
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1891243
면역 체크포인트 저해제 시장 - 업계 동향과 세계 예측(-2030년) - 주요 면역 체크포인트 표적별, 대상 적응증별, 작용기서별, 사용되는 치료 모달리티별, 치료법별, 주요 지역별Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market: Industry Trends and Global Forecasts, till 2030 - Distribution by Key Immune Checkpoint Targets, Target Indications, Mechanism of Action, Therapeutic Modalities Used, Therapy and Key Geographical Regions |
||||||
면역 체크포인트 저해제 시장 - 개요
면역 체크포인트 저해제 시장 규모는 2025년에 620억 달러 규모에 달할 것으로 예측되며, 2035년에는 2,460억 달러 규모로 성장하며, 예측 기간 중 CAGR 14.7%로 확대할 것으로 전망되고 있습니다.
시장 규모 및 기회 분석은 다음 매개 변수를 기반으로 세분화됩니다.
면역관문억제제 시장
시장 규모 및 기회 분석은 다음과 같은 매개 변수를 기준으로 구분됩니다.
면역 체크포인트 단백질 유형
- PD-1
- PD-L1
- CTLA-4
- 기타
대상 적응증
- 폐암
- 유방암
- 방광암
- 자궁경부암
- 대장암
- 악성 흑색종
- 호지킨 림프종
- 기타
치료법 유형
- 항체 단편
- 모노클로널 항체
- 저분자 화합물
- 기타 치료법
투여 경로
- 정맥내
- 피하
- 세포내
- 기타
지역적 지역
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 라틴아메리카
면역관문억제제 시장 - 성장과 동향
암은 전 세계에서 주요 사망 원인으로 인식되고 있으며, 2019년 미국에서만 60만 명이 사망한 것으로 보고되었습니다. 세계보건기구(WHO)는 향후 20년간 전 세계 신규 암 환자 수가 70% 증가할 것으로 예측했습니다. 화학요법, 수술, 방사선 치료와 같은 전통적 치료법은 여전히 확립된 표준 치료법입니다. 그러나 그 효과는 특히 진행성 암 치료에 있어서는 그 효과가 크게 제한되어 있습니다. 또한 화학요법과 방사선 치료의 비특이적이고 매우 독성이 높은 특성은 환자의 삶의 질에 큰 영향을 미치는 것으로 알려져 있습니다.
현재 시장에는 수많은 표적 암 치료제가 유통되고 있으며, 개발중인 치료법도 다수 존재합니다. 그 중에서도 면역 체크포인트 치료는 종양 세포가 면역 감시를 회피하는 것을 억제하는 효과적이고 강력한 치료 옵션으로 큰 가능성을 보여주고 있습니다. 2011년 브리스톨 마이어스 스퀴브의 항 CTLA-4 단일클론 항체인 야보이(R)(이필리맙)가 전이성 흑색종 치료제로 FDA의 승인을 받은 최초의 면역관문억제제가 되었습니다. 이필리맙을 비롯한 초기 면역관문억제제(PD-1/PD-L1 및 CTLA-4를 표적으로 하는 약물)는 진행성 암 환자의 생존기간을 크게 연장시킬 수 있는 가능성을 보여주었습니다. 그러나 PD-1/PD-L1 면역관문억제제의 효과에도 불구하고 일부 환자군에서는 뚜렷한 치료 저항성이 발견되어 비교적 새로운 치료 범주의 치료 효과를 저해하는 요인으로 작용하고 있습니다.
수년 동안 면역 체크포인트 조절에 대한 연구는 상당한 진전을 이루었고, 현재 차세대 면역 체크포인트 표적치료제 개발에 활용되고 있는 다양한 억제성 수용체(LAG-3, TIM-3, TIGIT, VISTA, B7-H3) 및 자극성 수용체(OX40, ICOS, GITR, 4- 1BB, CD40)가 밝혀졌습니다. 또한 새로 발견된 체크포인트와 기존 면역 체크포인트 억제 요법을 포함한 면역 체크포인트 억제와 공동 자극의 병용 요법에 대한 임상 연구는 치료 효과를 높일 수 있는 가능성을 보여주고 있습니다. 이 분자들이 면역 관용을 조절하고 자가면역질환을 예방하거나 치료하는 능력도 보여주고 있다는 점이 중요합니다. 따라서 유망한 임상 결과와 후기 개발 단계에 있는 치료제의 적용 범위 확대에 힘입어 면역관문억제제 및 자극제 시장은 예측 기간 중 큰 폭의 성장을 보일 것으로 예측됩니다.
면역관문억제제 시장 - 주요 연구 결과
이 보고서는 세계 면역관문억제제 시장의 현황을 상세하게 분석하고 업계의 잠재적인 성장 기회를 파악합니다. 보고서의 주요 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
- 임상연구의 성공 여부는 임상연구의 평가지표와 결과지표에 따라 크게 좌우됩니다. 이는 명확하고 신뢰할 수 있으며, 쉽게 측정할 수 있고, 민감도가 높으며, 임상적으로 의미가 있는 것이어야 합니다.
