
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1852202
일당 간호사 파견 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Per Diem Nurse Staffing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
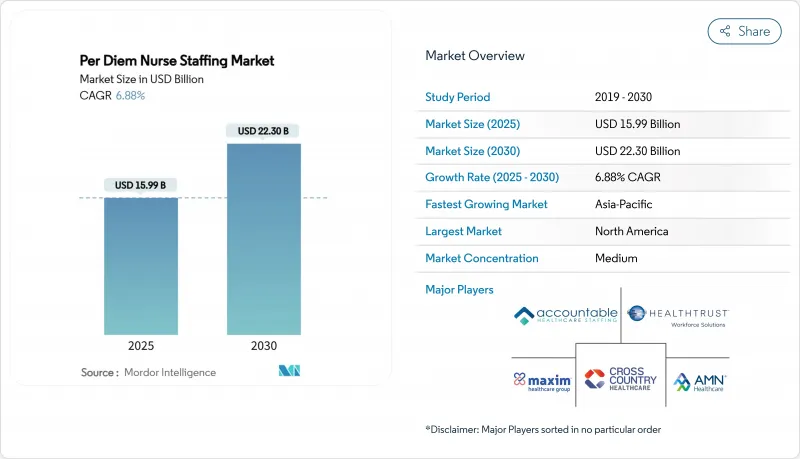
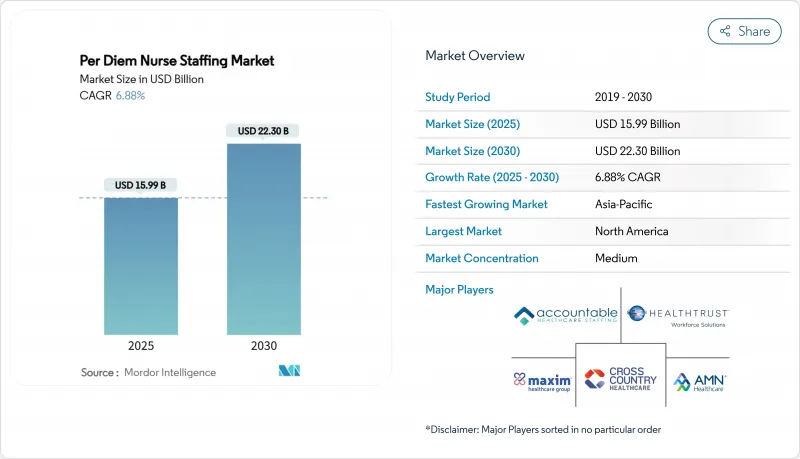
일당 간호사 파견 시장 규모는 2025년에 159억 9,000만 달러, 2030년에는 223억 달러에 이르고, CAGR 6.88%로 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다.
유연한 간호사 공급에 대한 의존도 증가, 이미 병원 운영비의 60%를 소비하고 있는 인건비 압력 확대, 세계보건기구(WHO)가 예측하는 410만명의 세계 간호사 부족이 온디맨드 대응에 대한 수요를 지지하고 있습니다. 디지털 스케줄링 플랫폼, 병원 인구조사 변동, 가치 기반 상환 인센티브는 채택을 더욱 강화하고 있습니다. 또한, 의료기관 간부는 번아웃(불타는)에 의한 이직을 막는 헤지로서 인재 파견을 파악하고 있어, 장시간의 오리엔테이션 없이 고도 급성기 병동에 배속할 수 있는 간호사에게는 할증 임금을 지불하고 싶습니다. 기술이 인재 배치 마찰을 줄이면서 가격 투명성과 실시간 자격 증명이 경쟁 요인의 핵심이 되고 있습니다.
세계 일당 간호사 파견 시장 동향과 통찰
심각화하는 세계 간호사 부족
WHO의 데이터에 따르면, 2023년에는 세계 간호사 수는 2,980만명으로 증가하는 것, 간호사의 78%는 세계 인구의 49%에 불과한 나라에서 근무하고 있으며, 심각한 지역적 불균형이 노출되어 있습니다. 미국에서는 보건복지성이 2027년까지 등록 간호사의 부족이 10%에 가까워질 것으로 예측하고 있으며, 이는 많은 병원이 법적으로 의무화된 인원 비율을 충족할 수 없게 되는 수준입니다. 유럽의 2025년 1월 '간호 액션' 이니셔티브도 마찬가지로 EU의 의료 전문직 전체에서 1,800만 명의 노동력 부족을 인정하고 있습니다. 이러한 적자는 의료 제공업체들이 적은 노동력을 빼앗기 때문에 일당계약은 자유재량이 아니게 되어 구조적인 것이 되고 있습니다. 일당의 인상은 당연한 일이며, 일당의 하한이 설정되어 자주성을 선호하는 임상의를 끌어들이게 됩니다.
