
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1836711
구제역 백신 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Foot And Mouth Disease Vaccines - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
2025년 구제역 백신 시장은 28억 7,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 CAGR 7.02%로 성장할 전망이며, 40억 3,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.

왕성한 수요는 기후 변화가 바이러스를 한때 온대였던 지역으로 밀어내면서 발생 시 대응에서 일상적인 예방 접종으로 이행하고 있는 것을 반영하고 있습니다. 가축 무역 활성화, 정부 백신 뱅크의 신설, DIVA 기술의 보급으로 대량 생산에 유리한 예측 가능한 조달 사이클이 강화되고 있습니다. 아시아태평양과 중동 항원 은행은 대량 구매를 간소화하고, 피하 투여 형식은 농민의 컴플라이언스를 향상시키며, 동물의 스트레스를 완화합니다. 특히 아프리카와 남미의 원격지에서는 냉장 창고 및 공급 능력에 관한 공급망에 대한 제약이 여전히 성장의 브레이크가 되고 있습니다.
세계의 구제역 백신 시장 동향 및 인사이트
월경 감염 및 인수 공통 감염에 의한 아웃 브레이크 증가
2025년 1월 독일에서 발생한 구제역 사례는 1988년부터 처음으로 5대륙에 걸친 수입 금지 조치의 방아쇠가 되었습니다. 분자 추적의 결과, SAT2 XIV의 토폴로 유형이 동아프리카에서 도착한 것으로 밝혀졌고, 현대 물류가 역사적인 장벽을 어떻게 지울 수 있는지가 밝혀졌습니다. 2024년 리비아에서 발생한 감염은 백신 도착 지연으로 미스라타의 암소 그룹이 치명적인 타격을 입었습니다. 인근 오스트리아는 여러 국경 경비소를 폐쇄하고 대응했지만, 이는 봉쇄가 이제 지역의 검역뿐만 아니라 지역의 백신 접종 태세에 의존하고 있음을 나타냅니다. 기후 변화로 인해 기온이 낮은 지역에서는 바이러스의 생존 기간이 길어지기 때문에 이전에 감염되지 않은 지역에서의 예방 백신 접종이 구제역 백신 시장을 계속 확대하고 있음을 시사합니다.
동물성 단백질 및 소군 크기 수요 증가
아시아와 아프리카에서 중류 계급의 식생활 확대는 구제역의 경제적 위험을 증가시키고 당국은 생산을 보호할 필요가 있습니다. 동아프리카에서는 대륙의 40%의 가축이 사육되고 있지만, 정기적인 예방 접종률은 15% 미만이며, 이 갭은 현재, 6개월간의 면역력을 높이는 1,768만 달러의 AgResults 4종 혼합 프로그램의 대상이 되고 있습니다. 13성에서 6.05%의 BVDV 양성률을 기록한 중국의 낙농 확대는 백신 접종이 수출 허가의 기초가 되는 유사한 스케일업의 필요성을 반영합니다. 남아프리카의 2024년 캠페인은 63만 4,000마리의 암소에 백신 접종을 실시하였으며, 식량 안보의 의무화에 의해 산발적인 예방 접종이 매년 항례가 되고 있음을 나타냅니다. FMD 무발생 국가가 즐길 수 있는 수출 프리미엄은 백신 접종의 지출이 가격 상승에 따라 지불하고, 보다 광범위한 예방접종 프로그램으로 자본이 확실히 환류한다는 것을 증명합니다.
콜드체인 및 보관 비용 부담
전력망의 신뢰성이 낮은 경우 2-8℃의 무결성을 유지하는 것은 어렵습니다. 네팔에서 실시한 시험에서 온도가 상승하면 효능이 떨어지고 부피가 큰 쿨러가 라스트 마일의 운송을 방해하는 것으로 나타났습니다. FAO(유엔 식량농업기관) 가이드라인은 농촌 지역에서의 캠페인이 잘 되지 않는 주된 이유는 콜드체인 실패라고 반복합니다. 동결 건조는 이를 해결할 수 있지만, 3-6%의 수분 함량이 감염성을 유지한다는 조사 결과가 있음에도 불구하고, 현재의 비용으로는 가격에 민감한 시장에서의 도입이 제한되고 있습니다. 남미에서는 146.1%의 소가 체계적인 백신 접종을 받고 있는 반면 사하라 이남의 아프리카에서는 불과 5%밖에 받지 않기 때문에 콜드체인의 갭이 구제역 백신 시장을 크게 제한하고 있습니다.
