
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1808961
6G 통신 : RIS(Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface) 재료 및 하드웨어 시장과 기술(2026-2046년)6G Communications: Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface RIS Materials and Hardware Markets, Technology 2026-2046 |
||||||
요약
6G 통신의 RIS(Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface)는 메타서피스 시장에서 가장 큰 시장이 될 수 있습니다. 이로 인해 수십억 달러 규모의 비즈니스가 생길 것입니다. 그러나 부가가치 소재와 하드웨어를 제조하는 기업의 경우 RIS 기회를 이해할 때 딜레마가 존재합니다. 연구자들은 종종 같은 의미를 가진 여러 용어를 구분하면서 난해한 이론 연구에 몰두하고 있으며, RIS 시스템을 개발하는 기업은 당연히 비밀주의적입니다. 따라서 이 분야와 같이 급속히 진화하는 주제에서는 전통적인 시장 조사가 도움이 되지 않습니다.
최신 실태를 깊이 이해하기 위해
이러한 상황을 타파하는 것이 본 보고서입니다. 본 보고서는 주로 2025년까지 발표된 방대한 새로운 연구 성과와 최근의 기업 활동에 초점을 맞추어 전체 591페이지에서 모든 측면을 포괄하고 있습니다. 상업적인 관점을 중시하고, 10건의 SWOT 분석, 11장 구성, 2026-2046년에 걸친 25개의 예측 라인, 30의 주요 결론, 41의 새로운 인포그램, 106사를 커버하고 있습니다. 또한 6G가 2030년에 시작됨에 따라 5G 주파수 대역 또는 그 부근에서의 RIS의 우선도와 비대각형, 모핑, 투명하고 전방위형 RIS, 액티브 RIS, 항공우주용 RIS, 대면적 RIS 등 신흥 분야에서의 최신 획기적 성과도 많이 다루고 있습니다.

목차
제1장 주요 요약, 총론, 로드맵, 예측
- 본서의 목적
- 조사 방법
- RIS 배경
- 6G에 필요한 다양한 RIS의 유형
- 6G통신 전반에 관한 10가지 주요 결론
- 인포그램 : 주요 6G 시스템의 목적
- 6G RIS의 재료 및 부품 기회에 대한 7가지 주요 결론
- 6G RIS의 비용 문제에 대한 7가지 주요 결론
- 6G RIS 및 리플렉트 어레이 제조 기술에 대한 6가지 주요 결론
- SWOT 평가
- 5G 및 6G RIS 로드맵(4라인)
- 6G RIS 및 리플렉트 어레이 시장 예측
- 6G RIS 시장 규모
- 6G RIS 판매 면적
- 6G RIS 평균 가격(공장 출하 베이스, 전자 부품 포함)
- 6G RIS 시장가치 : 액티브형 vs 4유형의 세미패시브형, 주파수별
- 6G RIS 판매 면적 vs 평균 패널 면적, 패널 판매 수량, 누계 전개 패널 수
- 6G RIS 시장 가치 : 기지국 vs 전파 경로
- 세계의 RIS 하드웨어 시장 가치의 지역별 점유율
- 세미 패시브형 vs 액티브형 RIS 시장(0.1-1THz vs 비6G THz 일렉트로닉스)
- 6G 완전 패시브형 메타물질 리플렉트 어레이 시장
- 보충 정보
제2장 서론
- 개요
- RIS의 기능과 유용성 및 자세한 인사이트
- 6G RIS와 관련된 표준화 단체 및 인플루언서의 활동
- 6G 및 6G RIS의 목적 확대 vs 축소, 스마트 무선 환경
- 용어의 난립
- 산업 및 연구 동향의 변화
- 고주파 대역에서의 도달 거리 개선 : 트래젝토리 엔지니어링
- 기타 18의 연구 진전에 관한 분석
- 6G 세계 아키텍처 제안 및 보완 시스템
제3장 궁극의 6G RIS 하드웨어 툴킷 : 불가시, 광역, 자율전원, 자기 학습, 자기 적응, 자기 복구, 자기 청소, 유비쿼터스, 자율형, 긴 수명, AI 대응, 동적 스펙트럼 공유, 기타 눈
- 개요
- 불가시 RIS - 투명 또는 시야에 들어가지 않는 형태
- 광역 RIS를 포함한 대규모 지능형 표면(LIS) 및 초대규모 안테나 어레이(ELAA)
- RIS는 자율전원화하여 제로에너지 클라이언트 디바이스 가능
- 긴 수명 : 설치 후 유지 보수를 필요로하지 않는 자체 복구 재료
- 최적화·자기 학습·자기 적응·자율화를 실현하는 RIS를 위한 AI와 머신러닝
- 다중 모드/다중 주파수, 동적 스펙트럼 공유(DSS) 및 6G 및 그 RIS
제4장 Beyond Diagonal(BD) RIS 아키텍처가 6G RIS의 제약에 대응 : 진전이 급증(-2025년)
- 정의, 재료면에서의 과제, 적용 가능성
- BD-RIS의 잠재적인 이점
- BD-RIS 하드웨어의 과제
- 실천과 개선의 필요성
제5장 STAR RIS, ISAC, SWIPT를 포함한 다기능·멀티 모드 RIS
- 연구, 산업 동향 및 가능성 검토 등 개요(2025년)
- 투과와 반사를 동시에 실시하는 STAR RIS
- 기타 다기능·멀티 모드 RIS
제6장 기지국, UM-MIMO, 빈탑(HAPS) 및 기타 UAV RIS
- 개요
- UM-MIMO로의 진전
- RIS 대응 및 자율 전원형의 초대규모 6G UM-MIMO 기지국 설계
- 대규모 MIMO 기지국용 RIS : 청화대학, 에머슨
- 스몰셀 기지국으로서의 RIS
- RIS 대응 MIMO 및 기지국의 기타 중요한 진전(2025년)
