
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1848122
택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장 규모는 2025년에 6,868억 달러로 평가되었고, 2030년에는 8,855억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 2025-2030년의 CAGR은 5.21%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

이러한 전망은 팬데믹 시대의 급증에서 프리미엄 서비스, 네트워크 자동화, 선별적 역량 확장을 주도하는 보다 안정적인 성장으로의 전환을 시사합니다. 전자상거래는 여전히 핵심 물량 동력이지만, 운영사들은 이제 동적 가격 책정, 기술 기반 경로 설정, 의료 물류와 같은 부가가치 수직 통합을 통해 마진 보호에 주력하고 있습니다. 중소기업 수출업체들이 디지털 마켓플레이스에 의존하는 비중이 증가함에 따라 국경 간 물류 흐름이 확대되는 반면, 성숙한 지역에서는 국내 물량이 정체되고 있습니다. 자본은 항공 운송 능력, 지역 도로 운송 차량, 외부 배송 지점을 통합해 비용과 속도를 최적화할 수 있는 디지털 중심 네트워크로 계속 유입되고 있습니다. DSV의 DB 셴커 인수를 통해 부각된 업계 통합은 노동력 부족, 연료 중립 차량, 항공 화물 제약으로 운영 문턱이 높아지면서 규모의 전략적 가치를 강조합니다.
세계의 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP) 시장 동향 및 인사이트
전자상거래의 보급이 아시아태평양 신흥 지역의 B2C 소포 운송량을 주도
온라인 구매자의 57%가 휴대기기에서 구매하게 되어 스마트폰 주도의 쇼핑이 소포 수요를 주도하고 있습니다. 2030년까지 8조 5,000억 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되는 소셜커머스 매출과 연동해 월경 취급고도 증가. 2025년에는 21조 4,000억 위안(3조 100억 달러)의 디지털 소매 부문과 함께 중국 국경을 넘어서는 소포의 흐름이 증가하고, 사업자들은 다양한 수하물프로파일을 관리하는 유연한 허브의 배치를 촉진하고 있습니다. 동남아시아 전역의 네트워크 투자는 보다 넓은 농촌 지역에 도달하고 배달 시간의 확실성을 목표로 하여 도시 시장과 동등한 서비스를 보장합니다.
유럽 지역에서 디지털 마켓플레이스를 활용한 국경 간 중소기업 수출
유럽 중소기업들은 온라인 마켓플레이스를 통해 글로벌 고객에게 직접 배송하는 비중이 증가하면서 통합 통관 수요가 급증하고 있습니다. 90개 WTO 회원국 간 협상은 절차적 마찰을 줄이기 위한 공통 전자상거래 규칙 마련을 모색 중입니다. 자동화된 신고 및 블록체인 기반 문서는 평균 무역 비용을 11% 절감할 수 있습니다. 표준화된 국경 간 서비스는 운영사들이 물량을 통합하고 단위 비용을 낮추며 택배, 특송 및 소포을 확대할 수 있게 합니다.
태평양 횡단 노선의 항공 운송 능력 제약
2024년 화물기 공급량은 8% 증가했으나, 2025년 중국 수요는 20% 급증할 전망으로 공간 부족과 스팟 요금 전년 대비 15% 상승을 초래할 것입니다. 신규 항공기 인도량 제한으로 향후 성장률은 4.4% 수준에 머무를 전망입니다. 운영사들은 고가치 화물을 우선시하고 2차 허브를 모색하지만, 상승한 비용이 택배 시장 연평균 성장률(CAGR)에 부담을 주고 있습니다.
부문 분석
고령화 인구 증가로 온도 관리 배송 수요가 확대되며 의료 부문이 2025-2030년 간 5.75%의 가장 높은 CAGR을 기록할 전망입니다. DHL과 UPS는 각각 의료 부문 매출을 108억 달러, 200억 달러로 확대할 계획으로 전략적 집중도를 강조하고 있습니다. 실시간 데이터 로거는 규정 준수를 보장하여 택배, 특송 및 소포 전반의 가격 정책에 반영된 프리미엄 요금을 정당화합니다.
