
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1921889
리튬이온 배터리용 LMFP 특허 상황 분석(2026년)LMFP for Li-ion Batteries Patent Landscape Analysis 2026 |
||||||
LMFP: 특허 활동은 급속한 성장과 변화를 보이고 있으며,차세대 리튬이온 배터리의 유망한 양극 재료
전기자동차(EV)와 대규모 에너지 저장 시스템(ESS)의 보급으로 인해 고효율 및 친환경 에너지 저장 솔루션에 대한 세계 수요가 급증함에 따라 첨단 리튬이온 배터리(LIB)용 양극재 개발이 중요한 초점이 되고 있습니다. 올리빈 구조의 리튬인산철(LFP)은 높은 안전성, 안정성, 저비용, 친환경성으로 널리 평가받고 있지만, 작동 전압이 상대적으로 낮고(보통 약 3.4V/Li/Li+), 에너지 밀도가 제한적이기 때문에 고성능 용도 증가하는 요구 사항을 충족시키기에 충분하지 않습니다. 이러한 과제에 대해 올리빈 구조에서 철을 망간으로 부분적으로 대체한 리튬망간인산철리튬(LMFP)이 유망한 대체 재료로 등장했습니다. 이 조성물은 LFP의 높은 열 안정성과 비용 효율성을 계승하면서 망간의 높은 산화환원전위를 활용하여 LFP 대비 10-20%의 에너지 밀도 향상을 실현했습니다. 그러나 이러한 장점에도 불구하고 LMFP에는 고유한 과제가 존재합니다. 구체적으로는 낮은 전자 및 이온 전도도, 느린 리튬이온 확산 속도, 망간 용출 문제, 그리고 Mn3+에 의한 얀텔러 효과와 관련된 용량 저하 등을 들 수 있습니다. 이를 위해 지난 10년간 활발한 특허 활동을 바탕으로 광범위한 조사가 진행되어 왔습니다.
IP 신규 진출기업 발굴
2023년 이후, 중국 기업은 LMFP 특허 정세에서 지배적인 신규 진출기업으로 자리매김했습니다. 2023년 이후 410개 이상의 신규 IP 기업이 LMFP 특허 정세에 진입했으며, 그 중 약 80%가 중국 기업입니다. 신규 진출기업 중 20개 이상은 중국 외의 스타트업 기업입니다. 중국 주요 기업은 소재 제조업체와 배터리 제조업체인 반면, 다른 아시아 신규 진출기업은 주로 R&D 기관과 소재 제조업체입니다. 미국의 신규 진출기업에는 스타트업과 기존 기업 모두 포함됩니다. 기타 비아시아권에서 진출한 기업은 주로 R&D 기관, 배터리 제조업체, 소재 공급업체로 구성되어 있습니다.
이 보고서에서 다루는 기업(발췌)
산업 : CATL, LG Chem/LG Energy Solutions, Samsung, Dynanonic, BYD, EVE Energy, Murata/Sony, ATL, Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy/Gotion, SVOLT, Toyota, Taiheiyo Cement, Toshiba, Sumitomo Chemical/Tanaka Chemical, Tinci Materials Technology, Envision/AESC, Global Graphene, COSMX/COSLIGHT, Sumitomo Metal Mining, Sunwoda, General Motors, Rongbay Technology, HydroQuebec, Reliance New Energy/Lithium Werks, Epsilon Carbon/Johnson Matthey 등
연구개발 기관 : SEL, Kyushu University, AIST, Tokyo Metropolotan University, Central South University, Institute of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing Institute of Technology, Hanyang University, UNIST, KAIST, RIST, KERI, CEA, CNRS, Fraunhofer, Universite de Montreal, University of Chicago, University of Michigan, Lockheed Martin/UT-Battelle 등
이 보고서는 리튬 망간 인산철 인산철(LMFP) 관련 특허 현황을 종합적으로 분석하여 7,800건 이상의 특허 엑셀 데이터베이스와 함께 세계 특허 동향, 주요 기업의 특허 포트폴리오 등의 정보를 제공합니다.