- 2000년 이후 PD-1/PD-L1을 표적으로 하는 면역관문억제제 평가에 초점을 맞춘 3,600개 이상의 임상시험이 전 세계에서 등록되었습니다.
- 현재, 완료된 임상시험 및 진행 중인 임상시험의 결과를 담은 과학 논문은 450여 편에 달할 전망입니다. 이들 출판물의 대부분은 영향력 지수가 1에서 20에 이르는 영향력 지수(Impact Factor)가 있는 학술지에 게재되어 있습니다.
- 이 보고서에는 승인 및 개발중인 PD-1/PD-L1 표적 치료제의 결과를 소개 및 인사이트한 85개 이상의 임상 연구 논문에서 도출된 주요 연구 결과를 상세하게 요약하여 수록했습니다.
- 이 보고서에서 다루고 있는 임상 1상 시험은 전이성 암을 포함한 다양한 종양의 치료를 목적으로 PD-1 신호전달을 차단하도록 설계된 다양한 신규 분자 실체를 특징으로 합니다.
- 임상 2상 시험은 주로 치료법의 안전성과 유효성에 초점을 맞추었습니다. 일반적으로 이러한 시험은 특정 적응증에 대해 실시되며, 약제나 치료법 조합을 검토할 수 있습니다.
- 임상연구의 3상 시험은 전 세계에서 확립된 선정 기준에 따라 선별된 환자들을 대상으로 한 정교한 다기관 공동 연구입니다. 부작용 프로파일을 이해하는 것이 주요 목적입니다.
- 시험 설계의 중요성은 매우 높으며, 프로세스를 최적화하고 효율화할 뿐만 아니라 조사의 방향을 결정하는 중요한 목적(우월성, 비열등성, 동등성 등)을 정의하는 데에도 도움이 됩니다.
- 현재 임상연구 현장에서는 다수의 신규 PD-1/PD-L1 억제제가 평가되고 있으며, 이미 승인된 여러 제품들이 다른 제품군과의 병용요법으로 연구되고 있습니다.
- 이러한 치료법은 표적 특이적이기 때문에 면역 체크포인트 억제를 목적으로 하는 치료제의 임상시험을 설계할 때 PD-L1의 발현이 중요한 기준으로 여겨지고 있습니다.
- 많은 임상시험은 새로운 치료제나 병용요법이 추가 연구를 정당화할 만큼 충분한 생물학적 활성을 가지고 있는지 여부를 객관적으로 판단하기 위해 고안된 것입니다.
- 후기 임상시험의 초점은 일반적으로 다양한 환자군에서의 장기 치료 관련 결과 및 관련 독성 평가에 초점을 맞추었습니다.
- PD-1/PD-L1을 표적으로 하는 여러 약물이 이미 시장에 출시되어 있으며, 몇 가지 새로운 생물학적 약물 후보물질이 평가 중에 있으며, 가까운 시일 내에 시장에 출시될 것으로 예측됩니다.
면역관문억제제 시장 대표 기업 사례
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Incyte
- Novartis
- Trillium Therapeutics
면역관문억제제 시장 - 연구 범위
- 시장 규모 및 기회 분석 : 이 보고서는 세계 면역관문억제제 시장에 대해(A) 주요 면역 체크포인트 표적,(B) 표적 적응증,(C) 작용기전,(D) 사용되는 치료법,(H) 치료 유형,(I) 투여 경로,(J) 주요 지역적 지역,(K) 주요 시장 세분화에 초점을 맞춘 상세한 분석을 제공합니다. H)치료 유형,(I)투여 경로,(J)주요 지역적 영역
- 시장 현황: 시판 중인 제품/개발중인 분자에 대해(A) 후보물질의 개발 단계,(B) 표적 면역 체크포인트,(C) 작용기전,(D) 치료법 유형,(E) 투여 경로,(F) 표적 질환 적응증,(G) 표적 치료 영역,(H) 치료법 유형 등 다양한 파라미터를 고려한 종합적 평가 종합적으로 평가합니다.
- 기업 개요: 차세대 면역 체크포인트 조절제에 대한 자세한 기업 개요을 확인할 수 있습니다. 주로(A) 기업 개요,(B) 재무 정보(가능한 경우),(C) 제품 포트폴리오,(E) 최근 동향 및 미래 전망에 초점을 맞출 것입니다.
- 보조금 분석 : 차세대 면역 체크포인트 치료 관련 프로젝트에 참여하는 연구기관에 수여된 490여 건의 보조금을 아래 항목에 따라 상세하게 분석합니다. (A)지원연도,(B)지원금액,(C)지원금 관리기관,(D)지원기관,(E)지원기간,(F)지원신청 유형,(G)지원목적,(H)지원 메커니즘,(I)주요 표적 면역 체크포인트,(J)담당 연구부문,(K)중점분야,(L)주요 프로그램 책임자,(M)수혜기관 유형.
- 파트너십 및 공동연구: 이 분야의 이해관계자들 간에 체결된 다양한 공동연구 및 파트너십에 대한 종합적인 분석.(A) 파트너십 체결 연도,(B) 파트너십 유형,(C) 지역별 활동을 기준으로 분석.
- 표적 경쟁 분석 : 특정 표적에 기반한 리드 분자 수,(A) 후보 치료제 개발 단계,(B) 보조금 수,(C) 논문 수를 고려한 생물학적 표적에 대한 상세 분석. 가장 일반적인 면역 체크포인트 표적을 강조하는 5차원 거미줄 분석.
- 대형 제약사: 대형 제약사에 대한 심층 분석. A) 개발중인 치료제 수,(B) 대상 질환 적응증,(C) 제휴 활동,(D) 타겟 포트폴리오를 기준으로 합니다.
목차
제1장 서문
제2장 개요
제3장 서론
- 챕터 개요
- 암 면역치료 입문
- 암 면역치료 기초
- 면역 체크포인트 조절 요인
- 제1세대 면역 체크포인트 조절약
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 조절 요인
- 면역 체크포인트 조절 요법에 관련된 과제
- 향후 전망
제4장 현재 시장 구도 : 판매가 끝난 상태 및 개발 파이프라인
- 챕터 개요
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 저해제 및 자극제 : 출시 및 개발중인 파이프라인
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 저해제 및 자극제 : 파이프라인 분석
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 저해제 및 자극제 : 의약품 개발자 리스트
제5장 시장 구도 : CD47를 표적으로 한 치료
- 챕터 개요
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 저해제 : CD47 표적 치료제의 개발 파이프라인
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 저해제 : CD47 표적 치료제 파이프라인 분석
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 저해제 : CD47 표적 치료제를 개발하고 있는 기업 리스트
제6장 시장 구도 : 4-1 BB를 표적으로 한 치료법
- 챕터 개요
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 자극제 : 4-1 BB표적 치료제의 개발 파이프라인
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 자극약 : 4-1 BB 표적치료 파이프라인 분석
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 자극제 : 4-1 BB 표적치료를 개발하고 있는 기업 리스트
제7장 임상시험 분석
- 챕터 개요
- 범위와 조사 방법
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 저해제 및 자극제 : 임상시험 분석
제8장 기업 개요 : 차세대 저해제 및 자극제
- 챕터 개요
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Incyte
- Novartis
- Trillium Therapeutics
제9장 학술 보조금 분석
- 챕터 개요
- 범위와 조사 방법
- 차세대 면역 체크포인트 저해제 및 자극제 : 국립 위생연구 연구소(NIH)별 보조금의 분석
제10장 파트너십과 협업
제11장 표적 경쟁력 분석
제12장 대형 제약회사 구상
제13장 시장 규모 평가와 기회 분석
제14장 결론
제15장 이그제큐티브 인사이트
제16장 부록 1 : 표형식 데이터
제17장 부록 2 : 기업·단체 리스트
KSA 25.12.29Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market: Overview
As per Roots Analysis, the immune checkpoint inhibitors market is estimated to be worth USD 62 billion in 2025 and reach USD 246 billion in 2035, growing at a CAGR of 14.7% during the forecast period.
The market sizing and opportunity analysis has been segmented across the following parameters:
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market
The market sizing and opportunity analysis has been segmented across the following parameters:
Type of Immune Checkpoint Proteins
- PD-1
- PD-L1
- CTLA-4
- Others
Target Disease Indication
- Lung Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Bladder Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Melanoma
- Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Others
Type of Therapeutic Modality
- Antibody Fragments
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Small Molecules
- Other Modalities
Route of Administration
- Intravenous
- Subcutaneous
- Intracellular
- Others
Geographical Regions
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market: Growth and Trends
Cancer is recognized as a major cause of mortality globally, responsible for 0.6 million fatalities in 2019, in the US alone. The World Health Organization projects that the global incidence of new cancer cases will increase by 70% in the next 20 years. Traditional treatment methods, including chemotherapy, surgical procedures, and radiation therapy, remain the established standard of care. Nonetheless, their effectiveness is significantly constrained, particularly in the treatment of advanced-stage cancers. Further, the non-specific and extremely toxic characteristics of chemotherapy and radiation therapy are recognized to considerably affect the quality of life of individuals.
Numerous targeted cancer treatments are currently available in the market, in addition to the therapies under development. Among these, immune checkpoint therapies have demonstrated significant potential as effective and powerful treatment alternatives, capable of hindering tumor cells from escaping immune detection. In 2011, Yervoy(R) (ipilimumab), an anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody from Bristol-Myers Squibb, was the first immune checkpoint inhibitor approved by the FDA for treating metastatic melanoma. Yervoy(R), together with other early immune checkpoint inhibitors (focusing on PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4), demonstrated potential to significantly extend the lives of individuals with advanced tumors. Nonetheless, despite the effectiveness of PD 1 / PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors, a significant level of resistance to treatment was observed in some patient groups, which hindered the therapeutic effectiveness of this relatively new category of treatments.
Throughout the years, considerable advancements have happened in immune checkpoint modulation research, uncovering various inhibitory (LAG-3, TIM-3, TIGIT, VISTA, and B7-H3) and stimulatory receptors (OX40, ICOS, GITR, 4-1BB, and CD40) that are currently being utilized for the creation of next-generation immune checkpoint-focused therapies. Additionally, clinical research on combinatorial immune checkpoint blockade and co-stimulation, which includes both newly discovered checkpoints and established immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies, has shown the ability to enhance therapeutic advantages. It is important to note that these molecules have also demonstrated the ability to regulate immune tolerance and to prevent or treat autoimmune diseases. Consequently, supported by encouraging clinical outcomes and increasing applicability of therapies under late-stage investigation, the immune checkpoint inhibitors and stimulators market is expected to experience significant growth throughout the forecast period.
Immune checkpoint Inhibitors Market: Key Insights
The report delves into the current state of global immune checkpoint inhibitors market and identifies potential growth opportunities within industry. Some key findings from the report include:
- The success of any clinical research study is heavily dependent on its endpoints and outcome measures used, which should be well defined and reliable, readily measurable, sensitive, and clinically meaningful.
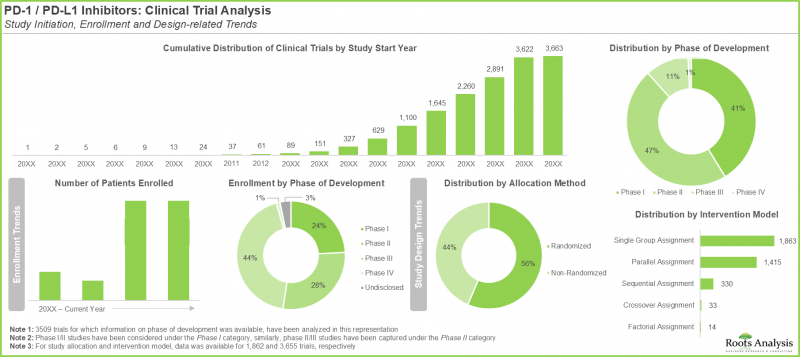
- Since 2000, over 3,600 clinical trials focused on the evaluation of PD-1 / PD-L1 targeting immune checkpoint inhibitors have been registered across the world.
- Presently, there are over 450 scientific articles showcasing the results of completed and ongoing clinical studies; most of these publications are featured in peer-reviewed journals having impact factors ranging from 1 to 20.
- The report features detailed summaries of the key takeaways from 85+ clinical research publications, which showcase and discuss the results of both approved and under development PD-1 / PD-L1 targeting drugs.
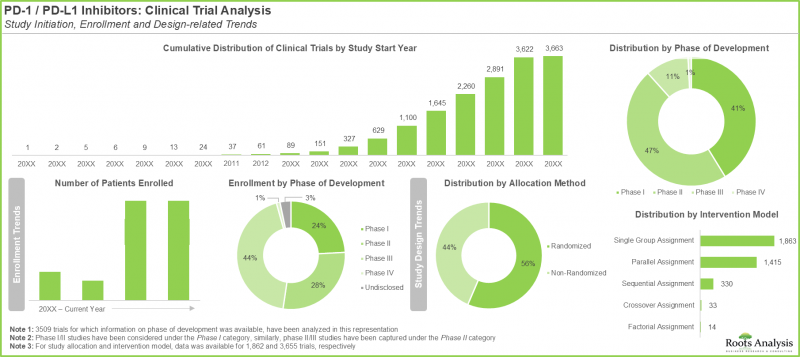
- Phase I trials captured in the report feature a variety of new molecular entities designed for PD-1 signaling blockade for the treatment of various types of tumors, including metastatic cancers.
- Phase II trials are primarily focused on how safe a treatment is and how well it works; typically, these studies are conducted for specific indications and may involve combinations of drugs / therapies.
- Phase III of clinical research is an elaborate, multicenter study, involving patients shortlisted based on established selection criteria from across the world; understanding the side effects profile is a key objective.