- 위성과 UAV가 6G RIS를 지원하고 때때로 그 혜택을 받는 방법 : 진전(-2025년)
- 중요한 진전(2024년)
- 성층권에서의 대규모 HAPS RIS
제7장 RIS 튜닝용 하드웨어의 목표와 연구 진전(-2025년)
- 개요
- RIS 튜닝에 관한 조사로부터의 교훈 : 2025년 이전
- 개별 튜닝 구성 요소의 진행 상황의 상세한 분석
- 6G RIS에서 0.1-1THz 및 근적외(NearIR)용 이산 부품을 대체하는 조정 재료의 우선화
- 대규모 RIS 및 시장의 기타 갭
제8장 6G용 광무선통신(ORIS) : 주요 진전(-2025년)
- RIS를 포함한 그 주파수대에서의 OWC가, 6G에 있어서 매력적인 추가 요소가 되는 이유
- 광 RIS(ORIS)의 가능성과 과제 - SWOT 분석에 의한 평가
- ORIS의 실장 순서
- 장거리·지하·수중·우주에 있어서의 광 무선 통신(OWC)과 RIS : 연구 진전(-2025년)
- 단거리 및 실내광 무선통신(OWC)과 그 RIS : 연구 진전(-2025년)
- 6G에 이용할 수 있는 광학 재료
- 6G용 메타 렌즈(진전 포함, -2025년)
- 미러 어레이 ORIS 설계
제9장 6G 모핑형 플렉서블 인텔리전트 메타서피스(FIM), 6G 하이퍼서페이스, 메타물질의 기초
- 개요
- 6G 관련 메타물질 연구에 있어서의 주요 진전의 평가(-2025년)
- 메타물질의 기초
- 메타서피스의 기초
- 메타물질 전체의 장기적인 전망
- GHz, THz, 적외선, 광 메타물질의 새로운 응용
- 열 메타물질
- 메타물질과 메타 서페이스 전반의 SWOT 평가
- 모핑형 FIM의 기초와 연구 진전(-2025년)
제10장 RIS 및 리플렉트 어레이의 제조·검사·시험·비용 내역
- 박막 및 투명 일렉트로닉스의 최첨단 기술
- 디스크리트 기판, 적층 필름으로부터 완전한 스마트 재료 통합에의 트렌드
- 플렉서블, 층상, 2D 에너지 수확 및 센싱의 중요성
- 6G RIS에 있어서의 광학, 저THz대, 고THz대에서의 제조 기술의 차이
- 6G RIS 검사 및 테스트 : 새로운 진보(2025년)
- RIS 비용 분석
제11장 6G RIS 기업 : 제품, 계획, 특허, Zhar에 의한 평가(2025-2026년)
- 개요와 특허 취득
- AGC Japan
- Alcan Systems Germany
- Alibaba China
- Alphacore USA
- China Telecom China Mobile, China Unicom, Huawei, ZTE, Lenovo, CICT China collaboration
- Ericsson Sweden
- Fractal Antenna Systems USA
- Greenerwave France
- Huawei China
- ITOCHU Japan
- Kymeta Corp. USA
- Kyocera Japan
- Metacept Systems USA
- Metawave USA
- NEC Japan
- Nokia Finland with LG Uplus South Korea
- NTT DoCoMo and NTTJapan
- Orange France
- Panasonic Japan
- Pivotal Commware USA
- Qualcomm USA
- Samsung Electronic South Korea
- Sekisui Japan
- SensorMetrix USA
- SK Telecom South Korea
- Sony Japan
- Teraview USA
- Vivo Mobile Communications China
- VTT Finland
- ZTE China
Summary
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces RIS for 6G Communications may become the largest market for metasurfaces. Billion-dollar businesses will be created providing them. However, companies making added-value materials and hardware face a dilemma when seeking to understand their RIS opportunities. Researchers largely indulge in obscure theoretical studies using many terms to mean the same thing. Companies developing RIS systems are understandably secretive and old market research is useless in such a fast-moving subject.
Deep understanding of latest realities