목차
서론
하이라이트
주요 특허 양도
특허 상황 개요
- 특허 공개의 시계열적 변화
- 특허 공개의 추이 : 출원 국가별
- 주요 IP 기업의 타임라인
- 주요 IP 기업 : 기업 유형별
- 주요 IP 기업 : 유형별, 본사 소재지별
- 주요 특허권자의 순위 : 유형별
- 주요 스타트업 기업/순수 기업 : 출신 국가별
- 특허권자의 순위
- 주요 특허권자와 현재 특허 출원자
- 주요 특허권자의 유효한 특허 보유국
- 2023년 이후, 가장 활발한 IP 기업
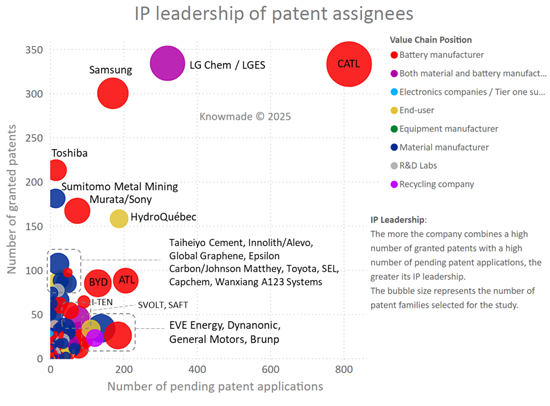
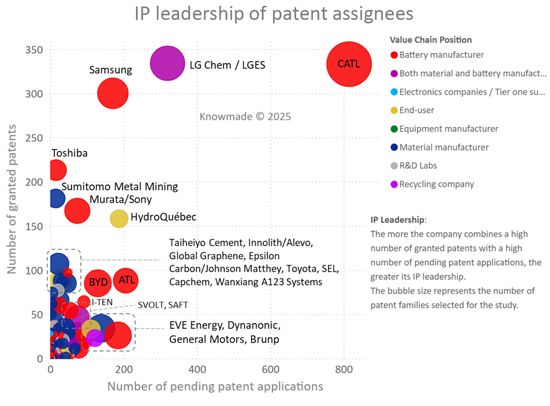
- 특허권자의 IP 리더십
- 주요 기업의 IP 포트폴리오 지역적 범위
- 세계의 특허권자 IP 전략
- 특허 활동 : 기술 부문별(전구체, 양극재료, 정극, 배터리 셀, 기타 컴포넌트)
- 특허 공개의 추이 : 부문별(전구체, 양극재료, 정극, 배터리 셀, 기타 컴포넌트)
- 주요 특허권자 : 부문별(전구체, 양극재료, 정극, 배터리 셀, 기타 컴포넌트)
IP 신규 참여 기업에 대한 초점
- 주요 IP 신규 참여 기업(2023년 이후에 최초의 LMFP 관련 특허가 공개된 기업) : 출신 국가별, 부문별
기술 부문에 대한 초점
LMFP 전구체
LMFP 양극재료
LMFP 전극
LMFP 배터리 셀
각 부문
- 특허 공개의 추이
- 특허 활동 : 출원 국가별
- 주요 IP 기업 : 유형별, 본사 소재지별
- 주요 IP 기업과 IP 신규 참여 기업
- 특허권자의 IP 리더십
- IP 기업의 선행 기술 블로킹 가능성
- 기업의 강제력 있는 IP 포트폴리오의 강도 지수
- 주요 특허
- 최근 특허 출원에 의해 주장되고 있는 발명의 개요
출원국에 대한 초점
중국
일본
한국
유럽
미국
각국
- 특허 공개의 추이
- 특허 패밀리, 출원중 및 취득 특허 : 부문별(전구체, 양극재료, 정극, 배터리 셀, 기타 컴포넌트)
- 특허권자의 IP 리더십
주요 IP 기업에 대한 초점
각 IP 기업 : IP 역학과 특허 활동 레벨, 지역적·기술적 커버 범위, IP의 강점, 강화의 가능성.
- 일본 기업 : Murata Manufacturing/Sony Battery, Toshiba, Panasonic/Sanyo, GS Yuasa, Hitachi, Furukawa, Taiheiyo Cement, Sumitomo Chemical/Tanaka Chemical, Sumitomo Metal Mining, Asahi Kasei, MU Ionic Solutions, Mitsubishi Chemical, Denka, Toda Kogyo, Zeon, Toyota, Nissan 등
- 한국 기업 : LG Chem/LG Energy Solution, Samsung, SK Group, L&F, Posco, EcoPro, Hyundai/kia 등
- 유럽 기업 : SAFT, Blue Solutions, I-TEN, Innolith/Alevo, BASF, Solvay/Syensqo, Umicore, Arkema, Daimler, Renault/Ampere 등.
- 북미 기업 : Amprius/Berzelius, Ignis Lithium, Quantumscape, Global Graphene, Dow, PIDC(Pacific Industrial Development Corporation), Nano One, General Motors, Rivian, Hydro-Quebec 등.
- 중국 기업 : CATL, BYD, EVE Energy, ATL, Gotion/Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy, SVOLT, Envison/AESC, COSMX/COSLIGHT, Sunwoda, Cornex New Energy, CALB(China Aviation Lithium Battery), Wanxiang A123 Systems, Tafel New Energy Technology/Zenergy, JEVE(Tianjin EV Energy), Deyi Energy Technology, Lishen, Phylion, Hithium Energy Storage Technology, Ganfeng Lithium, NIO, GAC Group, Geely Holding, Trina Storage, FAW, Dongfeng Motor, Li-Auto, Battero Technology, WeLion New Energy Technology, Liongo New Energy Technology, Hengtron Nanotech 등
- 기타 기업 : Epsilon Carbon/Johnson Matthey, Aleees(Advanced Lithium Electrochemistry), Reliance New Energy(Lithium Werks/Valence Tech. 포함), Ola Electric Mobility 등
부록
KnowMade 프레젠테이션
KSAKey Features
- PDF with > 400 slides
- Excel file > 7,80 patent families
- Global patenting trends, including time evolution of patent publications, countries of patent filings, etc.
- Main patent assignees and IP newcomers grouped by geographical area
- Key players' IP position and the relative strength of their patent portfolio
- Patents categorized by supply chain segments (precursors, cathode active materials, cathode, battery cells).
- For each segment: IP dynamics, ranking of main patent assignees, IP newcomers, key IP players, key patents, and recent developments
- Excel database containing all patents analyzed in the report, including hyperlinks to an updated online database.
LMFP: A promising cathode material for next-generation Li-ion batteries witnessing a fast-growing and shifting patenting activity
The burgeoning global demand for highly efficient and environmentally friendly energy storage solutions, driven primarily by the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and large-scale energy storage systems (ESS), has made the development of advanced lithium-ion battery (LIB) cathode materials a critical focus. While the olivine-structured lithium iron phosphate (LFP) is widely valued for its high safety, stability, low cost, and environmental friendliness, its relatively low operating voltage, typically around 3.4 V (vs. Li/Li+), limits its energy density and falls short of the increasing requirements for high-performance applications. Lithium manganese iron phosphate (LMFP), developed by partially substituting iron with manganese in the olivine structure, has emerged as a promising alternative. This composition incorporates the high thermal stability and cost-effectiveness of LFP while leveraging the higher redox potential of manganese, resulting in a 10% to 20% higher energy density than LFP. Despite these advantages, LMFP faces intrinsic challenges notably poor electronic and ionic conductivity, sluggish lithium-ion diffusion kinetics, manganese dissolution issues, and capacity degradation related to the Jahn-Teller effect induced by Mn3+. Consequently, extensive research, supported by robust patent activity, has been performed for the last ten years.
