
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1842700
폐쇄 시스템 약물 전달 장치(CSTD) : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Closed System Transfer Devices (CSTD) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
폐쇄 시스템 약물 전달 장치 시장 규모는 2025년에 14억 3,000만 달러로 평가되었고 예측기간 중(2025-2030년) CAGR은 13.20%를 나타낼것으로 예측되며, 2030년에 26억 7,000만 달러에 달할 전망입니다.

성장 동력은 다음과 같습니다. 많은 병원에서 폐쇄적 취급을 의무화하는 강화된 산업안전 규정, 전 세계적으로 꾸준히 증가하는 항암제 사용량, 그리고 완벽한 밀폐가 필요한 고효능 생물학적 제제의 확대 사용. 하드웨어와 함께 교육 및 환경 모니터링 서비스를 패키지화하는 공급업체들은 다년간 계약을 확보하고 있으며, 이는 구매자들이 CSTD를 독립형 제품이 아닌 광범위한 안전 생태계의 일부로 인식하고 있음을 시사합니다. 기존 업체들은 독점적 연결 메커니즘으로 시장 점유율을 방어하고 있으나, 신규 진입업체들은 안전 기준을 저하시키지 않으면서도 지리적 범위를 확대하기 위해 저비용 키트로 서비스가 부족한 지역을 공략하고 있습니다. 약국 리더들이 정확도를 높이고 직원 노출을 동시에 줄이는 기술을 모색함에 따라 CSTD를 통합한 로봇 조제 시스템도 주목받고 있습니다.
세계의 폐쇄 시스템 약물 전달 장치(CSTD) 시장 동향 및 인사이트
암 발병률 증가로 인한 글로벌 화학요법 규모 확대
암 발병률은 지속적으로 증가하여 2025년 미국에서만 204만 건의 신규 사례가 발생할 것으로 예상됩니다. 사례 증가로 인해 주입 세션이 늘어나면서 모든 조제 작업대와 병상에서 CSTD 수요가 급증하고 있습니다. 병원에서는 고령 환자 비율이 증가하고 있으며, 이 인구 집단은 종종 다제 요법을 처방받아 투여량당 직업적 노출 위험이 높아집니다. 따라서 의료 기관들은 증기와 비말 모두를 차단하는 장치를 위해 자본 예산을 배정하고 있으며, 이러한 연계성은 현재 많은 신규 종양학 병동 건립 지원 제안서에 반영되고 있습니다. 주목할 만한 변화는 조달 위원회가 제안된 장치의 영향을 노출 데이터뿐만 아니라 직원 병가 감소 예상치로도 측정하는 경우가 늘어나면서 안전 투자를 인력 계획 지표와 연계하고 있다는 점입니다.
위험 약물 취급 기준을 강화하는 엄격한 직업 안전 규정
USP 800은 2023년 11월 공식 적용되었으며, 30개 이상의 주에서 채택되어 위험 약물 지침을 권고사항에서 의무사항으로 전환했습니다. 캐나다 주정부 규정과 업데이트된 미국 직업안전보건청(OSHA)의 유해 약물 취급 기준에서도 유사한 시행 동향이 관찰됩니다. 규제 기관이 이제 제품 모델 번호 단위까지 준수 여부를 감사할 수 있게 되면서, 구매 결정 과정에 법무 또는 리스크 관리 부서가 정기적으로 참여하게 되어 이해관계자 범위가 확대되었습니다. 이러한 추가적인 감시는 공급업체들이 제3자 격리 데이터를 쉽게 이해할 수 있는 대시보드 형태로 공개하도록 유도하며, 이는 규제가 측정 가능한 성과에 중점을 두는 점을 반영한 마케팅 트렌드를 보여줍니다. 신흥 추론은 규제 압박이 일회성 검증보다 지속적인 준수 증명을 추구하는 기관들로 인해 환경 모니터링 면봉과 같은 부수적 제품 수요를 간접적으로 촉진한다는 점입니다.
표준 IV 컴포넌트 대비 CSTD 도입의 높은 수명 주기 비용
CSTD의 완전한 도입은 구매, 직원 교육, 워크플로 재설계, 폐기 과정을 수반하여 소규모 클리닉에 비용 장벽을 조성합니다. 표준 IV 구성품과 달리 CSTD는 종종 유해 폐기물로 처리되어야 하며, 이는 중량당 더 높은 폐기 비용을 수반합니다. 따라서 병원들은 잠재적 근로자 노출 사고에 달러 가치를 부여하는 비용 회피 모델링을 수행하며, 이는 재무 담당자들 사이에서 주목받는 전략입니다. 일부 시스템은 공급업체와 물량 기반 리베이트를 협상하지만, 약물 처리량이 적은 농촌 시설은 이러한 협상력을 갖추지 못해 도시-농촌 간 도입 격차를 심화시킵니다. 분산된 클리닉의 수요를 집약하는 그룹 구매 조직이 대안으로 부상 중이며, 이는 자원 제약 환경에서 장치당 가격 인하와 진입 장벽 완화를 가능케 합니다.
부문 분석
2024년 폐쇄 시스템 약물 전달 장치 시장 점유율은 니들리스 시스템이 64.3%를 차지하고, 이 우위는 날카로운 물체 제거와 증기 봉쇄라는 이중 이점에 기인합니다. 의료진은 무침 커넥터 사용 훈련을 이미 받은 인력이 유해 약물 작업 흐름으로 원활히 전환할 수 있어 이러한 장치의 간소화된 자격 인증 절차를 높이 평가합니다. 새로운 관측으로는 많은 기관들이 안전 및 감염 관리를 위한 원스톱 솔루션을 추구하며 무침 CSTD와 항균 IV 포트를 함께 사용하는 동향입니다.
멤브레인 투 멤브레인 부문은 2025년부터 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 14.29%로 성장하여 폐쇄 시스템 약물 전달 장치 시장 규모의 점유율을 꾸준히 확대할 것으로 예측됩니다. 듀얼 멤브레인 아키텍처는 중복 밀봉 기능을 제공하며, 이는 고효능 항암제 및 신흥 항체-약물 접합체(ADC)에 특히 매력적인 특징입니다. 약국 관리자들은 높은 단가를 정당화할 때 증기 차단 데이터를 점점 더 많이 인용하고 있으며, 이는 가치 분석 위원회가 차단 효율성을 핵심 지표로 채택했음을 보여줍니다. 이 부문의 부상은 간접적으로 학제 간 협력을 촉진합니다. 공학 부서가 HVAC 압력 관계가 새로운 작업 흐름을 지원하는지 검증해야 하기 때문입니다.
루어-락(Luer-Lock) 방식 장치는 2024년 폐쇄 시스템 약물 전달 장치 시장 점유율 38.3%를 유지하며, ISO 80369-7 표준화를 활용해 기존 주입 생태계에 호환됩니다. 많은 기관이 재교육 비용을 제거하고 장비 호환성 검증을 단순화하는 루어-락 방식을 선호합니다. 그러나 연결부를 비틀어 고정하는 방식의 편의성으로 인해 대량 조제 약국에서 부분 결합 오류가 가끔 발생하여 안전 팀이 대안을 모색하게 합니다.
푸시-투-턴 시스템은 2030년까지 연평균 16.12% 성장률을 기록할 것으로 전망되어 폐쇄 시스템 약물 전달 장치 산업 내 가장 빠르게 확장되는 하위 범주가 될 것입니다. 또한 클릭-투-락 시스템의 잠금 시 청각적, 촉각적 피드백은 실시간 확인을 제공하여 업무량이 정점에 달한 시기에 잘못된 나사 연결 발생률을 감소시킵니다. 보완적 트렌드로, 결합 부품을 시각적으로 정렬하는 색상 코드식 클릭-투-락 변형 제품이 부상하고 있습니다. 이는 어두운 화학요법실에서 상황 인식을 지원하는 인체공학적 개선점입니다. 조달 데이터에 따르면 이러한 직관적 커넥터는 투여당 설정 시간을 단축시켜 약사가 절약된 시간을 검증 작업에 재배분할 수 있게 합니다.
지역 분석
북미는 2024년 폐쇄 시스템 약물 전달 장치 시장에서 43.5%의 점유율을 차지하며, 이는 USP <800>의 강력한 시행과 업데이트된 NIOSH 유해 약물 목록에 기반합니다. 미국 병원 그룹들은 종종 CSTD 투자를 광범위한 항생제 관리 프로그램과 연계하여 화학적 격리와 감염 관리 지표를 연결합니다. 캐나다는 유사한 경로를 따르지만 주별 차이를 보여 공급업체들이 주별로 출시 일정을 맞춤화하도록 유도합니다. 멕시코의 민간 종양학 클리닉들은 국경을 넘는 환자 유입에 힘입어 국제 고객을 유치하기 위해 점점 더 미국의 안전 프로토콜을 반영하고 있습니다. 미국 기반 단체 구매 조직은 대륙 전역에 걸쳐 유리한 계약 가격을 적용하여 접근성을 균일화하고 시장 침투를 가속화합니다.
유럽은 매출 기준 2위를 차지하며, 폐쇄 시스템 약물 전달 장치 산업은 유해 약물을 직업성 발암물질로 분류하는 유럽연합 발암물질 및 변이원성물질 지침의 영향을 받습니다. 독일과 프랑스 같은 국가들은 표면 오염 모니터링을 의무화하므로, 병원들은 종종 새로운 클린룸 건설을 포함한 다년간의 자본 프로젝트에 CSTD 도입을 통합합니다. 동유럽 병원들은 EU 구조 기금을 활용해 CSTD 도입을 지원함으로써 서유럽 대비 역사적 안전 격차를 좁혀가고 있습니다. 브렉시트로 영국은 별도의 규제 경로를 도입했으나, 대부분의 NHS 트러스트는 ISO 표준을 채택해 채널 간 제품 호환성을 유지하고 있습니다. 유럽 입찰에서 기기 재사용 횟수를 명시하는 사례가 증가하는 동향은 EU 그린딜 하의 환경 우선순위를 반영합니다.
아시아태평양 지역은 암 발병률 증가와 병원 인프라 확대로 2030년까지 연평균 15.23%의 복합 성장률을 보일 것으로 예상되는 가장 빠르게 성장하는 지역입니다. 중국의 신규 지방 암 센터들은 마스터 플랜에 CSTD 예산을 포함시키고 있어, 이 기술이 프리미엄 추가 기능이 아닌 기본 요건으로 인식되고 있음을 시사합니다. 일본의 성숙한 의료 시스템은 고가 생물학적 제제의 낭비를 최소화하기 위해 저데드스페이스(low-dead-space) 설계를 우선시하며, 이는 보험급여 압박이 기술 선호도를 어떻게 형성하는지 보여줍니다. 인도의 대도시 병원들은 저비용 CSTD 변형을 시범 운영하고 있으며, 농촌 의료기관들은 기기 공급과 폐기 서비스를 묶은 임대 모델을 실험 중인데, 이는 이질적인 구매력을 맞추기 위한 적응형 비즈니스 전략을 드러냅니다. 아시아-태평양 전역에서 기기 제조사들은 종종 현지 유통업체와 협력하여 언어별 라벨링 및 교육을 처리함으로써 도입 곡선을 단축합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 도입
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 증가하는 암 발병률로 인한 글로벌 화학요법 규모 확대
- 유해 약물 취급 기준을 강화하는 엄격한 산업 안전 규정
- 자동화 조제 및 로봇 플랫폼에 CSTD 통합
- 밀폐 취급이 필요한 유해 생물학적 제제 및 면역억제제 확
- 의료 시스템 내 포괄적 안전 문화 프로그램 도입 확대
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 표준 IV 컴포넌트 대비 CSTD 도입의 높은 수명 주기 비용
- 보편적 성능 기준 부재로 인한 조달 불확실성
- 기존 IV 및 주입 인프라와의 호환성 문제
- 공급망 분석
- 기술적 전망
- Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 시스템 유형별
- 니들리스 시스템
- 멤브레인 투 멤브레인 시스템
- 클로징 메커니즘별
- 컬러-투-컬러 얼라인먼트 시스템
- 루어-락 시스템
- 푸시-투-턴 시스템
- 클릭-투-락 시스템
- 컴포넌트별
- 주사기 안전 장치
- 바이알 액세스 장치
- 가방 액세스 장치
- 기타 액세서리
- 기술별
- 컴파트먼트식
- 다이어프램식
- 공기 여과 장치
- 최종 사용자별
- 병원
- 종양센터
- 기타
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Becton, Dickinson & Co.
- ICU Medical, Inc.
- B. Braun Melsungen AG
- Equashield LLC
- Baxter International Inc.
- Corvida Medical
- Simplivia Healthcare
- Yukon Medical LLC
- JMS Co., Ltd.
- CODAN Medizinische Gerate
- Vygon SA
- Terumo Corp.
- Fresenius Kabi AG
- Pfizer(Hospira) Inc.
- Caragen Ltd.
- Gerresheimer AG(Sensile Medical AG)
- Halyard Health
- Bespak
제7장 시장 기회와 전망
HBR 25.11.21The Closed System Transfer Devices (CSTD) Market size is estimated at USD 1.43 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 2.67 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 13.20% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
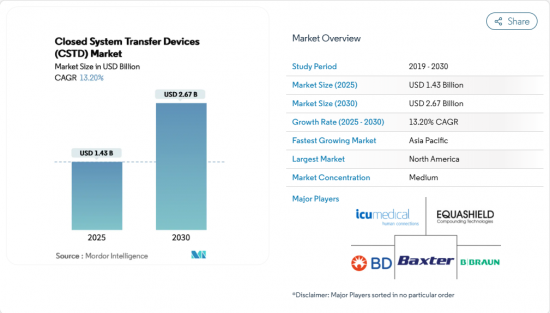
Growth is propelled by stricter occupational-safety rules that now make closed handling mandatory in many hospitals, a steady rise in global chemotherapy volumes, and the widening use of potent biologics that demand airtight containment. Providers that bundle training and environmental-monitoring services with their hardware are capturing multi-year contracts, suggesting that buyers increasingly view CSTDs as part of a broader safety ecosystem rather than stand-alone items. Established players defend share through proprietary connection mechanisms, yet new entrants target underserved regions with lower-cost kits, broadening geographic reach without diluting safety standards. Integrated robotic compounding suites incorporating CSTDs are also gaining traction, as pharmacy leaders seek technology that simultaneously improves accuracy and reduces staff exposure.
Global Closed System Transfer Devices (CSTD) Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Global Chemotherapy Volume from Rising Cancer Incidence
Cancer incidence continues to climb, with 2.04 million new cases projected in the United States alone for 2025. Larger case volumes translate into more infusion sessions, creating a cascade of demand for CSTDs at every preparation bench and bedside. Hospitals now treat higher proportions of older patients, a demographic often prescribed multi-agent regimens that elevate occupational exposure risk per dose. Facilities therefore allocate capital budgets toward devices that promise both vapor and droplet containment, a linkage that now appears in many grant proposals for new oncology wings. One noteworthy shift is that procurement committees increasingly measure proposed device impact not only by exposure data but by projected reductions in staff sick days, aligning safety investments with workforce-planning metrics.
Stricter Occupational Safety Regulations Elevating Hazardous-Drug Handling Standards
USP <800> became compendially applicable in November 2023 and has been adopted by more than 30 states, pivoting hazardous-drug guidance from recommendation to mandate. Similar enforcement traction is visible in provincial Canadian rules and in updated Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) references to hazardous-drug handling. Because regulators can now audit compliance down to product model numbers, purchasing decisions routinely involve the legal or risk-management office, widening the stakeholder pool. That additional scrutiny prompts suppliers to publish third-party containment data in readily digestible dashboards, evidencing a marketing trend that mirrors the regulation's emphasis on measurable performance. An emergent inference is that regulatory pressure indirectly boosts demand for ancillary products such as environmental monitoring swabs, as institutions seek proof of ongoing compliance rather than one-time validation.
High Lifecycle Cost of CSTD Implementation vs Standard IV Components
Full deployment of CSTDs entails acquisition, staff training, workflow redesign, and disposal, creating cost hurdles for smaller clinics. Unlike standard IV components, CSTDs must often be discarded as hazardous waste, which carries higher disposal fees by weight. Hospitals therefore perform cost-avoidance modeling that assigns dollar values to potential worker-exposure incidents, a tactic gaining traction among financial officers. Some systems negotiate volume-based rebates with suppliers, but rural facilities with lower drug throughput lack such leverage, reinforcing an urban-rural adoption divide. An emerging workaround is group purchasing organizations that aggregate demand from distributed clinics, enabling lower per-device pricing and easing entry barriers in resource-constrained settings.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Integration of CSTDs into Automated Compounding & Robotics Platforms
- Expansion of Hazardous Biologics & Immunosuppressants Requiring Closed Handling
- Lack of Universal Performance Standards Causing Procurement Uncertainty
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Needle-less systems hold 64.3% Closed System Transfer Devices market share in 2024, and that dominance roots in their dual benefit of sharps elimination and vapor containment. Hospitals value the simplified credentialing these devices provide because staff already trained on needle-free connectors transition seamlessly to hazardous-drug workflows. A fresh observation is that many institutions now pair needle-less CSTDs with antimicrobial IV ports, seeking a one-stop solution for safety and infection control.
The membrane-to-membrane segment is forecast to grow at a 14.29% CAGR between 2025 and 2030, steadily enlarging its share of the Closed System Transfer Devices market size. Dual-membrane architectures provide redundant seals, a feature especially appealing for high-potency chemotherapy and emerging antibody-drug conjugates. Pharmacy managers increasingly cite vapor-containment data when justifying the higher unit price, showing value analysis committees have adopted containment efficacy as a core metric. This segment's rise indirectly encourages cross-disciplinary collaboration because engineering departments must verify that HVAC pressure relationships support the new workflow.
Luer-Lock devices maintain 38.3% Closed System Transfer Devices market share for 2024, leveraging ISO 80369-7 standardization to plug into existing infusion ecosystems. Many institutions prefer Luer-Lock because it removes retraining costs and simplifies equipment compatibility audits. Yet the ease of twisting connections occasionally produces partial engagement errors in high-volume pharmacies, prompting safety teams to explore alternatives.
Push to Turn Systems are projected to register a 16.12% CAGR through 2030, making them the fastest-expanding subcategory within the Closed System Transfer Devices industry. Furthermore, audible and tactile feedback during locking in Click-to-Lock systems provides real-time confirmation, reducing incidence of mis-threaded connections during peak workload periods. A complementary trend is the rise of color-coded Click-to-Lock variants that visually align mating parts, an ergonomic twist that supports situational awareness in dimly lit chemotherapy units. Procurement data reveal that these intuitive connectors cut setup time per dose, allowing pharmacists to reallocate saved minutes toward verification tasks.
The CSTD Market Report is Segmented by System Type (Needle-Less Systems, and Membrane-To-Membrane Systems), Closing Mechanism (Color To Color Alignment Systems, Luer-Lock Systems, and More), Component (Syringe Safety Devices, Vial Access Devices, and More), Technology (Compartmentalized Devices, and More), End-User (Hospitals, Oncology Centers, and Others) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America's 43.5% share of the Closed System Transfer Devices market in 2024 is anchored by robust enforcement of USP <800> and updated NIOSH hazardous-drug lists. U.S. hospital groups often tie CSTD investments to broader antimicrobial stewardship programs, linking chemical isolation with infection-control metrics. Canada follows a similar trajectory but exhibits provincial variation that encourages vendors to customize rollout timelines province by province. Mexico's private oncology clinics, stimulated by cross-border patient flows, increasingly mirror U.S. safety protocols to attract international clientele. US-based group purchasing organizations extend favorable contract pricing across the continent, harmonizing access and accelerating penetration.
Europe ranks second by revenue, with its Closed System Transfer Devices industry shaped by the European Union's Carcinogens and Mutagens Directive, which classifies hazardous drugs as occupational carcinogens. Countries such as Germany and France mandate surface contamination monitoring, so hospitals often integrate CSTD deployment into multi-year capital projects that include new clean-room construction. Eastern European clinics tap into EU structural funds to finance CSTD adoption, thereby narrowing a historical safety gap with Western counterparts. Brexit has introduced separate regulatory paths for the United Kingdom, yet most NHS trusts converge on ISO standards, sustaining cross-channel product interchangeability. A discernible pattern is that European tenders increasingly specify device reusability counts, reflecting environmental priorities under the EU Green Deal.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing geography, projected to compound at 15.23% annually through 2030 as cancer incidence rises and hospital infrastructure expands. China's new provincial cancer centers include CSTD budgets in their master plans, signaling that the technology is perceived as a baseline requirement rather than a premium add-on. Japan's mature health system prioritizes low-dead-space designs to minimize wastage of high-cost biologics, illustrating how reimbursement pressure shapes technical preference. India's metro hospitals pilot low-cost CSTD variants while rural centers experiment with rental models that bundle device supply with disposal services, revealing adaptive business strategies to match heterogeneous purchasing power. Across Asia-Pacific, device makers often partner with local distributors that handle language-specific labeling and training, shortening the adoption curve.
- Beckton Dickinson
- ICU Medical
- B. Braun
- Equashield LLC
- Baxter
- Corvida Medical
- Simplivia Healthcare
- Yukon Medical LLC
- JMS Co., Ltd.
- CODAN Medizinische Gerate
- Vygon
- Terumo Corp.
- Fresenius
- Pfizer (Hospira) Inc.
- Caragen
- Gerresheimer AG (Sensile Medical AG)
- Halyard Health
- Bespak
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating Global Chemotherapy Volume from Rising Cancer Incidence
- 4.2.2 Stricter Occupational Safety Regulations Elevating Hazardous-Drug Handling Standards
- 4.2.3 Integration of CSTDs into Automated Compounding & Robotics Platforms
- 4.2.4 Expansion of Hazardous Biologics & Immunosuppressants Requiring Closed Handling
- 4.2.5 Growing Adoption of Comprehensive Safety-Culture Programs in Healthcare Systems
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Lifecycle Cost of CSTD Implementation vs Standard IV Components
- 4.3.2 Lack of Universal Performance Standards Causing Procurement Uncertainty
- 4.3.3 Compatibility Challenges with Legacy IV & Infusion Infrastructure
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By System Type
- 5.1.1 Needle-less Systems
- 5.1.2 Membrane-to-Membrane Systems
- 5.2 By Closing Mechanism
- 5.2.1 Color-to-Color Alignment Systems
- 5.2.2 Luer-Lock Systems
- 5.2.3 Push-to-Turn Systems
- 5.2.4 Click-to-Lock Systems
- 5.3 By Component
- 5.3.1 Syringe Safety Devices
- 5.3.2 Vial Access Devices
- 5.3.3 Bag Access Devices
- 5.3.4 Other Accessories
- 5.4 By Technology
- 5.4.1 Compartmentalized Devices
- 5.4.2 Diaphragm-based Devices
- 5.4.3 Air-Filtration Devices
- 5.5 By End-User
- 5.5.1 Hospitals
- 5.5.2 Oncology Centers
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Australia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.4.1 GCC
- 5.6.4.2 South Africa
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5 South America
- 5.6.5.1 Brazil
- 5.6.5.2 Argentina
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Becton, Dickinson & Co.
- 6.3.2 ICU Medical, Inc.
- 6.3.3 B. Braun Melsungen AG
- 6.3.4 Equashield LLC
- 6.3.5 Baxter International Inc.
- 6.3.6 Corvida Medical
- 6.3.7 Simplivia Healthcare
- 6.3.8 Yukon Medical LLC
- 6.3.9 JMS Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.10 CODAN Medizinische Gerate
- 6.3.11 Vygon SA
- 6.3.12 Terumo Corp.
- 6.3.13 Fresenius Kabi AG
- 6.3.14 Pfizer (Hospira) Inc.
- 6.3.15 Caragen Ltd.
- 6.3.16 Gerresheimer AG (Sensile Medical AG)
- 6.3.17 Halyard Health
- 6.3.18 Bespak
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment
