보고서에서 분석된 기타 촉진요인 및 억제요인
- 정부 자금에 의한 백신 접종 프로그램 및 의무 사항
- 무역 친화적인 DIVA와 재조합 백신 출시
- 셀로 유형 매칭 규제 지연
부문 분석
이 부문의 2024년 수익의 56.61%는 불활성화 제제로 인한 것이지만, 개량형 생백신 플랫폼은 연간 7.89% 증가할 것으로 예측됩니다. 이 증가는 더 강하고 오래 지속되는 면역과 DIVA를 준수하는 약독주의 가용성이 증가함에 기인합니다. 차세대 보조제는 체액성 반응과 세포 반응을 향상시키면서 부반응을 감소시키기 때문에 생백신은 혈청형의 출현에 직면하는 지역에서 선호되는 선택이 되었습니다. 이와 대조적으로, 불활성화 백신은 성숙한 규제 경로에 의존하지만, 항원 드리프트가 제조 사이클을 초과하면 폐기 위험에 직면합니다. mRNA와 재조합 단백질을 이용한 새로운 방법은 신속한 균주 갱신을 약속하는 것으로, 향후 10년간 구제역 백신 시장을 재정의할 수 있습니다.
2세대 제품은 제형과 루트 효율을 연결합니다. 동결 건조 펠릿, 오일 에멀젼 안정제, 나노입자 캐리어는 보존 기간을 연장하고 콜드체인에 대한 의존도를 최소화하기 위한 연구가 진행되고 있으며, 고성장이면서 인프라가 부족한 지역에 직접 대응할 수 있습니다. 효력, 안정성, DIVA 적합성의 균형을 이룰 수 있는 제조업체는 확대하는 구제역 백신 시장에서 압도적인 점유율을 획득할 수 있을 것으로 보입니다.
2024년 매출 점유율은 근육내 주사가 76.45%로 우위를 유지하며 전달 기술에서 구제역 백신 시장 규모의 최대 부분을 차지합니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 피하 투여는 정확성을 필요로 하지 않으며, 지육의 상처 위험을 줄이고 복지 규제에도 맞추기 때문에 CAGR 7.97%로 상승하고 있습니다. 장시간 작용하는 피하 저장소는 곧 투여 횟수를 반감시킬 수 있으며, 수의사의 방문은 산발적인 목축 시스템에서 컴플라이언스를 촉진합니다.
피하 투여를 위해 제형을 사용자 정의하는 경우 섭취의 지연을 보완하기 위해 유제의 점도를 변경하거나 항원량을 늘려야 합니다. 양 루트에 대한 백신을 조정하는 기업은 신속성을 우선하는 대규모 상업 사료 생산 농가뿐만 아니라 유연한 기술을 필요로 하는 영세 농가에게도 어필할 수 있어 구제역 백신 시장에서 대응 가능한 총량을 확대할 수 있습니다.
지역별 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년 구제역 백신 시장의 50.43%를 차지했습니다. 중국의 낙농 지방에서는 검사를 받은 소군의 6.05%가 BVDV 항체를 나타내며 백신 접종 예산이 강화되고 있음을 이야기하고 있습니다. 인도 하리아나의 감시에서는 5.3%의 NSP 혈청 반응자를 기록했지만, 혈청형 O, A, Asia-1에 대한 높은 방어 역가는 프로그램의 효능을 보여줍니다. 인도네시아가 호주에서 400만 명을 받은 것은 공급 안정을 위한 국경을 넘어서는 협력 체제를 보여줍니다. Tier1 생산자의 예방 접종률은 포화에 가까워지고 있지만, 수출 지향의 축산 모델로 이행하고 있는 동남아시아의 신흥 경제권에서는 성장이 계속되고 있습니다.
중동 및 아프리카는 CAGR 8.02%로 성장을 이끌고 있습니다. 2024년 리비아의 손실은 백신 출하가 수요에 뒤처진 취약점을 강조했습니다. 동부 케이프의 9만 7,000마리를 포함한 63만 4,000마리의 소에 백신을 접종한 남아프리카 캠페인은 선택적 예방 접종에서 종합적 예방 접종으로의 축족을 보여줍니다. 동부 아프리카의 AgResults 프로젝트는 6개월간의 면역을 보장하는 4가 백신을 개발하여 지금까지 농민의 접종을 방해했던 성능 격차를 메우려고 합니다. 에티오피아의 소군은 규모가 크고 충분한 서비스가 제공되지 않기 때문에 콜드체인에 의한 자금 조달과 규제의 신속화가 개선되면 잠재적인 생산량이 현재화될 가능성이 있습니다.
