 Followers
- 4.3.4.4 Niche players
- 4.3.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.3.1 Financial performance comparison
- 4.4 Key developments, 2021-2024
- 4.4.1 Mergers and acquisitions
- 4.4.2 Partnerships and collaborations
- 4.4.3 Technological advancements
- 4.4.4 Expansion and investment strategies
- 4.4.5 Sustainability initiatives
- 4.4.6 Digital transformation initiatives
- 4.5 Emerging/ startup competitors landscape
Chapter 5 Market estimates and forecast, By Type, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Cargo transfer vehicles
- 5.3 Crew transfer vehicles
- 5.4 Refueling vehicles
- 5.5 Satellite servicing & debris removal vehicles
- 5.6 Others
Chapter 6 Market estimates and forecast, By Vehicle Type, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Single Use OTVs
- 6.3 Reusable OTVs
Chapter 7 Market estimates and forecast, By Propulsion System, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Chemical propulsion
- 7.3 Electric propulsion
- 7.4 Nuclear thermal propulsion
- 7.5 Others
Chapter 8 Market estimates and forecast, By Payload Capacity, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Small payload (up to 200 kg)
- 8.3 Medium payload (200 kg to 1,000 kg)
- 8.4 Large payload (1,000 kg and above)
Chapter 9 Market estimates and forecast, By Application, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 Satellite deployment
- 9.3 Space exploration
- 9.4 Inorbit servicing
- 9.5 Space tourism
- 9.6 Space station resupply & crew rotation
- 9.7 Others
Chapter 10 Market estimates and forecast, By End Use, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 Government space agencies
- 10.3 Commercial space companies
- 10.4 Public-private partnerships
Chapter 11 Market estimates and forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 11.1 Key trends
- 11.2 North America
- 11.2.1 U.S.
- 11.2.2 Canada
- 11.3 Europe
- 11.3.1 Germany
- 11.3.2 UK
- 11.3.3 France
- 11.3.4 Spain
- 11.3.5 Italy
- 11.3.6 Netherlands
- 11.4 Asia Pacific
- 11.4.1 China
- 11.4.2 India
- 11.4.3 Japan
- 11.4.4 Australia
- 11.4.5 South Korea
- 11.5 Latin America
- 11.5.1 Brazil
- 11.5.2 Mexico
- 11.5.3 Argentina
- 11.6 Middle East and Africa
- 11.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 11.6.2 South Africa
- 11.6.3 UAE
Chapter 12 Company profiles
- 12.1 Global Key Players
- 12.1.1 SpaceX
- 12.1.2 Blue Origin LLC
- 12.1.3 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 12.1.4 Thales Alenia Space S.A.
- 12.1.5 ArianeGroup SAS
- 12.1.6 United Launch Alliance LLC (ULA)
- 12.1.7 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 12.1.8 China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT)
- 12.1.9 Roscosmos / Energia
- 12.1.10 ISRO / Antrix Corporation
- 12.2 Regional Key Players
- 12.2.1 North America
- 12.2.1.1 Rocket Lab USA Inc.
- 12.2.1.2 Momentus Inc.
- 12.2.1.3 Epic Aerospace LLC
- 12.2.1.4 Quantum Space LLC
- 12.2.1.5 Impulse Space Inc.
- 12.2.1.6 Firefly Aerospace
- 12.2.1.7 Relativity Space
- 12.2.1.8 Sierra Space
- 12.2.1.9 Moog Inc.
- 12.2.1.10 Altius Space Machines Inc.
- 12.2.2 Europe
- 12.2.2.1 D-Orbit S.p.A.
- 12.2.2.2 OHB SE
- 12.2.2.3 Orbital Operations Ltd
- 12.2.2.4 Gama Space SAS
- 12.2.2.5 MaiaSpace SAS
- 12.2.3 Asia-Pacific
- 12.2.3.1 CASIC / ExPace
- 12.2.3.2 Space Machines Company Pty Ltd
- 12.2.1 North America
- 12.3 Disruptors / Niche Players
- 12.3.1 Starfish Space Inc.
- 12.3.2 Atomos Space LLC
- 12.3.3 Astroscale Holdings Inc.
- 12.3.4 Virgin Galactic