전자상거래는 2024년 매출의 36.94%를 차지했으나 성숙 지역에서 점진적 둔화세를 보이고 있습니다. 제조업 및 도매업은 안정적인 B2B 물류를 제공하지만, 금융 서비스 물류는 디지털화로 인한 물리적 문서 교환 감소로 감소세를 보입니다.
국제 소포 시장은 2025년부터 2030년까지 연평균 5.57% 성장할 전망입니다. 무역 협정과 전자 통관 절차 간소화로 국경 간 물류 흐름과 연계된 택배 시장 규모가 확대될 것입니다. 2024년 국내 배송은 69.09% 점유율을 유지했으나, 성숙한 전자상거래 보급률이 성장을 제한하고 있습니다.
BEST Inc.의 킬로그램당 7위안(0.98달러) 서비스와 같은 기술 기반 서비스는 동남아시아 소비자와 중국 판매자를 연결하며, 통합 수출을 통한 비용 절감을 보여줍니다. WTO 디지털 무역 프레임워크와 RCEP 관세 조화는 중소기업의 국제 배송을 더욱 촉진하여 기존 통합업체의 고마진 운송 경로를 확장합니다.
지역 분석
북미는 2024년 매출의 36.76%를 차지했으며, 이는 2일 배송에 대한 소비자 기대와 발전된 라스트마일 자산에 기반합니다. 지속적인 운전자 부족은 운영 비용을 증가시켜 자동화 시범 운영과 UPS-앤드라우어(UPS-Andlauer)와 같은 의료 전문가 인수를 촉진하여 성장 틈새 시장을 확보하고 있습니다. 도시형 마이크로 풀필먼트 센터와 당일 배송 서비스는 물량 증가가 완화되는 상황에서도 프리미엄 요금 안정성을 지원합니다.
아시아태평양 지역은 2025-2030년 연평균 6.77% 성장률로 가장 빠르게 성장하는 지역으로, 국경 간 전자상거래와 소비자 소득 증가가 성장 동력입니다. 중국의 21조 4천억 위안(3조 100억 달러) 규모 디지털 소매 기반이 택배 밀도를 주도하는 가운데, RCEP 관세 조화로 마찰이 감소합니다. 야마토 홀딩스는 2027 회계연도까지 2-2조 4천억 엔(2,800-3,300억 달러) 매출을 목표로 하며, 지역 지속가능성 요구사항에 부응하기 위해 탄소중립 약속을 내재화합니다. 유럽은 기존 우편 인프라와 적극적인 탈탄소화 정책을 결합하고 있습니다. 2035년까지 신규 내연기관 밴 판매 금지로 차량 전기화가 가속화되며, 포스트NL은 2030년까지 베네룩스 지역 배송의 100% 무배출을 계획 중입니다. DHL과 에브리의 합병은 국제 및 국내 역량을 통합해 연간 10억 개 이상의 영국 택배를 처리할 수 있게 했습니다.
중동 및 아프리카는 GCC 다각화 프로그램의 혜택을 받고 있습니다. 사우디아라비아의 자동화 허브는 이 지역을 대륙 간 교통의 교량으로 포지셔닝하는 투자의 모범 사례입니다. 주요 통로에서의 안보 위험과 분산된 인프라로 인해 성장은 여전히 제한적이며, 현지 전문성을 제공하는 국가 우편 사업자와의 협력이 유리합니다. 남미는 규모는 작지만 브라질의 ‘레메사 콘포르메(Remessa Conforme)’ 프로그램과 같은 관세 개혁을 통해 데이터 품질과 규정 준수를 개선하며 글로벌 플랫폼의 국경 간 서비스 확장을 촉진하고 있습니다. 통화 변동성과 불규칙한 도로망은 유연하고 국가별 맞춤형 접근이 필요합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 인구통계
- 경제 활동별 GDP 분포
- 경제활동별 GDP 성장률
- 인플레이션
- 경제성과 및 프로파일
- 전자상거래 업계 동향
- 제조업의 동향
- 운송 및 저장 부문 GDP
- 수출 동향
- 수입 동향
- 연료 가격
- 물류 성능
- 인프라
- 규제 프레임워크
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 신흥 아시아태평양에서의 전자상거래의 침투가 B2C 소포 취급량을 주도
- 유럽 지역의 디지털 마켓플레이스를 활용한 중소기업(SME)의 국경 간 수출
- 북미에서의 당일 배달의 프리미엄화
- GCC 국가들의 우편망 현대화를 위한 정부 추진
- 북유럽 지역의 외부 PUDO 네트워크 도입
- 일본의 헬스케어 CEP에 대한 콜드 체인 규정 준수 요구 사항
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 태평양 횡단 노선에서 목격된 항공 운송 능력 제약
- 미국과 영국의 만성적인 운전자 부족이 라스트 마일 비용에 영향
- EU27에서 배송 차량 배출량에 대한 규제 상한선 시행
- 아프리카 중앙 회랑 루트에서 안보 위험 증가
- 시장에서의 기술 혁신
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 마무리
- 국내
- 국제
- 배송 속도
- 익스프레스
- 비익스프레스
- 모델
- 기업간 거래(B2B)
- 기업 대 소비자(B2C)
- 소비자간(C2C)
- 배송 중량
- 중량
- 경량
- 중중량
- 교통 수단
- 항공
- 도로
- 기타
- 최종 사용자 업계
- 전자상거래
- 금융 서비스(BFSI)
- 헬스케어
- 제조업
- 제1차 산업
- 도매 및 소매업(오프라인)
- 기타
- 지역
- 아시아태평양
- 호주
- 중국
- 인도
- 인도네시아
- 일본
- 말레이시아
- 파키스탄
- 필리핀
- 태국
- 베트남
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 유럽
- 알바니아
- 불가리아
- 크로아티아
- 체코 공화국
- 덴마크
- 에스토니아
- 핀란드
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 헝가리
- 아이슬란드
- 이탈리아
- 라트비아
- 리투아니아
- 네덜란드
- 노르웨이
- 폴란드
- 루마니아
- 러시아
- 슬로바키아 공화국
- 슬로베니아
- 스페인
- 스웨덴
- 스위스
- 영국
- 기타 유럽
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 카타르
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 이집트
- 나이지리아
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 미국
- 기타 북미
- 남미
- 아르헨티나
- 브라질
- 칠레
- 기타 남미
- 아시아태평양
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 주요 전략적 움직임 s
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Aramex
- Australian Postal Corporation
- Canada Post Corporation(Including Purolator, Inc.)
- China Post
- CJ Logistics
- Deppon Logistics Co., Ltd.
- DHL Group
- Empresa Brasileira de Correios e Telegrafos
- FedEx
- InPost Sp. z oo
- International Distribution Services PLC
- JD.com, Inc.(Including JD Logistics, Inc.)
- La Poste Group(Including DPD Group)
- LX International Corp.(Including LX Pantos Co., Ltd.)
- Osterreichische Post AG(Austrian Post)
- Poste Italiane
- PostNL NV
- PostNord AB
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- SG Holdings Co., Ltd.
- STO Express Co., Ltd.(Shentong Express)
- Swiss Post, Ltd.
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
- Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd.
- ZTO Express(Cayman), Inc.
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
HBR 25.11.12The courier express parcel market size is valued at USD 686.8 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 885.5 billion by 2030, advancing at a 5.21% CAGR between 2025-2030.