입원환자 증가
유행 후 입원 환자 수는 만성 질환의 만연과 치료 연기가 수렴함에 따라 2019년 기준선을 15-20% 웃도는 수준으로 안정되고 있습니다. 환자의 고령화로 인해 평균 재원일수가 길어지고, 침대당 간호사 노동시간이 증가하고, 급환 대응의 필요성이 높아지고 있습니다. 구급부에서는 보다 복잡한 다질환의 사례가 보고되고 있으며, 관리자는 상근 간호사의 채택에는 수개월을 필요로 하기 때문에 일 고용 간호사의 채택이 유일한 즉각적인 해결책이라고 하고 있습니다. 미국 간호사 프랙티셔너 협회(American Association of Nurse Practitioners)는 2025년 동향으로서 가장 긴급성이 높은 것은 노인 의료이며, 전문의의 배치 요구가 높아지고 있다고 지적하고 있습니다. 그 결과, 급성기 병원의 책임자는 일당 출근의 간호사 명부를 업무상의 쇼크 업소버로 간주하고 있습니다.
일과 수입의 불안정성
일당제 간호사는 보통 근무 시간 보증, 고용자 부담 복리 후생, 퇴직금 제도가 없습니다. 햇볕이 매력적이더라도, 경제적인 부담이 정해져 있는 간호사는 안정된 급여를 선호하는 경우가 많습니다. 2013년 이후 의료 전문직의 배상책임보험 합산율은 100%를 넘어 독립계약자의 보험료가 상승하고 있습니다. 경기 감속 시, 시설은 우선 재량 시프트를 차단하므로 불안정한 시나리오가 강화됩니다. 이러한 주름은 교대 기회가 산발적일 수 있는 병원의 밀도가 드문 지역에서의 채택을 특히 제한합니다.
부문 분석
병원은 2024년 청구액의 58.43%를 차지하고 엄청난 양과 서지 커버리지를 필요로 하는 지속적인 인구조사 변동으로 일당 간호사 파견 시장을 지원합니다. 대부분의 3차 의료 센터는 24-48시간 전까지 일당제 간호사를 예약하는 일일 스케줄링 알고리즘에 의존하고 있으며 예측 가능한 수요를 유지하고 있습니다. 독립 클리닉과 외래 전문센터는 일당제 스탭을 채택해 수술의 피크를 커버하고 있지만, 그 성장은 아직 점진적입니다. 양로원과 간병가있는 유료 양로원 운영 회사는 지속적인 인력 감축과 규제 조사에 직면하고 있으며 안정적이지만 2 차적인 기여가되고 있습니다.
CAGR 8.54%로 성장하는 재택치료 부서는 급성기에서 지역 의료로의 지불자 이동이 간호사의 근무 시간을 어떻게 바꾸고 있는지를 보여줍니다. CMS의 2025년 의무화로 인해 대행사는 환불 전에 충분한 인력 배치를 증명하게 되었고, 일당은 컴플라이언스 워크플로우에 효과적으로 통합되게 되었습니다. 상처공강관리, 복잡한 약물요법, 만성질환지도에 숙련된 간호사에게는 10-15%의 할증임금이 지급되는 경우가 많으며, 이는 간호사층의 매력을 더욱 높여줍니다. 원격 모니터링 기술이 보급됨에 따라, 가상과 재택의 하이브리드형 일당 당직 수요가 높아져, 현지에의 통근 거리를 넘은 채택 풀이 넓어질 것으로 보입니다.
2024년 긍정적인 간호사 점유율은 62.34%로 바닥 커버리지, 스텝 다운 유닛 및 응급 부문 운영 백본을 형성합니다. 병원이 의무화된 비율을 유지하면서 고정비 인플레이션을 방지하기 위해 간호사의 일당 간호사 파견 시장 규모는 꾸준히 확대됩니다. 어드밴스드 프랙티스 레지던트 간호사(Advanced Practice Registered Nurses)는 절대수는 적지만, 주가 진료범위에 관한 법률을 확대하고, 1차 케어의 격차가 확대됨에 따라 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 9.11%로 확대합니다. 노동통계국은 2023년부터 2033년까지 13만 5,500명의 NP를 신규 채택할 것으로 예측하고 있으며, 일자리 파견회사는 이미 이 파이프라인을 이용하고 있습니다.
라이선싱/직업 간호사는 필수적인 장기 관리 기능을 충족하며 인증 간호 조수는 기본 ADL을 지원합니다. 이 층들은 인플루엔자의 계절과 감염이 유행하는 시기에 수요가 급증합니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 숙련된 간호 시설에서는 보상 한도가 있기 때문에 수수료의 유연성이 제한되고 보다 고급 의료를 제공하는 카테고리에 비해 성장이 억제됩니다.
지역 분석
북미는 만성적인 노동력 부족, 엄격한 인력배치 의무, 확립된 일당 생태계를 통해 2024년 세계 매출의 45.43%를 차지했습니다. 미국의 일당 간호사 파견 시장 점유율은 디지털 플랫폼의 급속한 보급과 졸업률을 상회하는 정년 퇴직의 물결의 지속에 지지되어 계속 우위를 유지하고 있습니다. 캐나다는 국민 모두 보험 모델과 인구동태의 고령화에 의해 안정된 수요가 예상되고, 멕시코는 인프라 정비에 의해 국경을 넘은 대리점 전개의 기회가 태어납니다.
유럽에서는 국민 모두 보험 제도가 성숙하고 있지만, 단괴의 세대의 퇴직에 수반해 간호사 부족이 심각화하고 있습니다. EU가 자금을 제공하는 '간호 액션' 프로그램은 인재 확보, 유지, 정신 건강 지원에 자원을 투입하고 업무량 유연성을 제공하는 일당제 솔루션을 위한 공간을 확보하고 있습니다. 언어의 다양성과 엄격한 노동보호는 대행사의 자격인증을 늦출 수 있지만, 국경을 넘어서는 인정의 틀이 유동성을 완화하고 있습니다. Work Life Balance가 가장 중요시되는 북유럽 국가에서는 단체 교섭의 틀 안에서 일당제의 역학을 반영한 유연한 시프트 뱅크를 시험적으로 도입하고 있습니다.
CAGR7.54%로 확대될 것으로 예측되는 아시아태평양은 적극적인 병원 건설, 급증하는 중간층, 협조적인 간호사 교육 투자로부터 이익을 얻고 있습니다. 국제 간호사 협의회(International Council of Nurses)는 특히 인도와 동남아시아의 심각한 비율 격차를 강조하고 지역 기관 및 해외 파견 프로그램의 문을 열고 있습니다. ASEAN 회원국 간 간호사 면허의 상호 승인은 노동력 흐름을 더욱 원활하게 합니다. 규제 시행에 편차가 있거나 정규직 고용을 선호하는 문화적 취향에 과제는 남아 있지만, 도시의 거대도시에서는 환자의 급증에 대응하기 위해 앱을 이용한 기그스태핑의 도입이 급속히 진행되고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 전 세계 간호 인력 부족 심화
- 병원 환자 입원 가속화
- 의료시설에 있어서의 비용 최적화의 대처
- 유연한 노동력 모델로의 전환
- 디지털 인재 파견 플랫폼의 급속한 보급
- 외래 및 포스트 큐트 케어 네트워크의 확대
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 고용과 수입의 불안정성
- 대리점 수수료에 관한 규제상의 제한
- 사내 인재 풀의 이용 확대
- 직업배상책임비용 상승
- 규제 상황
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 최종 사용자별
- 병원
- 독립 클리닉
- 간병 시설
- 재택치료 기관
- 기타 간병 시설
- 간호사 유형별
- 등록 간호사(RN)
- 면허를 소지한 실무/직업 간호사(LPN/LVN)
- 공인 간호조무사(CNA)
- 고급 실무 등록 간호사(APRN)
- 교대 근무 시간별
- 8시간
- 10시간
- 12시간
- 플로트 풀/온 콜
- 스케줄링 플랫폼별
- 기존 인재 파견 회사
- 앱 기반 마켓플레이스
- 병원내 플로트 풀
- 지리
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 호주
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Accountable Healthcare Staffing
- AMN Healthcare
- ATC Healthcare
- Cross Country Healthcare
- Dedicated Nursing Associates(DNA)
- Favorite Healthcare Staffing
- HealthTrust Workforce Solutions(HCA)
- Interim HealthCare
- Maxim Healthcare Services
- Supplemental Health Care
- Aya Healthcare
- ShiftMed
- Nomad Health
- Trusted Health
- IntelyCare
- CareRev
- GHR Healthcare
- ProLink Healthcare
- Fastaff Travel Nursing
- Medical Solutions
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
SHW 25.11.19The per diem nurse staffing market size is valued at USD 15.99 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 22.30 billion by 2030, expanding at a 6.88% CAGR.
Increasing reliance on flexible nurse supply, widening labor-cost pressures that already consume 60% of hospital operating expenses, and the World Health Organization's forecasted 4.1 million global nurse shortfall are sustaining demand for on-demand coverage. Digital scheduling platforms, hospital census volatility, and value-based reimbursement incentives further reinforce adoption. Provider executives also view contingent staffing as a hedge against burnout-driven turnover, and they are willing to pay premiums for nurses who can step into high-acuity units without lengthy orientation. As technology lowers placement frictions, pricing transparency and real-time credentialing are becoming core competitive factors.
Global Per Diem Nurse Staffing Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Global Nursing Shortage
WHO data confirm that the worldwide pool climbed to 29.8 million in 2023, yet 78% of nurses still practice in countries that host just 49% of the global population, exposing severe regional imbalances. In the United States, the Department of Health and Human Services projects registered-nurse gaps approaching 10% by 2027, a level that would leave many hospitals unable to meet legally mandated staffing ratios. Europe's January 2025 "Nursing Action" initiative likewise acknowledges an 18 million-worker deficit across EU health professions. These deficits are making per diem contracts less discretionary and more structural as providers compete for scarce hands. Rate escalation follows naturally, setting a floor under per diem compensation and attracting clinicians who prefer autonomy.
Accelerated Hospital Patient Admissions
Post-pandemic admissions are stabilizing at volumes 15-20% above 2019 baselines as chronic disease prevalence and deferred care converge. Older patients drive longer average lengths of stay, raising nurse-minutes per bed and heightening the call for short-notice coverage. Emergency departments report more complex multimorbidity cases, and administrators cite per diem recruits as the only immediate fix because full-time hires can require months to onboard. The American Association of Nurse Practitioners flags geriatric demand as the most urgent 2025 trend, intensifying specialist placement needs. Acute-care directors consequently view per diem rosters as operational shock absorbers.
Perceived Job and Income Instability
Per diem roles typically exclude guaranteed hours, employer-sponsored benefits, and retirement funding. Nurses with fixed financial obligations often favor stable salaries even when per diem premiums are attractive. Liability insurance also weighs heavily: combined ratios for medical professional coverage have stayed above 100% since 2013, translating to rising premiums for independent contractors. During economic slowdowns, facilities trim discretionary shifts first, reinforcing the instability narrative. This hesitancy particularly limits adoption in regions with sparse hospital density, where shift opportunities can be sporadic.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cost-Optimization Initiatives in Healthcare Facilities
- Shift Toward Flexible Workforce Models
- Regulatory Limitations on Agency Fees
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Hospitals captured 58.43% of 2024 billings, anchoring the per diem nurse staffing market through sheer volume and continual census swings that necessitate surge coverage. Most tertiary centers rely on daily scheduling algorithms that book per diem nurses 24-48 hours ahead, sustaining predictable demand. Independent clinics and outpatient specialty centers employ per diem staff to cover procedural peaks, though growth remains incremental. Nursing homes and assisted-living operators face persistent attrition and regulatory scrutiny, making them steady but secondary contributors.
The home-health agency segment, growing at 8.54% CAGR, illustrates how payors' shift from acute to community settings is redirecting nurse hours. CMS's 2025 mandate that agencies attest to staffing sufficiency before reimbursement effectively embeds per diem supply into compliance workflows. Agencies often pay 10-15% premiums for nurses skilled in wound vac management, complex medication regimens, and chronic-disease coaching, reinforcing segment attractiveness. As remote-monitoring technology spreads, demand for hybrid virtual-and-in-home per diem roles will rise, broadening recruitment pools beyond local commuting distances.
Registered nurses held 62.34% share in 2024, forming the operational backbone for floor coverage, step-down units, and emergency departments. The per diem nurse staffing market size for RNs is set to expand steadily as hospitals guard against fixed-cost inflation while preserving mandated ratios. Advanced practice registered nurses, though smaller in absolute count, will expand at 9.11% CAGR through 2030 as states broaden scope-of-practice laws and as primary-care gaps widen. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 135,500 net new NP roles from 2023 to 2033, a pipeline that per diem agencies are already tapping.
Licensed practical/vocational nurses fill essential long-term care functions, while certified nursing assistants round out basic ADL support. For these tiers, agency demand spikes during flu seasons and infection outbreaks when isolation protocols intensify staffing needs. Nonetheless, reimbursement ceilings in skilled-nursing facilities constrain rate flexibility, tempering growth compared with higher-acuity categories.
