
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1781113
전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 예측(- 2032년) : 충전 시스템별, 추진력별, 충전 유형별, 컴포넌트별, 전원별, 차종별Wireless Charging Market for Electric Vehicles by Charging System (Inductive and Magnetic Power Transfer), Propulsion, Charging Type (Stationary and Dynamic Wireless Charger), Component, Power Supply, and Vehicle Type - Global Forecast to 2032 |
||||||
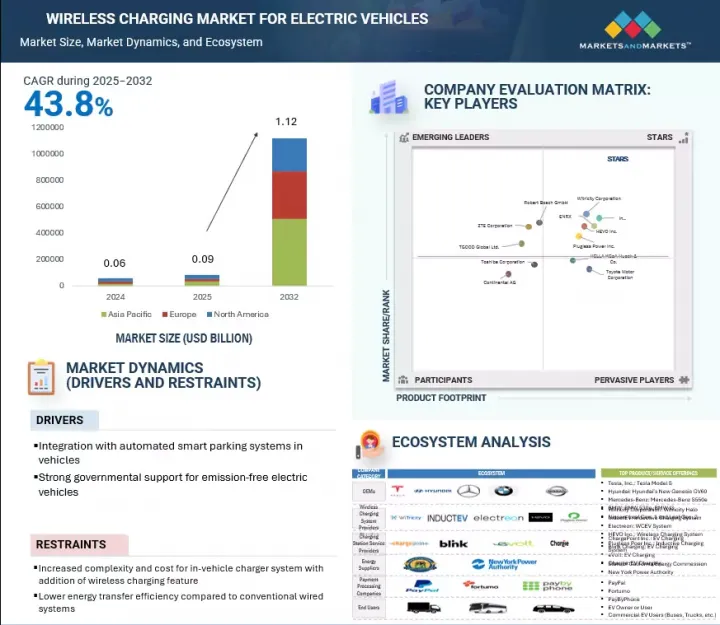
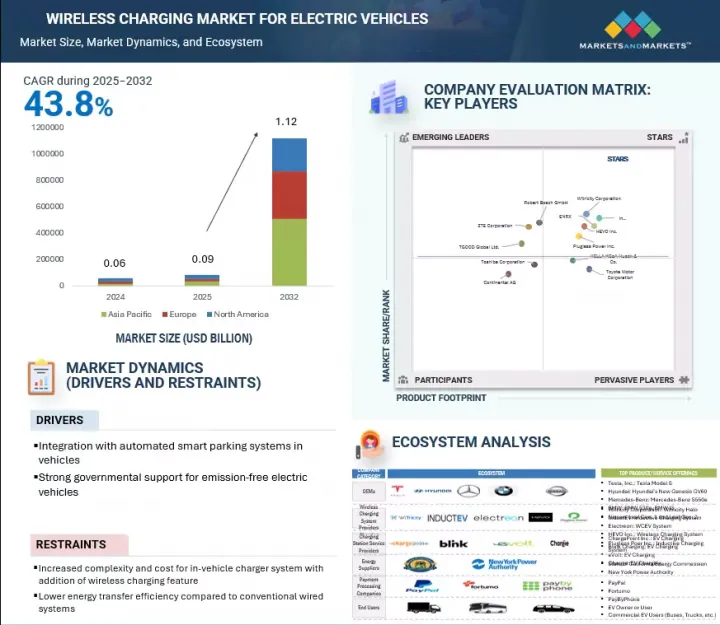
세계의 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 규모는 2025년 9,000만 달러에서 2032년까지 11억 2,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되며, CAGR로 43.8%의 성장이 전망됩니다.