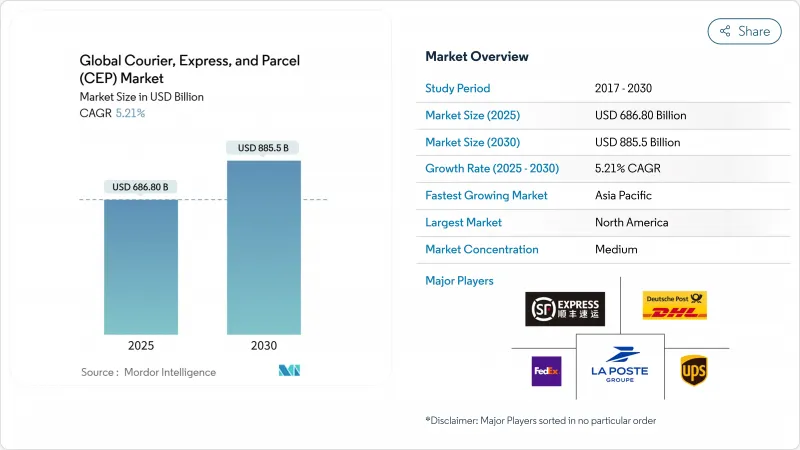
This outlook signals a transition from the pandemic-era surge toward steadier expansion led by premium services, network automation, and selective capacity additions. E-commerce remains the core volume engine, yet operators now emphasize margin protection through dynamic pricing, technology-enabled routing, and value-added verticals such as healthcare logistics. Cross-border flows are expanding as more small and medium exporters rely on digital marketplaces, while domestic volumes plateau in mature regions. Capital continues gravitating to digital-first networks able to integrate air capacity, regional road fleets, and out-of-home delivery points to optimize cost and speed. Consolidation, highlighted by DSV's purchase of DB Schenker, underlines the strategic value of scale as labor shortages, fuel-neutral fleets, and air-freight constraints raise operating thresholds.
Global Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) Market Trends and Insights
E-commerce Penetration Driving B2C Parcel Volumes in Emerging Asia-Pacific Region
Smartphone-led shopping now drives parcel demand as 57% of online buyers purchase via mobile devices. Cross-border volumes climb in tandem with social-commerce sales, projected at USD 8.5 trillion by 2030. China's cross-border parcel flows grew alongside a RMB 21.4 trillion (USD 3.01 trillion) digital-retail sector in 2025, prompting operators to deploy flexible hubs that manage varied package profiles. Network investments across Southeast Asia target wider rural reach and delivery-time certainty, ensuring service parity with urban markets.
Cross-Border SME Exports Leveraging Digital Marketplaces in Europe Region
European SMEs increasingly ship direct to global customers through online marketplaces, intensifying demand for harmonized customs clearance. Negotiations among 90 WTO members seek common e-commerce rules to reduce procedural friction. Automated declarations and blockchain-backed documents can cut average trade costs by 11%. Standardized cross-border services enable operators to pool volumes, lower unit costs, and enlarge the courier express parcel market.
Air-Capacity Constraints on the Trans-Pacific Lanes
Freighter supply rose 8% in 2024, yet demand from China is set to climb 20% in 2025, tightening space and lifting spot rates 15% year-on-year. Limited new-aircraft deliveries cap future growth near 4.4%. Operators prioritize high-value goods and explore secondary hubs, but elevated costs weigh on the courier express parcel market CAGR.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Same-Day Delivery Premiumization in Urban North America
- Government Push for Postal Network Modernization in GCC Countries
- Chronic Driver Shortage
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Healthcare recorded the fastest 5.75% CAGR between 2025-2030 as aging populations lift demand for temperature-controlled deliveries. DHL and UPS aim to grow healthcare revenues to USD 10.8 billion and USD 20 billion, respectively, underscoring strategic focus. Real-time data loggers ensure compliance, justifying premium fees embedded within the overall courier express parcel market pricing.
E-commerce still represented 36.94% of 2024 revenue but shows a gradual deceleration in mature regions. Manufacturing and wholesale trade offer steady B2B flows, while financial services shipments decline as digitization reduces physical document exchange.