남미에서는 보급이 성숙하고 있지만 기후 변화에 의한 무병 상태에 대한 위협에 직면하고 있습니다. 브라질의 경험은 예방 접종이 수출의 열쇠를 열고 있음을 증명하지만, 날씨 패턴의 변화가 다시 위험을 초래하고 수요가 재연될 수 있습니다. 북미와 유럽 시장은 한때 포스트 FMD로 간주되었지만 새로운 위험에 노출되었습니다. 독일의 2025년 사례와 이어지는 캐나다의 5,750만 달러의 은행 대출은 온대 지역이 어떻게 예방 능력을 높이고 있는지를 밝혔습니다. 위험의 지리적 재분배는 구제역 백신 시장 전체를 과거의 풍토병 기반을 넘어 확대하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 도입
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 월경 감염 및 인수 공통 감염증 증가
- 동물성 단백질에 대한 수요 증가 및 가축 군수 증가
- 정부에 의한 백신 접종 프로그램 및 의무화
- 무역 친화적인 DIVA 및 재조합 백신의 전개
- 지역 항원 은행에 의한 대량 조달
- 기후에 의한 FMD의 온대로의 이동
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 콜드체인 및 보관 비용 부담
- 혈청형 적합 규제의 지연
- 항원 드리프트에 의한 재고의 진부화
- 고역가 백신 공급 능력의 한계
- 규제 상황
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측 : 금액(달러)
- 제품별
- 개량 및 약독생 백신
- 불활화(킬드)
- 기타
- 투여 경로별
- 근육내
- 피하 투여
- 동물 유형별
- 소
- 돼지
- 양 및 염소
- 기타
- 유통 채널별
- 동물병원 및 진료소
- 정부기관
- 기타
- 지역별
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 한국
- 아시아태평양의 기타 국가
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 세계 기타 지역
- 아시아태평양
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Biogenesis Bago
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Brilliant Bio Pharma
- China Animal Husbandry(CAHIC)
- Indian Immunologicals
- Limor de Colombia
- Merck & Co. Inc./MSD Animal Health
- VECOL SA
- VETAL Animal Health
- Biovet
- Ceva Sante Animale
- Zoetis
- Jinyu Bio-technology
- Cavsavac(Biopharma Morocco)
- Intervac
- Shchelkovo Agrohim
- Indian Immunologicals Ltd
- Phibro Animal Health
- Selevac
- Inovet
제7장 시장 기회와 전망
AJY 25.10.27The foot and mouth disease vaccines market stands at USD 2.87 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 4.03 billion by 2030, registering a 7.02% CAGR.
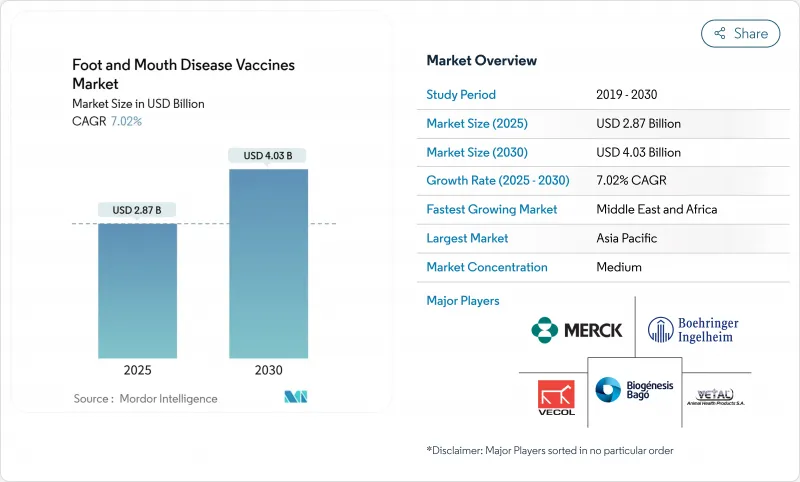
Strong demand reflects the move from reactive outbreak control toward routine preventive immunization as climate change pushes the virus into once-temperate zones. Intensified livestock trade, new government vaccine banks, and the wider use of DIVA technologies are reinforcing predictable procurement cycles that favor volume manufacturing. Regional antigen banks in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are streamlining bulk purchases, while subcutaneous delivery formats improve farmer compliance and reduce animal stress. Supply-chain constraints around cold storage and surge capacity remain the main brakes on growth, especially in remote regions of Africa and South America.
Global Foot And Mouth Disease Vaccines Market Trends and Insights
Rising Transboundary & Zoonotic Outbreaks
The January 2025 case in Germany, the country's first since 1988, triggered import bans across five continents and proved that a single incursion can shut billion-dollar trade channels . Molecular tracing showed the SAT2 XIV topotype arriving from East Africa, underscoring how modern logistics erase historical barriers. Libya's 2024 losses, where delayed vaccine arrival decimated Misrata herds, highlighted the cost of reactive strategies. Neighboring Austria responded by closing multiple border posts, signaling that containment now relies on regional vaccination readiness rather than local quarantine alone. Climate-linked shifts that lengthen viral survival in cooler zones suggest that preventive vaccination in once-free areas will continue to enlarge the foot and mouth disease vaccines market.
Growing Demand for Animal-Protein & Herd Size
Expanding middle-class diets in Asia and Africa increase the economic risk of FMD, compelling authorities to safeguard production. East Africa houses 40% of the continent's livestock, yet routine coverage is under 15%, a gap now targeted by the USD 17.68 million AgResults quadrivalent program that boosts six-month immunity. China's dairy expansion, with 6.05% BVDV positivity across 13 provinces, mirrors similar scale-up imperatives where vaccination becomes foundational to export licensing . South Africa's 2024 campaign vaccinated 634,000 cattle, showing how food-security mandates are turning sporadic inoculations into annual routines. Export premiums enjoyed by FMD-free nations prove that vaccination outlays pay for themselves via price uplift, ensuring capital flows back into wider coverage programs.
Cold-Chain & Storage Cost Burden
Maintaining 2-8 °C integrity is difficult where power grids are unreliable. Trials in Nepal found that temperature excursions cut potency and that bulky coolers hamper last-mile transport. FAO guidelines reiterate that cold-chain failure is the chief reason rural campaigns underperform. Freeze-drying can solve this, but current costs limit adoption in price-sensitive markets despite research showing 3-6% moisture content retains infectivity. As only 5% of cattle in sub-Saharan Africa receive systematic vaccination against 146.1% coverage in South America, cold-chain gaps materially restrict the foot and mouth disease vaccines market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government-Funded Vaccination Programs & Mandates
- Trade-Friendly DIVA and Recombinant Vaccine Roll-outs
- Serotype-Matching Regulatory Delays
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The segment generated 56.61% of 2024 revenue from inactivated formulations, yet modified live platforms are forecast to rise 7.89% annually. The rise stems from stronger, longer-lasting immunity and the growing availability of DIVA-compliant attenuated strains. Next-generation adjuvants reduce adverse reactions while improving both humoral and cellular responses, positioning live vaccines as the preferred choice in regions confronting emergent serotypes. In contrast, inactivated doses rely on mature regulatory pathways but face waste risk when antigenic drift outpaces production cycles. Emerging mRNA and recombinant protein methods promise rapid strain updates and could redefine the foot and mouth disease vaccines market over the next decade.
Second-generation products link formulation with route efficiency. Freeze-dried pellets, oil emulsion stabilizers, and nanoparticle carriers are under study to extend shelf life and minimize cold-chain reliance, directly addressing high-growth but infrastructure-poor geographies. Manufacturers able to balance potency, stability, and DIVA compatibility stand to capture an outsized share of the expanding foot and mouth disease vaccines market.
Intramuscular injection remained dominant with 76.45% revenue share in 2024, securing the largest slice of the foot and mouth disease vaccines market size for delivery technologies. Nevertheless, subcutaneous delivery is rising at 7.97% CAGR as it requires less precision, lowers carcass blemish risk, and aligns with welfare regulations. Long-acting subcutaneous depots could soon halve dosing frequency, driving compliance in pastoral systems where veterinary visits are sporadic.
Formulation customizations for subcutaneous use include modified emulsion viscosities and higher antigen loads to compensate for slower uptake. Companies that tailor vaccines for both routes can appeal to large commercial feedlots prioritizing speed as well as smallholder farmers needing flexible techniques, broadening total addressable volumes within the foot and mouth disease vaccines market.