In this context, the present report aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the patent landscape related to the lithium manganese iron phosphate, from materials to battery cells. Knowmade's analysts have selected and analyzed more than 7,800+ patent families (inventions) related to LMFP.
The general objectives of the present report are:
- to identify and map the key IP players in each chosen technological segment (precursors, cathode active materials, cathodes, battery cells).
- to assess the geographical distribution of patent families, current legal status of patents, helping stakeholders understand strategic positioning and navigate their competitive environment.
- to get an overview of key and recent patents across the value chain.
These strategic insights will support R&D, investment, and policy decisions in the evolving field of Li-ion battery.
Understanding the main trends, the key players' IP position and IP strategy
IP competition analysis should reflect the vision of players with a strategy to enter and develop their business in the LMFP Li-ion battery market. In this report, Knowmade's analysts provide a comprehensive overview of the competitive IP landscape and latest technological developments in this field. The report identifies the IP leaders, most active patent applicants, and new entrants in the IP landscape. It also sheds light on under-the-radar companies and new players in this field. The report covers IP dynamics and key trends in terms of patents applications, patent assignees, filing countries, and technological segment of interest (precursors, cathode active materials, cathode, battery cells, etc.). Dedicated sections of the report focus on the patent portfolios of key players from various countries.
Identify the IP newcomers
Since 2023, Chinese entities have established themselves as dominant newcomers in the LMFP patent landscape. Over 410 new IP players have entered the LMFP patent landscape since 2023, with around 80% coming from China. More than 20 newcomers are non-Chinese start-ups. The main Chinese entrants are material and battery manufacturers, while other Asian newcomers are primarily R&D institutes and material producers. American newcomers include both start-ups and established companies, whereas other non-Asian entrants consist mainly of R&D organizations, battery manufacturers, and material suppliers. Dedicated sections of the report focus on the patent portfolios of IP new entrants from various countries.
Deep dive into key and recent patents across LMFP value chain
All patents selected for this study have been categorized by supply chain segment (precursor, cathode material, cathode, battery cells).
For each supply chain segment, this report includes a time-evolution of patent applications, main and key patent assignees, and a description of key and recently patented technologies. An understanding of the current technical challenges addressed in the patents is also presented.
Useful Excel patent database
This report also includes an extensive Excel database with all patents analyzed in this study, including patent information (numbers, dates, assignees, title, abstract, etc.), hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), and supply chain segments (precursors, cathode active materials, cathodes, battery cells).
Companies mentioned in the report (non-exhaustive)
INDUSTRIALS: CATL, LG Chem/LG Energy Solutions, Samsung, Dynanonic, BYD, EVE Energy, Murata/Sony, ATL, Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy/Gotion, SVOLT, Toyota, Taiheiyo Cement, Toshiba, Sumitomo Chemical/Tanaka Chemical, Tinci Materials Technology, Envision/AESC, Global Graphene, COSMX/COSLIGHT, Sumitomo Metal Mining, Sunwoda, General Motors, Rongbay Technology, HydroQuebec, Reliance New Energy/Lithium Werks, Epsilon Carbon/Johnson Matthey and more.