To the rescue comes the new, readable Zhar Research report, "6G Communications: Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface RIS Materials and Hardware Markets, Technology 2026-2046". It concentrates mostly on the flood of new research through 2025 and latest company activity, with 591 pages to cover all aspects. Commercially oriented, it has 10 SWOT appraisals, 11 chapters, 25 forecast lines 2026-2046, 30 key conclusions, 41 new infograms and it covers 106 companies. There is much on the current priority of RIS at or near 5G frequencies for 6G launch in 2030 and recent breakthroughs in exciting emerging sectors such as beyond-diagonal, morphing, transparent all-round RIS, active RIS, aerospace RIS and large area RIS.
Quick read
The Executive Summary and Conclusions takes 73 pages to clearly present the 30 conclusions, the main SWOT reports, analysis of which materials and technologies will matter, roadmaps and forecasts as tables and graphs with explanation. Learn how RIS will be essential, later vanishing into the fabric of society yet assisting in the provision of stellar, ubiquitous performance involving multiple additional user benefits. All subsequent chapters are boosted by detail on the many research advances and initiatives through 2025. Miss those and you are misled.
Main report
Chapter 2. Introduction (100 pages) gives RIS definitions, clarifying the terminology thicket, design basics and future evolution to become smart materials, smart windows and more. Understand the disruptive, very-challenging 6G Phase Two essential for most of the promised 6G paybacks and benefits to society. RIS aspects introduced here include improved spatial coverage, macro-diversity, capacity enhancement, green communications, enabling large scale Internet of Things, reliability enhancement, sensing and localization. Grasp RIS from the systems and security viewpoint and the activities of standards bodies and influencers related to 6G RIS.
Chapter 3 takes 51 pages to cover the "Ultimate 6G RIS hardware toolkit: invisible, wide area, self-powered, self-learning, self-adaptive, self-healing, self-cleaning, ubiquitous, autonomous, everlasting, AI enabled, dynamic spectrum sharing, other". Importantly, it clarifies most of what can and should be achieved before looking at progress towards it in the rest of the report. Many new infograms and SWOT appraisals make it easy to grasp. Examples include routes to self-powered infrastructure, unpowered client devices, artificial intelligence for both RIS design and operation, spectrum sharing.
Chapter 4 covers the new realisation that RIS has only been designed to operate in a small subset of what is possible. This chapter is called "Beyond diagonal RIS architecture tackles 6G RIS limitations: Surge in advances through 2025" (26 pages). These more advanced options can provide more range, reach around obstructions and other benefits.
Chapter 5. "Multifunctional and multi-mode RIS including STAR-RIS, ISAC, SWIPT" covers these other emerging priorities, most of which can work with BD-RIS where appropriate. Learn how RIS will often be multi-mode such as with both active and semi-passive tiles, simultaneous transmission and reflection, multiple frequencies. Transparent STAR-RIS will give all-round coverage and there is now huge interest in integrating sensing and communication ISAC with RIS. Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer SWIPT is rather like Radio Frequency identification RFID backscatter on steroids, leading to similarly unpowered and sometimes battery-free devices.
We next move beyond RIS enhancing the propagation path to it enhancing transmission and the allied topic of assisting and using drones. Chapter 6. "Base station, UM-MIMO, Tower in the Sky HAPS and other UAV RIS" (36 pages) includes the RIS prospects with High Altitude Pseudo Satellites HAPS that have cost and other advantages over satellites. These solar drones can be repaired, repositioned, hold position, give faster response by being nearer and maybe eventually stay aloft for almost as long as a LEO satellite.
Chapter 7. "RIS tuning hardware objectives and progress with research through 2025" (71 pages) goes much deeper into this vital aspect, importantly with many new research advances assessed through 2025. What materials opportunities? Progress from discrete components to tuning materials in the metamaterial pattern? Problems that are your gaps in the market?
Chapter 8. Optical Wireless Communications ORIS for 6G: major progress through 2025 (65 pages) covers a RIS aspect often ignored in market surveys but increasingly in focus for later 6G. Learn why infrared and visible light are best optical options on current evidence and how they are complementary. See ORIS theory and practice.
Chapter 9. "6G Morphing Flexible Intelligent Metasurfaces FIM, 6G hypersurfaces, metamaterial basics" (49 pages) explains these, mostly new options that enjoyed a great surge of research advances through 2025. They are another way of providing much superior performance even at GHz and mmWave frequencies. They may be a route to reversing the reduced enthusiasm for THz frequency in 6G by making it viable outdoors when combined with other new approaches covered earlier.
Chapter 10. "RIS and reflect-array manufacture, inspection, testing, cost breakdown" (14 pages) covers these aspects, including recent changes of direction. Chapter 11. "6G RIS companies : products, plans, patents, Zhar appraisals: 2025-6" then closes the report with RIS-related work of 30 companies being separately assessed.
Essential source
The Zhar Research report, "6G Communications: Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface RIS Materials and Hardware Markets, Technology 2026-2046" is your essential reference as you address this emerging market of billions of dollars. It is constantly updated so you always get the latest information.
Caption: Some trending RIS topics shown by number of 2025 research papers. Source: Zhar Research report, "6G Communications: Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface RIS Materials and Hardware Markets, Technology 2026-2046".
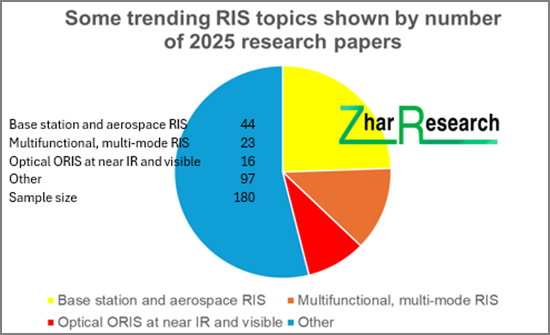
Table of Contents
1. Executive summary and conclusions with roadmap and forecast lines 2026-2046
- 1.1. Purpose of this report
- 1.2. Methodology of this analysis
- 1.3. Background to RIS
- 1.3.1. Useful for 5G but essential for 6G
- 1.3.2. RIS Google and research paper trends, trending RIS topics through 2025
- 1.3.3. Dreams of RIS everywhere: infograms
- 1.4. Many types of RIS needed for 6G