| 조사 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 조사 대상연도 | 2021-2032년 |
| 기준연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 기간 | 2025-2032년 |
| 단위 | 금액(1,000달러), 수량(대) |
| 부문 | 충전 유형, 컴포넌트, 용도, 충전 시스템, 추진력, 전원 범위, 차종, 지역 |
| 대상 지역 | 아시아태평양, 유럽, 북미 |
전기자동차가 세계 시장에서 지속적으로 성장하고 스마트 모빌리티 인프라가 발전하는 가운데, 무선 전기자동차 충전은 전기자동차 충전의 미래를 바꿀 기술로 떠오르고 있습니다. 고급 지향적인 소비자들은 최신 차량 디자인과 스마트홈 생태계에서 편리함과 고급 기술을 점점 더 많이 요구하고 있으며, 무선 충전 경험은 이러한 요구 사항에 부합합니다. 이 솔루션은 유도 전력 전송을 통한 비접촉식 무선 충전을 가능하게 함으로써 기존 플러그인 시스템과 관련된 중요한 운영상의 문제를 해결합니다. SAE J2954 표준에 따른 개발, 자기 정렬 기술의 개선, 스마트 주차 및 에너지 관리 플랫폼과의 통합을 통해 상업적 실행 가능성이 더욱 강화되었습니다. 자동차의 전기화가 확대되고 도시가 커넥티드 인프라를 도입함에 따라 무선 EV 충전은 효율적이고 인프라에 최적화된 전기 이동성을 구현하는 데 있으며, 매우 중요한 역할을 하게 될 것입니다.
"다이나믹 무선 충전은 각국이 무선 충전이 가능한 도로를 선택함에 따라 빠르게 성장하는 틈새 분야가 될 것으로 예측됩니다. "
전기자동차용 다이나믹 무선 충전 기술은 전기자동차 산업에서 큰 성장 잠재력을 가지고 있습니다. 다이나믹 무선 충전 시스템은 노상 충전 시스템으로도 알려져 있습니다. 유도 기술을 기반으로 한 동적 무선 충전 시스템은 주행 중인 전기자동차를 충전할 수 있습니다. 도로에 매설된 송신 패널은 전자기장을 발생시킵니다. 이 전자기장은 그 위를 주행하는 차량에 의해 포착되어 차량내 내장 시스템을 통해 전기로 변환됩니다. 다이나믹 무선 충전은 전기자동차의 주행거리 향상에 도움이 됩니다. 이 시스템이 있으면 소비자는 주행 중에 충전하기 위해 멈춰서서 충전할 필요가 없습니다. 다이나믹 무선 충전 시스템 시장은 무선 충전 시스템이 커버하는 도로의 길이와 전력 전송 속도에 따라 정의할 수 있습니다. 미래의 도로/고속도로에 이 기술이 도입될 것이고, 촉진요인은 이동 중에 전기자동차를 충전하기 위해 통행료를 지불하는 것이기 때문에 이 기술은 큰 성장 잠재력을 가지고 있습니다.
"유럽은 예측 기간 중 가장 빠르게 성장하는 시장이 될 것으로 예측됩니다. "
유럽의 자동차 산업은 무공해 모빌리티로의 급속한 전환을 보여주고 있습니다. 유럽 국가들은 교통 탈탄소화 및 EU의 야심찬 기후 변화 목표 달성을 위한 전략의 일환으로 EV를 적극적으로 모색하고 있습니다. 이 지역의 무선 충전에 대한 수요는 고급 전기자동차에 대한 시장 수요 증가에 힘입어 각 업체들이 무선 충전을 제공하기 위해 적극적으로 나서고 있습니다. 이 생태계를 지원하는 주요 기업으로는 독일의 IPT Technology GmbH와 Robert Bosch GmbH, 스웨덴과 영국의 InductEV, 노르웨이의 ENRX, 여러 시장에 걸쳐 있는 Electreon 등이 있습니다. 이들 기업의 기술은 승용차와 상용차 모두에 적합한 고효율, 저보수 무선 충전 솔루션을 검증하기 위한 파일럿 프로젝트에 적용되고 있습니다.
세계의 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장에 대해 조사분석했으며, 주요 촉진요인과 억제요인, 경쟁 구도, 향후 동향 등의 정보를 제공하고 있습니다.
목차
제1장 서론
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 개요
제4장 중요한 인사이트
- 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장에서의 매력적인 기회
- 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 차종별
- 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 추진력별
- 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 전원 범위별
- 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 충전 시스템별
- 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 컴포넌트별
- 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 지역별
제5장 시장 개요
- 서론
- 시장 역학
- 촉진요인
- 억제요인
- 기회
- 과제
- 가격 분석
- 에코시스템 분석
- 무선 EV 충전 시스템 프로바이더
- OEM
- 충전 서비스 프로바이더
- 최종사용자
- 밸류체인 분석
- 사례 연구 분석
- 투자와 자금조달 시나리오
- 특허 분석
- AI/생성형 AI의 영향
- 기술 분석
- 주요 기술
- 보완 기술
- 인접 기술
- EV용 무선 충전 시장 구조와 경쟁상의 우선순위
- 세계의 무선 충전 규격 정합
- 무선 EV 충전의 채택 : 승용차 부문과 상용차 부문의 비교
- 무선 EV 충전 에코시스템에서 자동차 OEM 포지셔닝
- 무선 전력 전송에서 기술적 제약
- 무선 EV 충전 인프라 성숙도와 상업화 타임라인
- 무선 EV 충전에서 공공 부문 투자와 민간 부문의 경영
- 무선 EV 충전 인프라와 통합 의존관계
- 공급업체 에코시스템과 기술의 차별화
- 유틸리티 조정과 스마트 그리드 통합
- 고부하 플릿 환경에서 무선 충전의 이용
- 동적 온로드 무선 EV 충전 시스템의 인프라 요건
- 무선 EV 충전에 대한 투자와 설비투자의 분석
- 자본 지출과 운영 효율 모델
- 부동산과 주차장 파트너십
- 보험과 보증에 관한 고려
- 규제의 개요
- 네덜란드
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 영국
- 중국
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 주요 컨퍼런스와 이벤트(2025-2026년)
- 주요 이해관계자와 구입 기준
- 고객 비즈니스에 영향을 미치는 동향과 혼란
제6장 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 충전 시스템별
- 서론
- 자기 전력 전송
- 유도 전력 전송
- 중요한 인사이트
제7장 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 충전 유형별
- 서론
- 고정식 무선 충전 시스템
- 동적 무선 충전 시스템
- 중요한 인사이트
제8장 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 용도별
- 서론
- 가정용 충전 유닛
- 상업용 충전소
- 중요한 인사이트
제9장 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 컴포넌트별
- 서론
- 기반 충전 패드
- 파워 컨트롤 유닛
- 차량 충전 패드
- 중요한 인사이트
제10장 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 전원 범위별
- 서론
- 3.7kW 이하
- 3.8-7.7kW
- 7.8-11kW
- 11kW 초과
- 중요한 인사이트
제11장 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 추진력별
- 서론
- 배터리 전기자동차(BEV)
- 플러그인 하이브리드 전기자동차(PHEV)
- 중요한 인사이트
제12장 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 차종별
- 서론
- 승용차
- 상용차
- 중요한 인사이트
제13장 전기자동차용 무선 충전 시장 : 지역별
- 서론
- 아시아태평양
- 거시경제 전망
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 유럽
- 거시경제 전망
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 네덜란드
- 노르웨이
- 스페인
- 스웨덴
- 스위스
- 영국
- 북미
- 거시경제 전망
- 캐나다
- 미국
제14장 경쟁 구도
- 서론
- 주요 참여 기업의 전략/강점
- 시장 점유율 분석(2024년)
- 주요 기업의 시장 순위 분석(2024년)
- 매출 분석(2020-2024년)
- 기업의 평가와 재무 지표
- 브랜드/제품 비교
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 주요 기업(2024년)
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 스타트업/중소기업(2024년)
- 경쟁 벤치마킹
- 경쟁 시나리오
제15장 기업 개요
- 주요 기업
- WITRICITY CORPORATION
- INDUCTEV
- ENRX
- PLUGLESS POWER INC.
- HEVO INC.
- ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
- TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION
- HELLA KGAA HUECK & CO.
- TGOOD GLOBAL LTD.
- ZTE CORPORATION
- CONTINENTAL AG
- TOSHIBA CORPORATION
- 기타 주요 기업
- IDEANOMICS, INC.
- LEAR CORPORATION
- VOLTERIO GMBH(ALLINONE CREATIVE)
- MOJO MOBILITY INC.
- BMW
- FORTUM CORPORATION
- MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
- HYUNDAI MOTOR COMPANY
- ELECTREON
- INTIS LTD.
- DELTA ELECTRONICS, INC.
- PULS GMBH
- DAIHEN CORPORATION
제16장 MARKETSANDMARKETS에 의한 제안
- 아시아태평양이 EV 무선 충전의 주요 시장이 된다.
- 무선 충전 프로바이더에 의한 상호운용성 표준의 중시
- 시장 침투를 높이기 위한 공급 계약에 대한 전략적 주력
- 결론
제17장 부록
KSA 25.08.11The global wireless charging market for electric vehicles is projected to grow from USD 0.09 billion in 2025 to USD 1.12 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 43.8%.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2021-2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Thousand), Volume (Units) |
| Segments | Charging type, component, application, charging system, propulsion, power supply range, vehicle type, and region |
| Regions covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, and North America |
As electric vehicles continue to gain momentum across global markets and smart mobility infrastructure advances, wireless EV charging is emerging as a transformative technology in the future of EV charging. As premium consumers increasingly seek convenience and high-end technology with modern vehicle design and smart home ecosystems, the wireless charging experience aligns with those requirements. By enabling contactless, wireless charging through inductive power transfer, this solution addresses key operational challenges associated with conventional plug-in systems. Developments aligned with SAE J2954 standards, improvements in magnetic alignment technologies, and integration with smart parking and energy management platforms are further reinforcing commercial viability. As vehicle electrification scales and cities adopt connected infrastructure, wireless EV charging is positioned to play a pivotal role in enabling efficient and infrastructure-optimized electric mobility.
"Magnetic power transfer is expected to be one of the leading segments of the market by charging system during the forecast period."
Magnetic resonance coupling and magnetic dynamic coupling achieve magnetic power transfer. In the magnetic resonance coupling method, power transfer between the transmitter pad and receiver pad is achieved through electromagnetic coupling. The electric power passes through the transmitter pad and is converted into magnetic waves by the primary coil attached to the transmitter coil. The receiver pad consists of a receiver coil, which picks up these waves and converts them back to electric power to charge the vehicle. Advantages of magnetic resonance coupling, which include longer charging distance and higher power, are expected to fuel the adoption of this charging system in the wireless charging market for electric vehicles. The efficiency of power transfer is approximately 90-93% in this technology, which is vital in narrowing the performance gap between wired and wireless charging, making it a viable alternative for adoption.
"Dynamic wireless charging expected to be a fast-growing niche with countries opting for wireless chargeable roads."
Dynamic wireless charging technology for electric vehicles has a huge growth potential in the electric vehicle industry. The dynamic wireless charging system is also known as the on-road charging system. Based on induction technology, a dynamic wireless charging system can charge an electric vehicle when it is in motion. The transmitter panels buried in the road generate an electromagnetic field. This electromagnetic field, captured by the vehicle when driving over it, gets converted into electricity via a built-in system inside the vehicle. Dynamic wireless charging can help improve the range of electric vehicles. With this offering, consumers would not need to stop while traveling to charge their vehicles. The market for dynamic wireless charging systems can be defined by the length of roads covered by the wireless charging systems and the power transfer rate. This technology thus has vast growth potential with future roads/highways expected to be equipped with this technology, and drivers pay tolls for charging their electric vehicles on the move.
"Europe is expected to be the fastest-growing market during the forecast period."
The European automotive industry is witnessing a rapid shift toward zero-emission mobility. These countries are actively exploring EVs as part of their strategies to decarbonize transport and meet the European Union's increasingly ambitious climate goals. The demand for wireless charging in the region is supported by a growing demand for luxury EVs in the market, and companies are actively working to provide a wireless charging offering. Key players supporting this ecosystem include IPT Technology GmbH and Robert Bosch GmbH in Germany, InductEV in Sweden and the UK, ENRX in Norway, and Electreon across multiple markets. Their technologies are being integrated into pilot projects aimed at validating high-efficiency, low-maintenance wireless charging solutions compatible with both passenger and commercial electric vehicles.
In-depth interviews were conducted with CXOs, managers, and executives from various key organizations operating in this market.
- By Company Type: OEMs - 24%, Tier I - 67%, Others- 9%,
- By Designation: CXOs - 33%, Managers- 52%, Executives- 15%
- By Region: North America- 32%, Europe - 27 %, Asia Pacific- 41%
The wireless charging market for electric vehicles is dominated by established players such as WiTricity Corporation (US), InductEV Inc. (US), ENRX (Norway), Plugless Power Inc. (US), and HEVO Inc. (US). These companies develop and supply wireless charging solutions for electric vehicles, ranging from factory-integrated systems to high-power fleet infrastructure.
Research Coverage:
The market study covers the wireless charging for electric vehicles market by charging system (inductive power transfer (IPT) and magnetic power transfer), by propulsion (battery electric vehicle (BEV) and plug-hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV)), by charging type (stationary wireless charger and dynamic wireless charger), by component (base charging pad, power control unit, vehicle charging pad) by power supply (up to 3.7 kW, above 3.7-7.7 kW, above 7.7 -11 kW, above 11 kW) and by vehicle type (passenger car and commercial vehicle). It also covers the competitive landscape and company profiles of the major players in the wireless charging market for electric vehicles.