International parcels are projected to expand at a 5.57% CAGR between 2025-2030. The courier express parcel market size tied to cross-border flows is set to widen as trade agreements and electronic customs procedures simplify clearance. Domestic deliveries keep a 69.09% share in 2024, but mature e-commerce penetration caps growth.
Technology-enabled services such as BEST Inc.'s CNY 7 (USD 0.98) per-kilogram offering connect Southeast Asian shoppers to Chinese merchants, illustrating cost reductions through consolidated exports. WTO digital-trade frameworks and RCEP customs harmonization further encourage SMEs to ship internationally, expanding high-margin lanes for established integrators.
The Global Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Report is Segmented by Destination (Domestic and International), by Speed of Delivery (Express and More), by Model (Business-To-Business and More), by Shipment Weight (Heavy Weight Shipments and More), Mode of Transport (Air and More), by End User Industry (E-Commerce and More), and by Geography (Asia-Pacific and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America commanded 36.76% of 2024 revenue, anchored by consumer expectations for two-day delivery and developed last-mile assets. Persistent driver shortages magnify operating costs, prompting automation pilots and the acquisition of healthcare specialists such as UPS-Andlauer to secure growth niches. Urban micro-fulfillment centers and same-day offerings support premium-rate stability even as volume growth moderates.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region at 6.77% CAGR between 2025-2030, propelled by cross-border e-commerce and rising consumer incomes. China's RMB 21.4 trillion (USD 3.01 trillion) digital retail base drives parcel density, while RCEP customs alignment lowers friction. Yamato Holdings targets JPY 2-2.4 trillion (USD 0.28-0.33 trillion) revenue by FY2027, embedding carbon-neutral pledges to align with regional sustainability mandates. Europe combines legacy postal infrastructure with aggressive decarbonization policies. The ban on new combustion vans by 2035 accelerates fleet electrification; PostNL plans 100% emission-free Benelux delivery by 2030. DHL's merger with Evri pools international and domestic strengths to handle more than 1 billion UK parcels per year.
Middle East and Africa benefit from GCC diversification programs. Saudi Arabia's automated hub exemplifies investments positioning the region as an intercontinental transit bridge. Security risks on central corridors and fragmented infrastructure still temper growth, favoring partnerships with national postal operators that bring local expertise. South America remains smaller but developing customs reforms, such as Brazil's Remessa Conforme program, improve data quality and compliance, encouraging global platforms to expand cross-border offerings. Currency volatility and patchy road networks require flexible, country-specific approaches.
- Aramex
- Australian Postal Corporation
- Canada Post Corporation (Including Purolator, Inc.)
- China Post
- CJ Logistics
- Deppon Logistics Co., Ltd.
- DHL Group
- Empresa Brasileira de Correios e Telegrafos
- FedEx
- InPost Sp. z o.o.
- International Distribution Services PLC
- JD.com, Inc. (Including JD Logistics, Inc.)
- La Poste Group (Including DPD Group)
- LX International Corp. (Including LX Pantos Co., Ltd.)
- Osterreichische Post AG (Austrian Post)
- Poste Italiane
- PostNL N.V.
- PostNord AB
- SF Express (KEX-SF)
- SG Holdings Co., Ltd.
- STO Express Co., Ltd. (Shentong Express)
- Swiss Post, Ltd.
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd.
- ZTO Express (Cayman), Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Infrastructure
- 4.13 Regulatory Framework
- 4.14 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.15 Market Drivers
- 4.15.1 E-commerce Penetration Driving B2C Parcel Volumes in Emerging Asia-Pacific Region
- 4.15.2 Cross-Border SME Exports Leveraging Digital Marketplaces in Europe Region
- 4.15.3 Same-Day Delivery Premiumization in Urban North America
- 4.15.4 Government Push for Postal Network Modernization in GCC Countries
- 4.15.5 Adoption of Out-of-Home PUDO Networks in Nordics
- 4.15.6 Cold-Chain Compliance Requirements for Healthcare CEP in Japan
- 4.16 Market Restraints
- 4.16.1 Air Capacity Constraints Witnessed on the Trans-Pacific Lanes
- 4.16.2 Chronic Driver Shortage Impacting Last-Mile Costs in the US and UK
- 4.16.3 Regulatory Caps Implementation on Delivery Fleet Emissions in EU27
- 4.16.4 Rising Security Risks on Africa's Central Corridor Routes
- 4.17 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.18 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.18.1 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.18.2 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.18.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.18.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.18.5 Threat of Substitutes
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
- 5.7 Geography
- 5.7.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.1.1 Australia
- 5.7.1.2 China
- 5.7.1.3 India
- 5.7.1.4 Indonesia
- 5.7.1.5 Japan
- 5.7.1.6 Malaysia
- 5.7.1.7 Pakistan
- 5.7.1.8 Philippines
- 5.7.1.9 Thailand
- 5.7.1.10 Vietnam
- 5.7.1.11 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.2 Europe
- 5.7.2.1 Albania
- 5.7.2.2 Bulgaria
- 5.7.2.3 Croatia
- 5.7.2.4 Czech Republic
- 5.7.2.5 Denmark
- 5.7.2.6 Estonia
- 5.7.2.7 Finland
- 5.7.2.8 France
- 5.7.2.9 Germany
- 5.7.2.10 Hungary
- 5.7.2.11 Iceland
- 5.7.2.12 Italy
- 5.7.2.13 Latvia
- 5.7.2.14 Lithuania
- 5.7.2.15 Netherlands
- 5.7.2.16 Norway
- 5.7.2.17 Poland
- 5.7.2.18 Romania
- 5.7.2.19 Russia
- 5.7.2.20 Slovak Republic
- 5.7.2.21 Slovenia
- 5.7.2.22 Spain
- 5.7.2.23 Sweden
- 5.7.2.24 Switzerland
- 5.7.2.25 United Kingdom
- 5.7.2.26 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.3 Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.3.1 Qatar
- 5.7.3.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.7.3.3 UAE
- 5.7.3.4 Egypt
- 5.7.3.5 Nigeria
- 5.7.3.6 South Africa
- 5.7.3.7 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.4 North America
- 5.7.4.1 Canada
- 5.7.4.2 Mexico
- 5.7.4.3 United States
- 5.7.4.4 Rest of North America
- 5.7.5 South America
- 5.7.5.1 Argentina
- 5.7.5.2 Brazil
- 5.7.5.3 Chile
- 5.7.5.4 Rest of South America
- 5.7.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Aramex
- 6.4.2 Australian Postal Corporation
- 6.4.3 Canada Post Corporation (Including Purolator, Inc.)
- 6.4.4 China Post
- 6.4.5 CJ Logistics
- 6.4.6 Deppon Logistics Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.7 DHL Group
- 6.4.8 Empresa Brasileira de Correios e Telegrafos
- 6.4.9 FedEx
- 6.4.10 InPost Sp. z o.o.
- 6.4.11 International Distribution Services PLC
- 6.4.12 JD.com, Inc. (Including JD Logistics, Inc.)
- 6.4.13 La Poste Group (Including DPD Group)
- 6.4.14 LX International Corp. (Including LX Pantos Co., Ltd.)
- 6.4.15 Osterreichische Post AG (Austrian Post)
- 6.4.16 Poste Italiane
- 6.4.17 PostNL N.V.
- 6.4.18 PostNord AB
- 6.4.19 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.20 SG Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.21 STO Express Co., Ltd. (Shentong Express)
- 6.4.22 Swiss Post, Ltd.
- 6.4.23 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- 6.4.24 Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.25 ZTO Express (Cayman), Inc.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment



