- 1.5. Ten key conclusions concerning 6G Communications generally
- 1.6. Infogram: Primary 6G systems objectives with major hardware opportunities starred
- 1.7. Seven key conclusions concerning 6G RIS materials and component opportunities
- 1.8. Seven key conclusions concerning 6G RIS cost issues
- 1.9. Six key conclusions concerning 6G RIS and reflect-array manufacturing technology
- 1.10. Eight SWOT appraisals
- 1.10.1. 6G RIS SWOT appraisal
- 1.10.2. SWOT appraisal of 6G adding sub-THz, THz, near infrared and visible frequencies
- 1.10.3. SWOT appraisal of BD-RIS for 6G
- 1.10.4. STAR-RIS SWOT appraisal
- 1.10.5. SWOT appraisal of 6G RIS for OWC
- 1.10.6. SWOT appraisal of visible light communication VLC
- 1.10.7. SWOT appraisal for metamaterials and metasurfaces generally
- 1.10.8. SWOT appraisal of morphing Flexible Intelligent Metasurfaces FIM
- 1.11. 5G and 6G RIS roadmaps in four lines 2026-2046
- 1.12. 6G RIS and reflect-array market forecasts 2026-2046
- 1.12.1. 6G RIS value market 2027-2046 $ billion with explanation
- 1.12.2. 6G RIS area sales yearly billion square meters 2027-2046 with explanation
- 1.12.3. Average 6G RIS price $/ square m. ex-factory including electronics 2028-2046 with explanation
- 1.12.4. 6G RIS value market $ billion: active vs four semi-passive categories by frequency 2026-2046 with explanation
- 1.12.5. 6G RIS area sales vs average panel area, panels sales number and total panels deployed cumulatively 2027-2046 with explanation
- 1.12.6. 6G RIS value market, base station vs propagation path $ billion 2027-2046
- 1.12.7. Percentage share of global RIS hardware value market by four regions 2029-2046
- 1.12.8. Market for semi-passive vs active RIS 0.1-1THz vs non-6G THz electronics 2027-2046
- 1.12.9. 6G fully passive metamaterial reflect-array market $ billion 2029-2046
- 1.13. Supporting information
- 1.13.1. Smartphone billion units sold globally 2024-2046 if 6G is successful
- 1.13.2. Market for 6G vs 5G base stations units millions yearly 2025-2046
- 1.13.3. Market for 6G base stations market value $bn if 6G successful 2029-2046
- 1.13.4. Location of primary 6G material and component activity worldwide 2026-2046
2. Introduction
- 2.1. Overview
- 2.1.1. Definitions and context
- 2.1.2. RIS operation modes, some key issues in providing planned 6G benefits
- 2.1.3. Important trend from moving parts to smart materials
- 2.1.4. Diverse functionalities and applications of RIS and allied intelligent metasurfaces
- 2.1.5. Examples of current approaches to RIS design and capability
- 2.1.6. Unique features of RIS vs traditional approaches and combinations through 2025
- 2.1.7. Transitional product towards RIS is liquid crystal phased array
- 2.1.8. RIS competing with traditional approaches
- 2.1.9. How 6G systems will mix and match many technologies in the propagation path
- 2.1.10. Active RIS becomes important: different envisaged potential and advances through 2025
- 2.2. RIS functionality and usefulness - a closer look
- 2.2.1. Improved spatial coverage and macro-diversity
- 2.2.2. Capacity enhancement, green communications and Internet of Things
- 2.2.3. Physical layer security, anti-jamming, and reliability enhancement
- 2.2.4. Enabling Large-Scale IoT Network Deployment
- 2.2.5. Wireless Sensing and Localization, HRIS, ISAC
- 2.2.6. RIS from the systems and security viewpoint with 2025 advances
- 2.3. Activities of standards bodies and influencers related to 6G RIS
- 2.4. Broadening vs retrenching 6G and 6G RIS objectives, smart radio environments
- 2.5. Terminology thicket
- 2.6. Changing industrial and research trends through 2025
- 2.6.1. Broadening theoretical studies useful but relative neglect of hardware is not
- 2.6.2. Backtracking on frequencies compromises capability at launch
- 2.6.3. 2025 research focussed on broadly 5G frequencies: GHz and mmWave for 6G through 2025
- 2.6.4. 0.1THz to 3THz 6G RIS research through 2025
- 2.7. Improving reach at the higher frequencies: trajectory engineering
- 2.8. Analysis of 18 other research advances through 2025
- 2.9. 6G global architecture proposals, complementary systems
3. Ultimate 6G RIS hardware toolkit: invisible, wide area, self-powered, self-learning, self-adaptive, self-healing, self-cleaning, ubiquitous, autonomous, everlasting, AI enabled, dynamic spectrum sharing, other
- 3.1. Overview
- 3.1.1. Some options to make RIS more acceptable, deployable and useful
- 3.1.2. Synergistic combination of advanced physical and RIS properties
- 3.2. Invisible RIS - transparent or out of sight
- 3.2.1. Potential transparent RIS capabilities
- 3.2.2. Transparent 6G RIS in 2025-6: companies, universities, ambitions
- 3.2.3. Transparent reflect arrays: Sekisui and others
- 3.3. Large Intelligent Surfaces LIS and Extremely Large-scale Antenna Array ELAA 2025 research including wide area RIS
- 3.3.1. Definitions and benefits
- 3.3.2. Large Intelligent Surfaces LIS RIS enhancing security, range, error reduction
- 3.3.3. Advances in protective coatings for wide area energy harvesting and RIS in 2025
- 3.4. RIS will become self-powered and enable zero energy client devices
- 3.4.1. Overview
- 3.4.2. Maturity of primary ZED enabling technologies in 2025
- 3.4.3. Ranking of most popular 6G ZED compounds and carbon allotropes in research
- 3.4.4. Context of ZED: overlapping and adjacent technologies and examples of long-life energy independence
- 3.4.5. SWIPT, STIIPT, AmBC and CD-ZED objectives and latest progress
- 3.4.6. 13 harvesting technologies for 6G ZED infrastructure and client devices 2026-2046
- 3.4.7. 6G active RIS and UM MIMO base station power demands matched to energy harvesting options
- 3.4.8. SWOT appraisal of batteryless storage technologies for ZED RIS and more
- 3.4.9. SWOT appraisal of circuits and infrastructure that eliminate storage
- 3.5. Long life: self-healing materials for fit-and-forget
- 3.6. Artificial intelligence and machine learning for optimising, self-learning, self-adaptive , autonomous RIS: Progress through 2025
- 3.7. Multimode and multifrequency, dynamic spectrum sharing DSS 6G and its RIS
4. Beyond diagonal RIS architecture tackles 6G RIS limitations: Surge in advances through 2025
- 4.1. Definitions, material challenges, applicability
- 4.1.1. Significance
- 4.1.2. The simple description
- 4.1.3. SWOT appraisal of BD-RIS for 6G
- 4.1.4. Coverage in this chapter and your opportunities
- 4.2. Potential benefits of BD-RIS
- 4.3. BD-RIS hardware challenges
- 4.4. Practical implementations and requirement for improvement
- 4.4.1. The challenge
- 4.4.2. First practical demonstrations of BD-RIS claimed in 2025
- 4.4.3. Terrestrial BD-RIS progress through 2025: many other advances and appraisals
- 4.4.4. Improving RIS in non terrestrial networks NTN
5. Multifunctional and multi-mode RIS including STAR RIS, ISAC, SWIPT
- 5.1. Overview with review of 2025 research, industrial trends and possibilities
- 5.2. Simultaneous transmissive and reflective STAR RIS
- 5.2.1. Overview
- 5.2.2. STAR-RIS optimisation
- 5.2.3. STAR-RIS-ISAC integrated sensing and communication system
- 5.2.4. TAIS Transparent Amplifying Intelligent Surface and SWIPT active STAR-RIS
- 5.2.5. STAR-RIS with energy harvesting and adaptive power
- 5.2.6. STAR RIS SWOT appraisal
- 5.3. Other multifunctional and multi-mode RIS
- 5.3.1. Overview
- 5.3.2. Multifunctional RIS: solid-state cooling functionality
- 5.3.3. Integrated sensing and communication ISAC
- 5.3.4. Multimode RIS ensuring system security: combined semi-passive and active RIS
6. Base station, UM-MIMO, Tower in the Sky HAPS and other UAV RIS
- 6.1. Overview
- 6.2. Progress to UM-MIMO
- 6.3. RIS-enabled, self-powered ultra-massive 6G UM-MIMO base station design
- 6.4. RIS for massive MIMO base station: Tsinghua University, Emerson
- 6.5. RIS as small cell base station
- 6.6. Other important advances in RIS-enabled MIMO and base stations in 2025
- 6.7. How satellites and UAVs will aid and sometimes benefit from 6G RIS: advances through 2025
- 6.8. Important advances in 2024
- 6.9. Large stratospheric HAPS RIS
- 6.1. Overview
- 6.2. Progress to UM-MIMO
- 6.3. RIS-enabled, self-powered ultra-massive 6G UM-MIMO base station design
- 6.4. RIS for massive MIMO base station: Tsinghua University, Emerson
- 6.5. RIS as small cell base station
- 6.6. Other important advances in RIS-enabled MIMO and base stations in 2025
- 6.7. How satellites and UAVs will aid and sometimes benefit from 6G RIS: advances through 2025
- 6.8. Important advances in 2024
- 6.9. Large stratospheric HAPS RIS
7. RIS tuning hardware objectives and progress with research through 2025
- 7.1. Overview
- 7.1.1. Primitive to advanced tuning
- 7.1.2. Tuning mechanisms in context
- 7.1.3. Examples of RIS external control stimuli used in research and trials
- 7.1.4. RIS tuning hardware options compared
- 7.1.5. Infogram: The Terahertz Gap demands different tuning materials and devices
- 7.2. Lessons from research carried out on RIS tuning: 2025 and earlier
- 7.2.1. Changing focus
- 7.2.2. Electrical and optical tuning and higher frequencies favoured
- 7.3. Detailed analysis of progress with discrete tuning components
- 7.3.1. General
- 7.3.2. Schottky diode RIS tuning vs other diodes
- 7.3.3. High-Electron Mobility Transistor HEMT RIS tuning
- 7.3.4. Less successful other options with reasons
- 7.4. Prioritisation of tuning materials replacing discretes for 6G RIS 0.1-1THz and NearIR
- 7.4.1. Winners on current evidence
- 7.4.2. Options for integrated tuning materials for higher frequency 6G
- 7.4.3. Vanadium dioxide: rationale and major progress through 2025, 2024
- 7.4.4. Chalcogenide phase change materials notably GST and GeTe
- 7.4.5. Graphene: rationale and major progress through 2025, 2024
- 7.4.6. Liquid crystal rationale and progress through 2025, 2024
- 7.5. Large RIS and other gaps in the market
8. Optical Wireless Communications ORIS for 6G: major progress through 2025
- 8.1. Why OWC including RIS at its frequencies is an attractive addition for 6G
- 8.1.1. Optical Wireless Communications OWC and subset Visible Light Communications VLC
- 8.1.2. The case for multi-frequency 6G Phase Two including optical "so one gets through"
- 8.1.3. Parameter comparison of Free Space Optical FSO with 3-300GHz communication
- 8.2. The potential and the challenges of Optical RIS ORIS with SWOT appraisals
- 8.2.1. Overview
- 8.2.2. ORIS benefits and the Distributed RIS DRIS option
- 8.2.3. ORIS challenges
- 8.2.4. SWOT appraisal of 6G RIS for OWC
- 8.2.5. SWOT appraisal of visible light communication
- 8.3. ORIS implementation procedures
- 8.4. Long range, underground, underwater and space OWC: RIS: research advances 2025 and earlier
- 8.4.1. General
- 8.4.2. RIS enhanced OWC vehicular networks and mobile environments
- 8.4.3. Hybrid RF-FSO RIS
- 8.4.4. Underwater UOWC systems
- 8.4.5. Underground OWC needing RIS
- 8.4.6. Laser stratospheric and space communications with RIS technology
- 8.5. Short range and indoor OWC and its RIS: research advances through 2025 and earlier
- 8.5.1. Indoors and short range in air
- 8.5.2. Leveraging other indoor and short-range outdoor systems such as LiFi with RIS
- 8.6. Potentially 6G optical materials
- 8.7. Metalenses for 6G including advances through 2025
- 8.8. Mirror array ORIS design
9. 6G Morphing Flexible Intelligent Metasurfaces FIM, 6G hypersurfaces, metamaterial basics
- 9.1. Overview
- 9.2. Appraisal of 6G-related metamaterial research major advances through 2025
- 9.2.1. New advances in metamaterial design
- 9.2.2. Hypersurfaces, stacked intelligent metasurfaces, swarms, bifunctional metasurfaces
- 9.2.3. Optimal metamaterial substrates and low loss, 6G glass TIRS
- 9.2.4. Optimal metamaterial substrates including transparent 6G glass
- 9.3. Metamaterial basics
- 9.3.1. The meta-atom and patterning options
- 9.3.2. Material and functional families
- 9.3.3. Metamaterial reflect-arrays for 5G and 6G Communications
- 9.3.4. Metamaterial patterns and materials
- 9.3.5. Six formats of communications metamaterial with examples
- 9.4. Metasurface basics
- 9.4.1. Metasurface design, operation and RIS
- 9.4.2. How metamaterial RIS hardware operates
- 9.4.3. RIS and reflect-array construction and potential capability
- 9.4.4. All dielectric and non-linear dielectric metasurfaces
- 9.5. The long-term picture of metamaterials overall
- 9.6. Emerging applications of GHz, THz, infrared and optical metamaterials
- 9.7. Thermal metamaterials
- 9.8. SWOT appraisal for metamaterials and metasurfaces generally
- 9.9. Morphing Flexible Intelligent Metasurfaces FIM basics and their research through 2025
- 9.9.1. Basics
- 9.9.2. FIM network topology and potential applications targetted
- 9.9.3. Many FIM research advances through 2025 assessed
- 9.9.4. SWOT appraisal of 6G FIM
10. RIS and reflect-array manufacture, inspection, testing, cost breakdown
- 10.1. Thin film and transparent electronics state-of-the-art
- 10.2. Trend from discrete boards, stacked films to full smart material integration
- 10.3. Importance of flexible, laminar and 2D energy harvesting and sensing
- 10.4. How manufacturing technologies differ for 6G RIS optical, low or high THz
- 10.4.1. Candidates: nano-imprinting, nano-lithography, lithography, gravure, inkjet, screen, flexo, spray, other
- 10.4.2. Special case: 3D printing with electron beam evaporation
- 10.4.3. Ultra-fast laser system
- 10.5. 6G RIS inspection and testing: new advances in 2025
- 10.5.1. Testing challenges
- 10.5.2. Progress in RIS inspection in 2025
- 10.6. RIS cost analysis
- 10.6.1. General assessment
- 10.6.2. NEC and other costed case studies
- 10.6.3. Outdoor semi-passive and active RIS cost analysis at high areas of deployment
- 10.6.4. Indoor semi-passive RIS cost analysis at volume
11. 6G RIS companies : products, plans, patents, Zhar appraisals: 2025-6
- 11.1. Overview and patenting
- 11.1.1. Rapidly changing situation 2025-6
- 11.1.2. RIS patenting and literature trends
- 11.2. AGC Japan
- 11.3. Alcan Systems Germany
- 11.4. Alibaba China
- 11.5. Alphacore USA
- 11.6. China Telecom China Mobile, China Unicom, Huawei, ZTE, Lenovo, CICT China collaboration
- 11.7. Ericsson Sweden
- 11.8. Fractal Antenna Systems USA
- 11.9. Greenerwave France
- 11.10. Huawei China
- 11.11. ITOCHU Japan
- 11.12. Kymeta Corp. USA
- 11.13. Kyocera Japan
- 11.14. Metacept Systems USA
- 11.15. Metawave USA
- 11.16. NEC Japan
- 11.17. Nokia Finland with LG Uplus South Korea
- 11.18. NTT DoCoMo and NTTJapan
- 11.19. Orange France
- 11.20. Panasonic Japan
- 11.21. Pivotal Commware USA
- 11.22. Qualcomm USA
- 11.23. Samsung Electronic South Korea
- 11.24. Sekisui Japan
- 11.25. SensorMetrix USA
- 11.26. SK Telecom South Korea
- 11.27. Sony Japan
- 11.28. Teraview USA
- 11.29. Vivo Mobile Communications China
- 11.30. VTT Finland
- 11.31. ZTE China



