Key Benefits of Buying the Report
The study also includes an in-depth competitive analysis of the key players in the market, along with their company profiles, key observations related to product and business offerings, recent developments, and key market strategies.
The report will help the market leaders/new entrants in this market with information on the closest approximations of the revenue numbers for the overall wireless charging market for electric vehicles and the subsegments. This report will help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain more insights to position their businesses better and plan suitable go-to-market strategies. The report also helps stakeholders understand the market pulse and provides information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities.
The report provides insights into the following points:
- Analysis of key drivers (integration with automated smart parking systems in vehicles, strong governmental support toward emission-free and safe electric vehicles), restraints (increased complexity and cost for in-vehicle charger system with addition of wireless charging feature, lower energy transfer efficiency compared to conventional wired systems), opportunities (integration of wireless charging in smart city infrastructure, increasing investments in dynamic wireless charging technology, increasing testing of wireless charging in government roadway projects), and challenges (lack of standardized vehicle integration, high setup and installation costs of public AC wireless charging compared to L2 wired charging) influencing the growth of wireless charging market for electric vehicles
- Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights into upcoming technologies, research & development activities, and product launches in the wireless charging market for electric vehicles
- Market Development: Comprehensive information about lucrative markets (the report analyzes the wireless charging market for electric vehicles across varied regions)
- Market Diversification: Exhaustive information about new products, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the wireless charging market for electric vehicles.
- Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, growth strategies, and service offerings of leading players like WiTricity Corporation (US), InductEV Inc. (US), ENRX (Norway), Plugless Power Inc. (US), and HEVO Inc. (US) in the wireless charging market for electric vehicles.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.2.1 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKETS COVERED AND REGIONAL SCOPE
- 1.3.2 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.5 UNIT CONSIDERED
- 1.6 STAKEHOLDERS
- 1.7 SUMMARY OF CHANGES
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.1.1.1 List of secondary sources
- 2.1.1.2 Key data from secondary sources
- 2.1.2 PRIMARY DATA
- 2.1.2.1 Primary interviews from demand and supply sides
- 2.1.2.2 Breakdown of primary interviews
- 2.1.2.3 List of primary participants
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.2 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 2.2.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 2.2.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 2.3 DATA TRIANGULATION
- 2.4 FACTOR ANALYSIS
- 2.5 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- 2.6 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS
- 2.7 RISK ASSESSMENT
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 4.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES
- 4.2 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- 4.3 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY PROPULSION
- 4.4 WIRELESS CHARGING FOR MARKET ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY POWER SUPPLY RANGE
- 4.5 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY CHARGING SYSTEM
- 4.6 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY COMPONENT
- 4.7 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY REGION
5 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.2.1.1 Enabling Automated, Cost-Efficient EV Charging for Scalable Urban Mobility
- 5.2.1.2 Increased involvement of OEMs in wireless charging market
- 5.2.1.3 Integration of wireless charging with automated smart parking systems
- 5.2.1.4 Strong governmental support for emission-free and safe electric vehicles
- 5.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 5.2.2.1 High cost and complexity of integrating in-vehicle charger systems
- 5.2.2.2 Lower energy transfer efficiency than conventional wired systems
- 5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 5.2.3.1 Rapid adoption of wireless charging in smart city infrastructure
- 5.2.3.2 Increased investments in dynamic wireless charging technology
- 5.2.3.3 Seamless charging for high-utilization electric fleets
- 5.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 5.2.4.1 Lack of standardized vehicle integration
- 5.2.4.2 Substantial setup and installation costs of public AC wireless charging
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.3 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.3.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND, BY PROPULSION
- 5.4 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 5.4.1 WIRELESS EV CHARGING SYSTEM PROVIDERS
- 5.4.2 OEMS
- 5.4.3 CHARGING SERVICE PROVIDERS
- 5.4.4 END USERS
- 5.5 VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.6 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.6.1 WITRICITY DRIVE 11 BY DAIHEN
- 5.6.2 WIRELESS LEVEL 2 CHARGING BY PLUGLESS POWER
- 5.6.3 DYNAMIC AND STATIONARY EV CHARGING INFRASTRUCTURE BY ELECTREON
- 5.6.4 WIRELESS EV CHARGING SOLUTION BY HEVO AND VEHYA
- 5.7 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO
- 5.8 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 5.9 IMPACT OF AI/GEN AI
- 5.10 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS
- 5.10.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.10.1.1 Moving-field inductive power transfer (MFIPT)
- 5.10.1.2 Resonant charging
- 5.10.1.3 Dynamic wireless charging
- 5.10.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.10.2.1 Capacitive wireless power transfer
- 5.10.2.2 Resonant inductive power transfer
- 5.10.2.3 Magnetic resonance charging
- 5.10.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.10.3.1 Bidirectional charging
- 5.10.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.11 MARKET STRUCTURING AND COMPETITIVE PRIORITIES OF WIRELESS CHARGING FOR EVS
- 5.11.1 GLOBAL ALIGNMENT OF WIRELESS CHARGING STANDARDS
- 5.11.2 ADOPTION OF WIRELESS EV CHARGING PASSENGER VS. COMMERCIAL SEGMENT
- 5.11.3 AUTOMOTIVE OEM POSITIONING IN WIRELESS EV CHARGING ECOSYSTEM
- 5.11.4 TECHNICAL CONSTRAINTS IN WIRELESS POWER TRANSFER
- 5.11.5 INFRASTRUCTURE MATURITY AND COMMERCIALIZATION TIMELINES FOR WIRELESS EV CHARGING
- 5.11.6 PUBLIC SECTOR INVESTMENT VS. PRIVATE SECTOR OPERATIONS IN WIRELESS EV CHARGING
- 5.12 WIRELESS EV CHARGING INFRASTRUCTURE AND INTEGRATION DEPENDENCIES
- 5.12.1 SUPPLIER ECOSYSTEM AND TECHNOLOGY DIFFERENTIATION
- 5.12.2 UTILITY COORDINATION AND SMART GRID INTEGRATION
- 5.12.3 WIRELESS CHARGING APPLICATIONS IN HIGH-DUTY FLEET ENVIRONMENTS
- 5.12.4 INFRASTRUCTURE REQUIREMENTS FOR DYNAMIC ON-ROAD WIRELESS EV CHARGING SYSTEMS
- 5.13 INVESTMENT AND CAPEX ANALYSIS FOR WIRELESS EV CHARGING
- 5.13.1 CAPITAL EXPENDITURE VS. OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCY MODELS
- 5.13.2 REAL ESTATE AND PARKING PARTNERSHIPS
- 5.13.3 INSURANCE AND WARRANTY CONSIDERATIONS
- 5.14 REGULATORY OVERVIEW
- 5.14.1 NETHERLANDS
- 5.14.2 GERMANY
- 5.14.3 FRANCE
- 5.14.4 UK
- 5.14.5 CHINA
- 5.14.6 US
- 5.14.7 CANADA
- 5.15 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2025-2026
- 5.16 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.16.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 5.16.2 BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.17 TRENDS AND DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
6 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY CHARGING SYSTEM
- 6.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.1.1 WIRELESS CHARGING TECHNOLOGIES ADOPTED BY LEADING PLAYERS
- 6.2 MAGNETIC POWER TRANSFER
- 6.2.1 MAGNETIC EV CHARGING POISED FOR GROWTH WITH OEM-READY EFFICIENCY AND DESIGN FLEXIBILITY
- 6.3 INDUCTIVE POWER TRANSFER
- 6.3.1 INDUCTIVE POWER TRANSFER: A SCALABLE, COST-EFFECTIVE, AND LOW-MAINTENANCE CHARGING SOLUTION
- 6.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
7 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY CHARGING TYPE
- 7.1 INTRODUCTION
- 7.1.1 COMPARATIVE DATA BETWEEN STATIONARY VS. DYNAMIC WIRELESS CHARGING FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES
- 7.2 STATIONARY WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEM
- 7.2.1 ENHANCING USER CONVENIENCE AND URBAN INTEGRATION
- 7.3 DYNAMIC WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEM
- 7.3.1 DYNAMIC WIRELESS CHARGING AS CATALYST FOR FLEET ELECTRIFICATION
- 7.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
8 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY APPLICATION
- 8.1 INTRODUCTION
- 8.1.1 WIRELESS CHARGER POWER RANGE OFFERED BY COMPANIES
- 8.2 HOME CHARGING UNIT
- 8.2.1 RISING SALES OF BEVS AND PHEVS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 8.3 COMMERCIAL CHARGING STATION
- 8.3.1 INCREASING CHARGING INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTMENTS AND CONCEPT OF ELECTRIC ROADS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 8.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
9 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY COMPONENT
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 BASE CHARGING PAD
- 9.2.1 SIMPLICITY, RELIABILITY, AND REDUCED USER INTERVENTION TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 9.3 POWER CONTROL UNIT
- 9.3.1 POWER CONTROL UNITS DRIVE WIRELESS CHARGING ADOPTION AMID INFRASTRUCTURE SURGE
- 9.4 VEHICLE CHARGING PAD
- 9.4.1 OEMS EMERGING AS KEY DRIVERS OF VEHICLE CHARGING PAD DEPLOYMENT
- 9.5 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
10 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY POWER SUPPLY RANGE
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.1.1 POWER SUPPLY RANGE OFFERED BY COMPANIES
- 10.2 UP TO 3.7 KW
- 10.2.1 LOWER POWER REQUIREMENT TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 10.3 3.8-7.7 KW
- 10.3.1 POWERING ROUTINE MOBILITY WITH COMPACT WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEMS
- 10.4 7.8-11 KW
- 10.4.1 FASTER CHARGING WITHOUT SIGNIFICANT INFRASTRUCTURE STRAIN TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 10.5 ABOVE 11 KW
- 10.5.1 HIGH-CAPACITY WIRELESS CHARGING FOR COMMERCIAL FLEET EV APPLICATIONS
- 10.6 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
11 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY PROPULSION
- 11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 11.2 BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLE (BEV)
- 11.2.1 INCREASING SALES OF BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 11.3 PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE (PHEV)
- 11.3.1 RISING POPULARITY OF LUXURY PHEVS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 11.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
12 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- 12.1 INTRODUCTION
- 12.2 PASSENGER CAR
- 12.2.1 PASSENGER ELECTRIC VEHICLES EMERGING AS KEY ADOPTERS OF WIRELESS CHARGING SOLUTIONS
- 12.3 COMMERCIAL VEHICLE
- 12.3.1 INCREASING STRINGENCY OF EMISSION NORMS FOR COMMERCIAL VEHICLES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 12.3.2 ELECTRIC BUS
- 12.3.3 ELECTRIC VAN
- 12.3.4 ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCK
- 12.3.5 ELECTRIC TRUCK
- 12.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
13 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY REGION
- 13.1 INTRODUCTION
- 13.2 ASIA PACIFIC
- 13.2.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.2.2 CHINA
- 13.2.2.1 Accelerating wireless EV charging leadership through policy, innovation, and market expansion
- 13.2.3 INDIA
- 13.2.3.1 Supportive government policies and innovation to drive market
- 13.2.4 JAPAN
- 13.2.4.1 Driving standardized wireless EV charging through Japan's public-private innovation model
- 13.2.5 SOUTH KOREA
- 13.2.5.1 Strategic investments by key players for wireless charging technology to drive market
- 13.3 EUROPE
- 13.3.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.3.2 FRANCE
- 13.3.2.1 National EV charging policy and public investment to expand wireless EV charging in France
- 13.3.3 GERMANY
- 13.3.3.1 Collaborations between OEMs and research institutes to enable development of wireless charging technologies
- 13.3.4 NETHERLANDS
- 13.3.4.1 Ambitious government targets and policy support for EV adoption to drive market
- 13.3.5 NORWAY
- 13.3.5.1 High EV adoption and government support to drive wireless EV charging in Norway
- 13.3.6 SPAIN
- 13.3.6.1 Public-sector investment in charging infrastructure to drive market
- 13.3.7 SWEDEN
- 13.3.7.1 Expansion of public road charging projects to drive market
- 13.3.8 SWITZERLAND
- 13.3.8.1 Public EV mandate and growing R&D to drive wireless charging growth in Switzerland
- 13.3.9 UK
- 13.3.9.1 Direct support from government for wireless charging technology to drive market
- 13.4 NORTH AMERICA
- 13.4.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.4.2 CANADA
- 13.4.2.1 Infrastructure investments and policy incentives to accelerate wireless charging expansion
- 13.4.3 US
- 13.4.3.1 OEM pilots, federal mandates, and increased R&D to drive wireless EV charging in the US
14 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 14.1 INTRODUCTION
- 14.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN
- 14.3 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 14.4 MARKET RANKING ANALYSIS OF KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 14.5 REVENUE ANALYSIS, 2020-2024
- 14.6 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS
- 14.6.1 COMPANY VALUATION
- 14.6.2 FINANCIAL METRICS
- 14.7 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 14.8 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 14.8.1 STARS
- 14.8.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 14.8.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 14.8.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 14.8.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 14.8.5.1 Company footprint
- 14.8.5.2 Region footprint
- 14.8.5.3 Charging type footprint
- 14.9 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 14.9.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 14.9.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 14.9.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 14.9.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 14.10 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING
- 14.11 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 14.11.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES AND DEVELOPMENTS
- 14.11.2 DEALS
- 14.11.3 EXPANSIONS
- 14.11.4 OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
15 COMPANY PROFILES
- 15.1 KEY PLAYERS
- 15.1.1 WITRICITY CORPORATION
- 15.1.1.1 Business overview
- 15.1.1.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.1.3 MnM view
- 15.1.1.3.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.1.3.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.1.3.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 15.1.2 INDUCTEV
- 15.1.2.1 Business overview
- 15.1.2.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.2.3 MnM view
- 15.1.2.3.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.2.3.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.2.3.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 15.1.3 ENRX
- 15.1.3.1 Business overview
- 15.1.3.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.3.3 MnM view
- 15.1.3.3.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.3.3.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.3.3.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 15.1.4 PLUGLESS POWER INC.
- 15.1.4.1 Business overview
- 15.1.4.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.4.3 MnM view
- 15.1.4.3.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.4.3.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.4.3.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 15.1.5 HEVO INC.
- 15.1.5.1 Business overview
- 15.1.5.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.5.3 MnM view
- 15.1.5.3.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.5.3.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.5.3.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 15.1.6 ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
- 15.1.6.1 Business overview
- 15.1.6.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.7 TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION
- 15.1.7.1 Business overview
- 15.1.7.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.8 HELLA KGAA HUECK & CO.
- 15.1.8.1 Business overview
- 15.1.8.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.9 TGOOD GLOBAL LTD.
- 15.1.9.1 Business overview
- 15.1.9.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.10 ZTE CORPORATION
- 15.1.10.1 Business overview
- 15.1.10.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.11 CONTINENTAL AG
- 15.1.11.1 Business overview
- 15.1.11.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.12 TOSHIBA CORPORATION
- 15.1.12.1 Business overview
- 15.1.12.2 Recent developments
- 15.1.1 WITRICITY CORPORATION
- 15.2 OTHER KEY PLAYERS
- 15.2.1 IDEANOMICS, INC.
- 15.2.2 LEAR CORPORATION
- 15.2.3 VOLTERIO GMBH (ALLINONE CREATIVE)
- 15.2.4 MOJO MOBILITY INC.
- 15.2.5 BMW
- 15.2.6 FORTUM CORPORATION
- 15.2.7 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
- 15.2.8 HYUNDAI MOTOR COMPANY
- 15.2.9 ELECTREON
- 15.2.10 INTIS LTD.
- 15.2.11 DELTA ELECTRONICS, INC.
- 15.2.12 PULS GMBH
- 15.2.13 DAIHEN CORPORATION
16 RECOMMENDATIONS BY MARKETSANDMARKETS
- 16.1 ASIA PACIFIC TO BE KEY MARKET FOR WIRELESS EV CHARGING
- 16.2 WIRELESS CHARGING PROVIDERS' EMPHASIS ON INTEROPERABILITY STANDARDS
- 16.3 STRATEGIC FOCUS ON SUPPLY CONTRACTS TO HELP INCREASE MARKET PENETRATION
- 16.4 CONCLUSION
17 APPENDIX
- 17.1 INSIGHTS FROM INDUSTRY EXPERTS
- 17.2 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 17.3 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 17.4 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 17.4.1 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY POWER SUPPLY, AT COUNTRY LEVEL (FOR COUNTRIES COVERED IN REPORT)
- 17.4.2 WIRELESS CHARGING MARKET FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES, BY VEHICLE TYPE, AT COUNTRY LEVEL (FOR COUNTRIES COVERED IN REPORT)
- 17.4.3 COMPANY INFORMATION
- 17.5 RELATED REPORTS
- 17.6 AUTHOR DETAILS



