R&D LABORATORIES: SEL, Kyushu University, AIST, Tokyo Metropolotan University, Central South University, Institute of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing Institute of Technology, Hanyang University, UNIST, KAIST, RIST, KERI, CEA, CNRS, Fraunhofer, Universite de Montreal, University of Chicago, University of Michigan, Lockheed Martin/UT-Battelle and more.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
- Scope of the report
- Methodology
- Essentials on Solid-state Batteries
- Essentials on Halide solid electrolytes
HIGHLIGHTS
MAIN PATENT TRANFERS
PATENT LANDSCAPE OVERVIEW
- Time evolution of patent publications
- Time evolution of patent publications by filing countries
- Timeline of main IP players
- Main IP players by typology of companies
- Main IP players by typology and headquarters countries
- Ranking of main patent assignees by typology
- Main start-ups/pure players by originating countries
- Ranking of patent assignees
- Main patent owners and current patent applicants
- Countries of active patents for main patent assignees
- Most active IP players since 2023
- IP leadership of patent assignees
- Geographical coverage of main players' IP portfolios
- Global IP strategy of patent assignees
- Patent activities by technological segments (precursors, cathode materials, cathode, battery cells, and other components)
- Time evolution of patent publications by segments (precursors, cathode materials, cathode, battery cells, and other components)
- Main patent assignees by segments (precursors, cathode materials, cathode, battery cells, and other components)
FOCUS ON IP NEWCOMERS
- Main IP newcomers (first LMFP-related patent published in 2023 or later) by originating countries and by segments
FOCUS ON TECHNICAL SEGMENTS
LMFP precursors
LMFP cathode materials
LMFP electrode
LMFP battery cells
For each segment:
- Time evolution of patent publications
- Patent activity by filing countries
- Main IP players by typology and headquarters countries
- Key IP players and IP newcomers
- IP leadership of patent assignees
- Prior-art blocking potential of IP players
- Strength index of players' enforceable IP portfolios
- Key patents
- Overview of inventions claimed by recent patent applications
FOCUS ON FILING COUNTRIES
China
Japan
South Korea
Europe
USA
For each country:
- Time evolution of patent publications
- Patent families, pending applications and granted patents by segments (precursors, cathode materials, cathode, battery cells, and other components)
- IP leadership of patent assignees
FOCUS ON MAIN AND KEY IP PLAYERS
Fore each IP players: IP dynamics and level of patent activity, geographical & technical coverage, IP strengths, and potential for reinforcement.
- Japanese companies: Murata Manufacturing/Sony Battery, Toshiba, Panasonic/Sanyo, GS Yuasa, Hitachi, Furukawa, Taiheiyo Cement, Sumitomo Chemical/Tanaka Chemical, Sumitomo Metal Mining, Asahi Kasei, MU Ionic Solutions, Mitsubishi Chemical, Denka, Toda Kogyo, Zeon, Toyota, Nissan, and more
- South Korean companies: LG Chem/LG Energy Solution, Samsung, SK Group, L&F, Posco, EcoPro, Hyundai/kia, and more
- European companies: SAFT, Blue Solutions, I-TEN, Innolith/Alevo, BASF, Solvay/Syensqo, Umicore, Arkema, Daimler, Renault/Ampere, and more.
- North American companies: Amprius/Berzelius, Ignis Lithium, Quantumscape, Global Graphene, Dow, PIDC (Pacific Industrial Development Corporation), Nano One, General Motors, Rivian, Hydro-Quebec and more.
- Chinese companies: CATL, BYD, EVE Energy, ATL, Gotion/Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy, SVOLT, Envison/AESC, COSMX/COSLIGHT, Sunwoda, Cornex New Energy, CALB (China Aviation Lithium Battery), Wanxiang A123 Systems, Tafel New Energy Technology/Zenergy, JEVE (Tianjin EV Energy), Deyi Energy Technology, Lishen, Phylion, Hithium Energy Storage Technology, Ganfeng Lithium, NIO, GAC Group, Geely Holding, Trina Storage, FAW, Dongfeng Motor, Li-Auto, Battero Technology, WeLion New Energy Technology, Liongo New Energy Technology, Hengtron Nanotech, and more
- Other companies: Epsilon Carbon/Johnson Matthey, Aleees (Advanced Lithium Electrochemistry), Reliance New Energy (Incl. Lithium Werks/Valence Tech.), Ola Electric Mobility, and more


