The Foot and Mouth Disease Vaccines Market is Segmented by Product (Modified/ Attenuated Live, and More), Route of Administration (Intramuscular and Subcutaneous), Animal Type (Cattle, Pigs, and More), Distribution Channel (Veterinary Hospitals and Clinics, Government Institutions, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific. Middle East and Africa, South America and More). The Market and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific held 50.43% of the foot and mouth disease vaccines market in 2024. China's dairy provinces, where 6.05% of tested herds showed BVDV antibodies, signal how intensification fuels vaccination budgets. India's Haryana surveillance recorded 5.3% NSP seroreactors, yet high protective titers against serotypes O, A, and Asia-1 point to program effectiveness. Indonesia's receipt of 4 million doses from Australia demonstrates cross-border cooperation to stabilize supply. Although coverage is nearing saturation in tier-one producers, growth continues in emerging Southeast Asian economies shifting toward export-oriented livestock models.
The Middle East & Africa region leads growth at an 8.02% CAGR. Libya's 2024 losses emphasized vulnerability when vaccine shipments lag demand. South Africa's campaign that vaccinated 634,000 cattle, including 97,000 in Eastern Cape, illustrates the pivot from selective to blanket immunization. Eastern Africa's AgResults project is developing quadrivalent doses that secure six-month immunity, closing performance gaps that previously discouraged farmer uptake. Ethiopia's large but under-served herd underscores latent volume that could materialize if cold-chain financing and regulatory fast-tracking improve.
South America shows mature penetration but faces climate-driven threats to disease-free status. Brazil's experience proves vaccination can unlock exports; yet shifting weather patterns may re-introduce risk, renewing demand. North American and European markets, once considered post-FMD, have acknowledged new exposure. Germany's 2025 case and Canada's subsequent USD 57.5 million bank reveal how temperate regions are adding proactive capacity. The geographic redistribution of risk is enlarging the overall foot and mouth disease vaccines market beyond its historical endemic base.
- Biogenesis Bago
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Brilliant Bio Pharma
- China Animal Husbandry (CAHIC)
- Indian Immunologicals
- Limor de Colombia
- Merck & Co. Inc. / MSD Animal Health
- VECOL S.A.
- VETAL Animal Health
- Biovet
- Ceva
- Zoetis
- Jinyu Bio-technology
- Cavsavac (Biopharma Morocco)
- Intervac
- Shchelkovo Agrohim
- Indian Immunologicals
- Phibro Animal Health
- Selevac
- Inovet
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising transboundary & zoonotic outbreaks
- 4.2.2 Growing demand for animal-protein & livestock herd size
- 4.2.3 Government-funded vaccination programs & mandates
- 4.2.4 Trade-friendly DIVA/recombinant vaccine roll-outs
- 4.2.5 Regional antigen banks securing bulk procurement
- 4.2.6 Climate-driven FMD migration into temperate zones
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cold-chain & storage cost burden
- 4.3.2 Serotype-matching regulatory delays
- 4.3.3 Antigenic drift causing inventory obsolescence
- 4.3.4 Limited surge capacity for high-potency vaccines
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porters Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Modified/ Attenuated Live
- 5.1.2 Inactivated (Killed)
- 5.1.3 Others
- 5.2 By Route of Administration
- 5.2.1 Intramuscular
- 5.2.2 Subcutaneous
- 5.3 By Animal Type
- 5.3.1 Cattle
- 5.3.2 Pigs
- 5.3.3 Sheep & Goats
- 5.3.4 Others
- 5.4 By Distribution Channel
- 5.4.1 Veterinary Hospitals and Clinics
- 5.4.2 Government Institutions
- 5.4.3 Others
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 South Korea
- 5.5.1.4 Rest of APAC
- 5.5.2 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.2.1 GCC
- 5.5.2.2 South Africa
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.3 South America
- 5.5.3.1 Brazil
- 5.5.3.2 Argentina
- 5.5.3.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.4 Rest of the World
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Biogenesis Bago
- 6.3.2 Boehringer Ingelheim
- 6.3.3 Brilliant Bio Pharma
- 6.3.4 China Animal Husbandry (CAHIC)
- 6.3.5 Indian Immunologicals
- 6.3.6 Limor de Colombia
- 6.3.7 Merck & Co. Inc. / MSD Animal Health
- 6.3.8 VECOL S.A.
- 6.3.9 VETAL Animal Health
- 6.3.10 Biovet
- 6.3.11 Ceva Sante Animale
- 6.3.12 Zoetis
- 6.3.13 Jinyu Bio-technology
- 6.3.14 Cavsavac (Biopharma Morocco)
- 6.3.15 Intervac
- 6.3.16 Shchelkovo Agrohim
- 6.3.17 Indian Immunologicals Ltd
- 6.3.18 Phibro Animal Health
- 6.3.19 Selevac
- 6.3.20 Inovet
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment