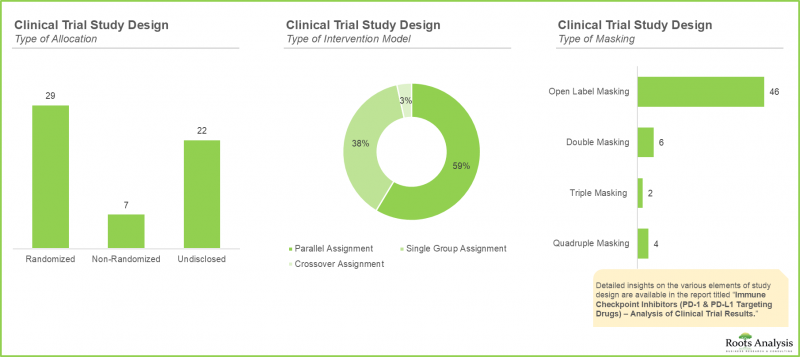
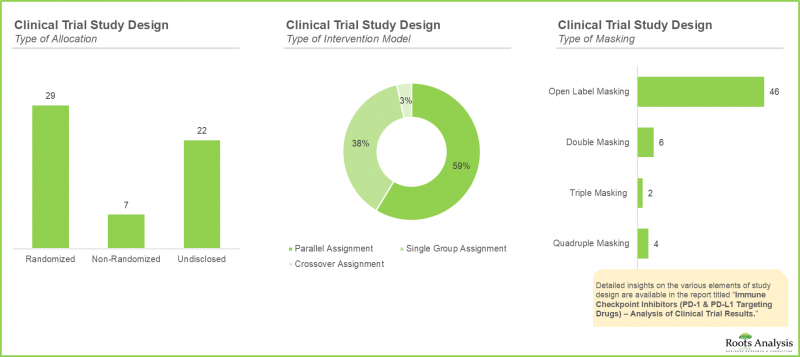
- The importance of trial design is paramount; it not only serves to optimize, and economize the process, but also helps define critical objectives (such as superiority, non-inferiority, or equivalence) directing the course of research.
- In the contemporary clinical research scenario, multiple new PD-1 / PD-L1 inhibitors are being evaluated, and several of the approved products are also being investigated in combination with other product classes.
- Considering the target-specific nature of these therapies, the expression of PD-L1 is considered an important criterion while designing trials of immune checkpoint blockade-directed treatment options.
- A number of trials have been designed to objectively determine whether the new therapeutic agent, or combination regimen, has sufficient biological activity in order to warrant further research.
- The focus of late phase clinical studies is usually on assessing long term therapy related outcomes and affiliated toxicities, across different groups of patients.
- Although multiple PD-1 / PD-L1 targeting drugs are already in the market, several new biological drug candidates are under evaluation and are likely to enter the market in the foreseen future.
Example Players in the Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Incyte
- Novartis
- Trillium Therapeutics
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market: Research Coverage
- Market Sizing and Opportunity Analysis: The report features an in-depth analysis of the global immune checkpoint inhibitors market, focusing on key market segments, including [A] key immune checkpoint targets, [B] target indication, [C] mechanism of action, [D] therapeutic modalities used, [H] type of therapy, [I] route of administration, and [J] key geographical regions
- Market Landscape: A comprehensive evaluation of marketed / pipeline molecules, considering various parameters, such as [A] phase of development of lead candidates, [B] target immune checkpoints, [C] mechanism of action, [D] type of therapeutic modality used, [E] route of administration and [F] target disease indication, [G] target therapeutic area and [H] type of therapy.
- Company Profiles: In-depth profiles of next generation immune checkpoint modulators, focusing on [A] company overview, [B] financial information (if available), [C] product portfolio, and [E] recent developments and an informed future outlook.
- Grants Analysis: An in-depth analysis of more than 490 grants that have been awarded to research institutes engaged in next generation immune checkpoint therapy-related projects, based on parameters, such as [A] year of grant award, [B] amount awarded, [C] administration institute center, [D] funding institute center, [E] support period, [F] type of grant application, [G] purpose of grant award, [H] grant mechanism, [I] popular target immune checkpoints, [J] responsible study section, [K] focus area, [L] prominent program officers, and [M] type of recipient organizations.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: A comprehensive analysis of various collaborations and partnerships that have been inked amongst stakeholders in this domain, based on [A] year of partnership, [B] type of partnership and [C] regional activity.
- Target Competitiveness Analysis: A detailed analysis of the biological targets, taking into consideration the number of lead molecules based on a particular target, [A] phase of development of candidate therapies, [B] number of grants and [C] number of publications, a five-dimensional spider-web analysis, highlighting the most popular immune checkpoint targets.
- Big Pharma Players: A detailed analysis of the big pharma players, based on parameters, such as [A] number of therapies under development, [B] target disease indications, [C] partnership activity, and [D] target portfolio.
Key Questions Answered in this Report
- How many companies are currently engaged in this market?
- Which are the leading companies in this market?
- What factors are likely to influence the evolution of this market?
- What is the current and future market size?
- What is the CAGR of this market?
- How is the current and future market opportunity likely to be distributed across key market segments?
Reasons to Buy this Report
- The report provides a comprehensive market analysis, offering detailed revenue projections of the overall market and its specific sub-segments. This information is valuable to both established market leaders and emerging entrants.
- Stakeholders can leverage the report to gain a deeper understanding of the competitive dynamics within the market. By analyzing the competitive landscape, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their market positioning and develop effective go-to-market strategies.
- The report offers stakeholders a comprehensive overview of the market, including key drivers, barriers, opportunities, and challenges. This information empowers stakeholders to stay abreast of market trends and make data-driven decisions to capitalize on growth prospects.
Additional Benefits
- Complimentary PPT Insights Packs
- Complimentary Excel Data Packs for all Analytical Modules in the Report
- 15% Free Content Customization
- Detailed Report Walkthrough Session with Research Team
- Free Updated report if the report is 6-12 months old or older
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. PREFACE
- 1.1. Scope of the Report
- 1.2. Research Methodology
- 1.3. Chapter Outlines
2. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3. INTRODUCTION
- 3.1. Chapter Overview
- 3.2. Introduction to Cancer Immunotherapy
- 3.3. Fundamentals of Cancer Immunotherapy
- 3.4. Immune Checkpoint Modulators
- 3.5. First Generation Immune Checkpoint Modulators
- 3.6. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Modulators
- 3.6.1. Types of Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Modulators
- 3.7. Challenges-related to Immune Checkpoint Modulation-based Therapy
- 3.8. Future Perspectives
4. CURRENT MARKET LANDSCAPE: MARKETED AND DEVELOPMENT PIPELINE
- 4.1. Chapter Overview
- 4.2. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators: Marketed and Development Pipeline
- 4.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators: Pipeline Analysis
- 4.3.1. Analysis by Phase of Development
- 4.3.2. Analysis by Target Immune Checkpoint
- 4.3.3. Analysis by Mechanism of Action
- 4.3.4. Analysis by Therapeutic Modality
- 4.3.5. Analysis by Route of Administration
- 4.3.6. Analysis by Target Disease Indication
- 4.3.7. Analysis by Therapeutic Area
- 4.3.8. Analysis by Popular Oncological Indication(s) and Popular Target Immune Checkpoint
- 4.3.9. Analysis by Popular Non-Oncological Indication(s) and Popular Target Immune Checkpoint
- 4.3.10. Analysis by Popular Disease Indication(s) and Popular Target Immune Checkpoint in Highest Phase of Development
- 4.4. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators: List of Drug Developers
- 4.4.1. Analysis by Year of Establishment
- 4.4.2. Analysis by Company Size and Geographical Location
- 4.4.3. Leading Developer Companies: Analysis by Number of Pipeline Therapies
- 4.4.4. Popular Targets: Distribution by Number of Developers
- 4.4.5 World Map Representation: Analysis by Geography
5. MARKET LANDSCAPE: THERAPIES TARGETING CD47
- 5.1. Chapter Overview
- 5.2. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Development Pipeline of CD47 Targeting Therapies
- 5.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Pipeline Analysis of CD47 Targeting Therapies
- 5.3.1. Analysis by Phase of Development
- 5.3.2. Analysis by Therapeutic Modality
- 5.3.3. Analysis by Route of Administration
- 5.3.4. Analysis by Target Disease Indication
- 5.4. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: List of Companies Developing CD47 Targeting Therapies
- 5.4.1. Analysis by Year of Establishment
- 5.4.2. Analysis by Company Size and Geographical Location
- 5.4.3. Leading Developers: Analysis by Number of Therapies
- 5.4.4. World Map Representation: Analysis by Geography
6. MARKET LANDSCAPE: THERAPIES TARGETING 4-1BB
- 6.1. Chapter Overview
- 6.2. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Stimulators: Development Pipeline of 4-1BB Targeting Therapies
- 6.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Stimulators: Pipeline Analysis of 4-1BB Targeting Therapies
- 6.3.1. Analysis by Phase of Development
- 6.3.2. Analysis by Therapeutic Modality
- 6.3.3. Analysis by Route of Administration
- 6.3.4. Analysis by Target Disease Indication
- 6.4. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Stimulators: List of Companies Developing 4-1BB Targeting Therapies
- 6.4.1. Analysis by Year of Establishment
- 6.4.2. Analysis by Company Size and Geographical Location
- 6.4.3. Leading Developers: Analysis by Number of Therapies
- 6.4.4. World Map Representation: Analysis by Geography
7. CLINICAL TRIAL ANALYSIS
- 7.1. Chapter Overview
- 7.2. Scope and Methodology
- 7.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators: Clinical Trial Analysis
- 7.3.1. Analysis by Trial Registration Year
- 7.3.2. Analysis by Trial Phase
- 7.3.3. Analysis by Trial Recruitment Status
- 7.3.4. Analysis by Trial Registration Year and Number of Patients Enrolled
- 7.3.5. Analysis by Study Design
- 7.3.6. Analysis by Sponsor / Collaborator
- 7.3.7. Leading Players: Analysis by Number of Registered Trials
- 7.3.8. Word Cloud: Key Focus Areas
- 7.3.9. Analysis by Target Immune Checkpoint
- 7.3.10. Analysis by Target Therapeutic Area
- 7.3.11. Popular Indications: Analysis by Number of Registered Trials
- 7.3.12. Popular Interventions: Analysis by Number of Registered Trials
- 7.3.13. Geographical Analysis by Number of Registered Trials
- 7.3.14. Geographical Analysis by Number of Patients Enrolled
8. COMPANY PROFILES: NEXT GENERATION INHIBITORS AND STIMULATORS
- 8.1. Chapter Overview
- 8.2. Bristol-Myers Squibb
- 8.2.1. Company Overview
- 8.2.2. Financial Information
- 8.2.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Therapeutics Portfolio
- 8.2.4. Recent Developments and Future Outlook
- 8.3. GlaxoSmithKline
- 8.3.1. Company Overview
- 8.3.2. Financial Information
- 8.3.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Therapeutics Portfolio
- 8.3.4. Recent Developments and Future Outlook
- 8.4. Incyte
- 8.4.1. Company Overview
- 8.4.2. Financial Information
- 8.4.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Therapeutics Portfolio
- 8.4.4. Recent Developments and Future Outlook
- 8.4. Novartis
- 8.4.1. Company Overview
- 8.4.2. Financial Information
- 8.4.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Therapeutics Portfolio
- 8.4.4. Recent Developments and Future Outlook
- 8.5. Trillium Therapeutics
- 8.5.1. Company Overview
- 8.5.2. Financial Information
- 8.5.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Therapeutics Portfolio
- 8.5.4. Recent Developments and Future Outlook
9. ACADEMIC GRANTS ANALYSIS
- 9.1. Chapter Overview
- 9.2. Scope and Methodology
- 9.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators: Analysis of Grants Awarded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- 9.3.1. Analysis by Year of Grant Award
- 9.3.2. Analysis by Amount Awarded
- 9.3.3. Analysis by Administering Institute Center
- 9.3.4. Analysis by Funding Institute Center
- 9.3.5. Analysis by Support Period
- 9.3.6. Analysis by Funding Institute Center and Support Period
- 9.3.7. Analysis by Type of Grant Application
- 9.3.8. Analysis by Purpose of Grant Award
- 9.3.9. Analysis by Grant Mechanism
- 9.3.10. Word Cloud: Emerging Focus Areas
- 9.3.11. Popular Target Immune Checkpoints: Analysis by Number of Grants
- 9.3.12. Analysis of Grant Amount Awarded by Target Immune Checkpoints
- 9.3.13. Analysis by Study Section Involved
- 9.3.14. Popular NIH Departments: Analysis by Number of Grants
- 9.3.15. Analysis by Types of Recipient Organizations
- 9.3.16. Popular Recipient Organizations: Analysis by Number of Grants
- 9.3.17. Prominent Program Officers: Analysis by Number of Grants
- 9.3.18. Regional Analysis of Recipient Organizations
10. PARTNERSHIPS AND COLLABORATIONS
- 10.1. Chapter Overview
- 10.2. Partnership Models
- 10.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators: List of Partnerships and Collaborations
- 10.3.1. Analysis by Year of Partnership
- 10.3.2. Analysis by Type of Partnership
- 10.3.3. Analysis by Number of Partnership and Target Immune Checkpoint
- 10.3.4. Analysis by Year of Partnership and Type of Partner
- 10.3.5. Analysis by Type of Partnership and Type of Partner
- 10.3.6. Most Active Players: Analysis by Number of Partnerships
- 10.4. Regional Analysis
- 10.4.1. Intercontinental and Intracontinental Agreements
11. TARGET COMPETITIVENESS ANALYSIS
- 11.1. Chapter Overview
- 11.2. Scope and Methodology
- 11.3. Key Parameters
- 11.4. Competitiveness Analysis: Key Targets for Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators
- 11.3.1. Four-Dimensional Bubble Analysis
- 11.3.2 Five-Dimensional Spider Web Analysis
12. BIG PHARMA INITIATIVES
- 12.1. Chapter Overview
- 12.2. Big Pharma Initiatives Focused on Next Generation Immune Checkpoint
- 12.2.1. Analysis by Number of Initiatives
- 12.2.2. Analysis by Number of Targets
- 12.2.3. Analysis by Product Development Strategy
- 12.2.4. Analysis by Target Immune Checkpoint
- 12.2.5. Grid Representation: Analysis by Product Development Strategy and Target Immune Checkpoint
- 12.2.6. Analysis by Type of Intervention
- 12.3. Analysis by Target Disease Indication(s)
- 12.3.1. Heat Map: Big Pharma Initiatives Focused on Oncological Indications
- 12.3.2. Heat Map: Big Pharma Initiatives Focused on Non-Oncological Indications
13. MARKET SIZING AND OPPORTUNITY ANALYSIS
- 13.1. Chapter Overview
- 13.2. Forecast Methodology and Key Assumptions
- 13.3. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market, Till 2030
- 13.4. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market: Individual Product Sales Forecasts
- 13.4.1. DARZALEX(R) (Janssen Pharmaceuticals)
- 13.4.1.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.1.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.4.2. SAR650984 (Sanofi)
- 13.4.2.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.2.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.4.3. RRx-001 (EpicentRx)
- 13.4.3.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.3.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.4.4. GSK3359609 (GlaxoSmithKline)
- 13.4.4.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.4.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.4.5. Omburtamab (Y-mAbs Therapeutics)
- 13.4.5.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.5.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.6.7. APXOO5M (Apogenix)
- 13.6.7.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.6.7.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.7.8. BI 655064 (Boehringer Ingelheim)
- 13.7.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.7.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.4.8. BMS-986015 (Bristol-Myers Squibb)
- 13.4.8.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.8.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.4.9. CFZ533 (Novartis)
- 13.4.9.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.9.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.4.10. GBR 830 (Glenmark)
- 13.4.10.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.10.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.4.11. KHK4083 (Kyowa Kirin)
- 13.4.11.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.4.11.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.12.13. LAG525 (Novartis)
- 13.12.13.1. Target Patient Population
- 13.12.13.2. Sales Forecast
- 13.4.1. DARZALEX(R) (Janssen Pharmaceuticals)
- 13.5. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market: Distribution by Region
- 13.5.1. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market in US, Till 2030
- 13.5.2. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market in UK, Till 2030
- 13.5.3. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market in Germany, Till 2030
- 13.5.4. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market in France, Till 2030
- 13.5.5. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market in Italy Till 2030
- 13.5.6. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market in Spain, Till 2030
- 13.5.7. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market in Australia, Till 2030
- 13.5.8. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market in Japan, Till 2030
- 13.5.9. Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market in India, Till 2030
- 13.6. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market: Distribution by Therapeutic Area
- 13.6.1. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Oncological Indications, Till 2030
- 13.6.2. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Non-oncological Indications, Till 2030
- 13.7. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market: Distribution by Target Disease Indication
- 13.7.1. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Atopic Dermatitis, Till 2030
- 13.7.2. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Breast Cancer, Till 2030
- 13.7.3. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Till 2030
- 13.7.4. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Colorectal Cancer, Till 2030
- 13.7.5. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Head and Neck Cancer, Till 2030
- 13.7.6. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Lung Cancer, Till 2030
- 13.7.7. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Lupus Nephritis, Till 2030
- 13.7.8. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Melanoma, Till 2030
- 13.7.9. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Multiple Myeloma, Till 2030
- 13.7.10. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Neuroblastoma, Till 2030
- 13.7.11. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Primary Sjogren's Syndrome, Till 2030
- 13.7.12. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Ulcerative Colitis, Till 2030
- 13.7. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market: Distribution by Target Immune Checkpoint
- 13.8.1. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for B7-H3 Targeting Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.8.2. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for CD38 Targeting Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.8.3. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for CD40 Targeting Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.8.4. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for CD47 Targeting Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.8.5. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for ICOS Targeting Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.8.6. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for KIR Targeting Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.8.7. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for LAG-3 Targeting Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.8.8. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for OX40 Targeting Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.9. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market: Distribution by Mechanism of Action
- 13.9.1. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Inhibitory Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.9.2. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Stimulatory Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.10. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market: Distribution by Type of Therapeutic Modality
- 13.10.1. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Monoclonal Antibody, Till 2030
- 13.10.2. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Small Molecules, Till 2030
- 13.11. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market: Distribution by Type of Therapy
- 13.11.1. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Monotherapy, Till 2030
- 13.11.2. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Combination Therapy, Till 2030
- 13.11.3. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Both, Till 2030
- 13.12. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market: Distribution by Route of Administration
- 13.12.1. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Intracerebroventricular Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.12.2. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Intravenous Therapies, Till 2030
- 13.12.3. Global Next Generation Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Stimulators Market for Subcutaneous Therapies, Till 2030
14. CONCLUDING REMARKS
- 14.1. Chapter Overview
- 14.2. Key Takeaways



