The Per Diem Nurse Staffing Market Report is Segmented by End User (Hospitals, Independent Clinics, and More), Nurse Type (Registered Nurses, and More), Shift Length (8-Hour Shifts, and More), Scheduling Platform (Traditional Staffing Agencies, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East & Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America generated 45.43% of global revenue in 2024 driven by chronic workforce deficits, stringent staffing mandates, and established per diem ecosystems. The per diem nurse staffing market share for the United States will remain dominant, supported by rapid digital-platform uptake and continuing retirement-wave attrition that outpaces graduation rates. Canada's universal coverage model and aging demographic reinforce steady demand, while Mexico's infrastructure upgrades create cross-border agency opportunities.
Europe presents a mature landscape with universal health systems but escalating nurse shortages as baby-boomer caregivers retire. The EU-funded Nursing Action program funnels resources toward recruitment, retention, and mental-health supports, paving space for per diem solutions that offer workload flexibility. Language diversity and rigid labor protections can slow agency credentialing, yet cross-border recognition frameworks are easing mobility. Nordic countries, where work-life balance is paramount, are piloting flexible shift banks that mirror per diem dynamics within collective-bargaining frameworks.
Asia-Pacific, forecast to expand at 7.54% CAGR, benefits from aggressive hospital construction, burgeoning middle classes, and concerted nurse-education investments. The International Council of Nurses underscores severe ratio gaps, particularly in India and Southeast Asia, opening doors for regional agencies and expatriate programs. Mutual recognition of nursing licenses across ASEAN members further lubricates workforce flows. Challenges remain in uneven regulatory enforcement and cultural preference for permanent employment, but urban megacities are quickly adopting app-based gig staffing to handle patient surges.
- Accountable Healthcare Staffing
- AMN Healthcare
- ATC Healthcare
- Cross Country Healthcare
- Dedicated Nursing Associates
- Favorite Healthcare Staffing
- HealthTrust Workforce Solutions
- Interim HealthCare
- Maxim Healthcare
- Supplemental Health Care
- Aya Healthcare
- ShiftMed
- Nomad Health
- Trusted Health
- IntelyCare
- CareRev
- GHR Healthcare
- ProLink Healthcare
- Fastaff Travel Nursing
- Medical Solutions
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating Global Nursing Shortage
- 4.2.2 Accelerated Hospital Patient Admissions
- 4.2.3 Cost Optimization Initiatives In Healthcare Facilities
- 4.2.4 Shift Toward Flexible Workforce Models
- 4.2.5 Rapid Adoption of Digital Staffing Platforms
- 4.2.6 Expansion of Outpatient and Post-Acute Care Networks
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Perceived Job and Income Instability
- 4.3.2 Regulatory Limitations on Agency Fees
- 4.3.3 Growing Use of Internal Staffing Pools
- 4.3.4 Rising Professional Liability Costs
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat Of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power Of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power Of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat Of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By End User
- 5.1.1 Hospitals
- 5.1.2 Independent Clinics
- 5.1.3 Nursing Homes
- 5.1.4 Home Healthcare Agencies
- 5.1.5 Other Long-Term Care Facilities
- 5.2 By Nurse Type
- 5.2.1 Registered Nurses (RN)
- 5.2.2 Licensed Practical/Vocational Nurses (LPN/LVN)
- 5.2.3 Certified Nursing Assistants (CNA)
- 5.2.4 Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRN)
- 5.3 By Shift Length
- 5.3.1 8-Hour Shifts
- 5.3.2 10-Hour Shifts
- 5.3.3 12-Hour Shifts
- 5.3.4 Float Pool / On-Call
- 5.4 By Scheduling Platform
- 5.4.1 Traditional Staffing Agencies
- 5.4.2 App-Based Marketplaces
- 5.4.3 Internal Hospital Float Pools
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials As Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Accountable Healthcare Staffing
- 6.3.2 AMN Healthcare
- 6.3.3 ATC Healthcare
- 6.3.4 Cross Country Healthcare
- 6.3.5 Dedicated Nursing Associates (DNA)
- 6.3.6 Favorite Healthcare Staffing
- 6.3.7 HealthTrust Workforce Solutions (HCA)
- 6.3.8 Interim HealthCare
- 6.3.9 Maxim Healthcare Services
- 6.3.10 Supplemental Health Care
- 6.3.11 Aya Healthcare
- 6.3.12 ShiftMed
- 6.3.13 Nomad Health
- 6.3.14 Trusted Health
- 6.3.15 IntelyCare
- 6.3.16 CareRev
- 6.3.17 GHR Healthcare
- 6.3.18 ProLink Healthcare
- 6.3.19 Fastaff Travel Nursing
- 6.3.20 Medical Solutions
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment









