
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1604918
<2025> 이차전지용 바인더 기술개발 현황 및 전망(-2035)<2025> Development Status and Outlook of Binder Technology for Secondary Batteries (~2035) |
||||||
LIB의 특성은 전극에 따라 크게 좌우되는데, 뛰어난 배터리 성능을 달성하기 위해서는 전극구조를 최적화하는 것이 최우선 과제라고 할 수 있습니다. 현재 상용화된 LIB에서 뿐만 아니라 연구 분야에서도 양극과 음극의 활물질은 많은 관심과 함께 연구 및 검토되고 있는데 비해, 전극반응에 참여하지 않는 비활성인 바인더는 낮은 중량비(≤5wt%)로 전극의 온전함을 유지하고 전기화학적 공정을 지원하며, 활물질과 도전재와 함께 전극의 성능 구현 측면에서 중요한 위치를 차지하지만 중요성에 비해 덜 주목받고 있는 것이 현실입니다.
바인더는 전극 내에서 차지하는 부분이 매우 작은 편이지만, 전극 전체 성능을 결정짓는 중요한 역할을 합니다. 바인더는 양극 및 음극의 활물질 및 도전재를 집전체인 각 극판에 잘 부착시키고, 내구성을 높이는 역할을 합니다. 바인더는 (1)전해질에 전기화학적으로 안정적이여야 하고, (2)유연성과 불용성을 가져야 하며, (3)특히 양극 바인더의 경우 산화에 의한 부식방지 기능이 있어야 합니다.
따라서, 활물질과 도전재를 집전체와 효과적으로 연결하고 부피 팽창을 수용하여 충방전 동안 우수한 전극 구조를 보장할 수 있는 높은 결합강도와 탄성을 지닌 기능성 바인더가 필요하니다. 최근 바인더 스크리닝(screening) 및 설계에 대한 더 많은 통찰력을 통해 연구의 초점이 기계적 안정화 관점에서 구조적 지지체 뿐만 아니라 전기화학적으로 이점을 제공하는 다기능성으로 이동하고 있습니다.
최근, 실리콘 음극재 채택이 늘어나면서 바인더가 리튬화(lithiation)반응에 많은 영향을 주어 전극 용량 및 사이클 안성성 향상에 도움이 된다는 연구가 나와 차세대 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있습니다. 기존 바인더는 양극재에는 주로 불소수지인 PVDF(PolyVinyliDeneFluoride)를, 음극재에는 합성고무인 SBR(Styrene-Butadiene-Rubber)과 CMC(Carboxyl Methyl Cellulose) 바인더를 사용했으나, 실리콘 음극재에서는 부피변화가 커서 사용에 부적합합니다. 최근에 양극재에는 PTFE(PolyTetraFluoroEthylene)바인더가 음극재에는 PAA(PolyAcrylicAcid), PI(PolyImide)계 등 수계 바인더 등이 각광을 받고 있습니다. PAA, PI 등의 바인더는 수계 바인더로, 물 기반 수계 용매를 전해질로 사용하는 실리콘 음극재에 사용됩니다. 위 바인더들은 기존 바인더에 비해 인장강도가 높고, 접착력이 높아 실리콘 음극재의 부피 팽창에 강하며 활물질을 감싸서 안정적인 SEI(Solid Electrolyte Interphase)층을 형성합니다. 차세대 양극재 바인더인 PTFE는 건식 전극공정용 바인더로 내화학성, 내열성이 매우 뛰어난 소수성 소재로 건식 전극공정이나 전고체전지에서 주목받을 것으로 보입니다. PVDF 바인더는 일본의 Kureha, 벨기에의 Solvay, 프랑스의 Arkema가 생산하고 있으며, SBR 바인더는 일본의 Zeon에서 생산하고 있어 모두 외국산 비중이 높은 고가 품목입니다. 양극재 바인더는 국내의 켐트로스, 음극재 바인더의 경우 국내의 한솔케미칼이 국산화에 성공하여 삼성SDI와 SK On에 공급하고 있으며, LG Chem.과 금호석유화학도 음극재 바인더 공급에 나서고 있습니다.
한편 SNE Research의 글로벌 리튬이온전지용 바인더에 대한 ’24.11월 수요 전망을 보면, 2025년 181.2kton에서 2030년 311.4kton으로 증가할 것으로 전망되며, 금액으로는 2025년 4.4조원에서 ’30년 6.11조원이 될 것으로 전망하고 있습니다.
24년판 리포트에서는 특히 최근 핫 이슈가 되고 있는 전고체전지, 나트륨전지(SIB)에 대한 바인더의 열적 특성, 분산 특성을 보강하였으며, 바인더의 작동 메커니즘 및 고장 메커니즘에 대한 부분을 추가하여 이해를 돕는데 노력하였습니다. 또한 최근 발표된 리튬이온 전지 전극을 위한 바인더 설계, 합성 및 전지에의 적용에 대한 지금까지의 문헌에 나온 정보를 시간대별로 상세하게 정리하였고, 해당 문헌과 함께 명기하여 좀 더 깊은 기술은 논문을 통하여 확인할 수 있도록 배려하였습니다.
한편, 당사의 리튬이온 전지에 대한 전망자료를 기초로 바인더에 대한 수요 및 시장을 전망하였으며, 부록에는 외부 리서치 기관의 시장규모 및 전망을 인용하여 독자들이 전체적인 규모를 파악하는데 도움을 주고자 하였습니다. 특히, PVDF, SBR, CMC 등 주요 바인더인 경우, 21년, 22년, 23년 상세 시장 data에서부터 24년 전망치까지 모두 수록하여 수요의 변천을 한 눈에 확인할 수 있도록 구성하였습니다.
마지막으로, 바인더 제조업체의 ’24년 가장 최근의 현황 및 주요 제품을 정리함으로써 이 분야의 연구자 및 관심있는 분들에게 전체적인 통찰력을 제공함으로써 전지의 에너지밀도, 급속 충전 능력 및 장기 수명 특성 등 전지의 성능을 향상시키는데 큰 도움이 될 것으로 기대합니다.
본 보고서의 Strong Point
- ① 바인더에 대한 전반적인 개요 및 풍부한 기술내용 수록
- ② 바인더의 개발사례를 통해 핵심 point인 설계, 합성 시 고려 사항을 수록
- ③ LIB뿐만 아니라 차세대 전지인 Li-S전지, 전고체전지, 나트륨전지(SIB)용 바인더 개발 현황 및 사례
분석 수록
- ④ SNE Research의 강점인 배터리 전망치에 근거한 바인더 시장 전망 및 LFP전지용 바인더 시장에 대한data 제공
- ⑤ 주요 바인더 기업의 가장 최근 개발 현황 및 제품 현황에 대한 상세한 정보 수록
[목 차]
1. 바인더 개요
- 1.1 서론
- 1.2 정의, 역할 및 요구 물성
- 1.2.1 역할 및 기능
- 1.2.1.1 기계적 성질
- 1.2.1.1.1 접착력 및 기계적 강도 향상
- 1.2.1.1.2 부피 변화 조절
- 1.2.1.2 계면 성능 저하 완화
- 1.2.1.3 전기적 특성
- 1.2.1.3.1 전기전도성 향상
- 1.2.1.3.2 이온전도도 향상
- 1.2.1.4 열적 특성
- 1.2.1.4.1 열 안전성 및 광범위한 온도 작동성 향상
- 1.2.1.5 분산 특성
- 1.2.1.5.1 전극 균질성 향상
- 1.2.1.1 기계적 성질
- 1.2.2 요구 물성
- 1.2.1 역할 및 기능
- 1.3 유형 및 종류
- 1.3.1 유형(types)
- 1.4 작동 메카니즘
- 1.5 바인더 고장 메커니즘
- 1.6 바인더 개발의 고급 전략
- 1.6.1 기계적 접합 강도 향상
- 1.6.2 화학적 결합 강도 향상
- 1.6.3 다기능 통합 바인더의 설계(multifunctional integrated binders)
- 1.7 바인더 특성화 기술
- 1.7.1 양극의 바인더 분포 및 조성 평가
2. 바인더의 종류 및 연구개발 사례
- 2.1 양극용 바인더
- 2.1.1 비수계 바인더
- 2.1.2 PVDF 양극 바인더의 산업 현황
- 2.1.3 (CMC+SBR) 음극 바인더 산업 현황
- 2.1.4 수계 바인더
- 2.1.5 기타 바인더
- 2.1.5.1 전도성 고분자
- 2.1.5.1.1 Polyacrylonitrile(PAN)
- 2.1.5.1 전도성 고분자
- 2.2. 음극용 바인더
- 2.2.1 삽입형 음극 바인더
- 2.2.1.1 흑연전극용 바인더
- 2.2.1.2 LTO용 음극 바인더
- 2.2.2 합금형 음극 바인더
- 2.2.2.1 선형 고분자 바인더
- 2.2.2.2 가교 고분자 바인더
- 2.2.2.3 갈래(branched: 분지) 및 초대형 고분자 바인더
- 2.2.2.4 전도성 고분자 바인더
- 2.2.1 삽입형 음극 바인더
- 2.3 차세대전지용 바인더 (1)
- 2.3.1 리튬-황(Li-S) 전지용 바인더
- 2.3.2 (4680)건식 공정용 바인더
- 2.3.3 Na이온전지(SIB)용 바인더
- 2.3.3.1 SIB용 바인더 개발
- 2.3.3.2 기존 바인더
- 2.3.3.2.1 PVDF
- 2.3.3.2.2 PAA(폴리아크릴산)
- 2.3.3.2.3 SA(Sodium Alginate)
- 2.3.3.2.4 CMC
- 2.3.3.3 신규 바인더
- 2.3.3.3.1전도성 바인더
- 2.3.3.3.2 가교 바인더(Cross-linking binders)
- 2.3.3.3.3 자가 치유 바인더(Self-healing binders)
- 2.4 차세대전지용 바인더 (2)
- 2.4.1 고체 전해질용 바인더
- 2.4.1.1 전고체전지 개요
- 2.4.1.2 황화물계 전고체전지 기술
- 2.4.1.3 전고체전지 제조 및 바인더의 필요성
- 2.4.1.4 양극용 바인더 기술
- 2.4.1.4.1 습식공정용 바인더 기술
- 2.4.1.4.2 건식공정용 바인더 기술
- 2.4.1.5 전해질층용 바인더 기술
- 2.4.1.6. 음극용 바인더 기술
- 2.4.1.6.1 흑연기반 음극용 바인더 기술
- 2.4.1.6.2 차세대 음극용 바인더 기술
- 2.4.1 고체 전해질용 바인더
3. 바인더 시장
- 3.1 바인더 시장 전체 전망(타 리서치기관 전망)
- 3.2 글로벌LIB용PVDF시장 전망
- 3.2.1 글로벌 배터리 시장 수요 전망
- 3.2.1.1 글로벌 LIB Form Factor별 수요 전망(GWh, %)
- 3.2.1.2 글로벌 LIB용 양극재 수요 전망(GWh, k ton)
- 3.2.1.3 글로벌 LIB용 음극재 수요 전망(k ton)
- 3.2.2 글로벌 LIB배터리용 바인더 수요 전망
- 3.2.3 LIB배터리용 바인더 가격 전망
- 3.2.4 LIB배터리용 바인더 시장규모 전망
- 3.2.5 글로벌 주요 배터리 업체별 양극재 바인더 수요 전망
- 3.2.6 글로벌 주요 배터리 업체별 음극재 바인더 수요 전망
- 3.2.7 실리콘계 음극용 바인더 시장 전망
- 3.2.8 실리콘 음극용 바인더PAA 시장 전망
- 3.2.9 글로벌 LFP용 바인더 수요 전망 (k ton)(CAGR 12%)
- 3.2.10 Tesla 4680 전지용 바인더 코스트 분석
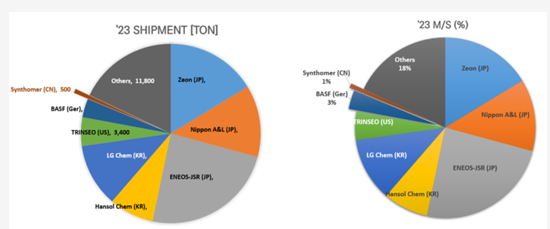
- 3.2.11 LIB 바인더 제조기업의 출하량(Shipment) 및 M/S(%)
- 3.2.12 PVDF binder 제조기업들의 출하량 및 M/S
- 3.2.13 SBR binder 제조기업들의 출하량 및 M/S
- 3.2.14 CMC binder 제조기업들의 출하량 및 M/S
- 3.2.1 글로벌 배터리 시장 수요 전망
4. 바인더 제조업체 현황
- [1] Arkema Group
- [2] BASF SE
- [3] Solvay
- [4] Kureha Corp.
- [5] ZEON Corp.
- [6] JSR Corp.
- [7] Fujian Blue Ocean Co. Ltd (BLUE OCEAN & BLACK STONE)
- [8] Dupont (CMC)
- [9] Ashland Inc.
- [10] MTI Corp.
- [11] TRINSEO
- [12] Xinxiang Jinbang Power Technology Co., Ltd.
- [13] Chongqing Lihong Fine Chemical (CMC바인더 제조사)
- [14] 캠트로스
- [15] 한솔케미칼
- [16] 금호석유화학
- [17] Daikin Industry
- [18] Nanografi Nano Technology
- [19] Nippon Paper Group(일본제지)
- [20] APV Engineered Coatings LLC
- [21] Sichuan Indigo Materials Science & Technology (INDIGO)
- [22] Guangzhou Songbai Chemical Co (Songbai)
- [23] Nippon A&L Inc.
- [24] Daicel Miraizu Ltd.
- [25] Sinochem Group Co
- [26] Ube Corp.
- [27] AOT Battery Equipment Technology
- [28] Shanghai Huayi 3F New Materials
- [29] GL Chem
5. 부록[참고용](수계 양극용 바인더 코스트 분석 외)
6. References
The characteristics of LIBs are largely determined by the electrodes, and optimizing the electrode structure is the top priority in order to achieve excellent battery performance. While the active materials of the cathode and anode are being studied and reviewed with much interest not only in currently commercialized LIBs but also in the research field, the inactive binder that does not participate in the electrode reaction maintains the integrity of the electrode with a low weight ratio (less than or equal to 5 wt%) and supports the electrochemical process, and occupies an important position in terms of implementing the performance of the electrode along with the active material and the conductive agent, but it is receiving less attention compared to its importance.
The binder occupies a very small portion of the electrode but plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance of the electrode. It helps active materials and conductive agents in both the cathode and anode adhere firmly to the current collector while enhancing durability. A binder must be (1) electrochemically stable in the electrolyte, (2) possess flexibility and insolubility, and (3) specifically for cathode binders, provide corrosion resistance against oxidation.
Therefore, a functional binder with high bonding strength and elasticity is required to effectively connect the active material and conductive agent to the current collector, accommodate volume expansion, and ensure a stable electrode structure during charge and discharge cycles. Recently, with deeper insights into binder screening and design, research has been shifting its focus from merely serving as a structural support for mechanical stabilization to developing multifunctional binders that also provide electrochemical advantages.
Recently, with the increasing adoption of silicon anode materials, research has shown that binders significantly influence the lithiation reaction, contributing to improved electrode capacity and cycle stability. This has led to active advancements in next-generation binder development. Traditionally, fluoropolymer-based PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) has been primarily used as a binder for cathodes, while SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) and CMC (Carboxymethyl Cellulose) have been used for anodes. However, due to the significant volume expansion of silicon anodes, these conventional binders are unsuitable for use with silicon-based materials.
Recently, PTFE (PolyTetraFluoroEthylene) binders have been gaining attention for cathodes, while water-based binders such as PAA (PolyAcrylic Acid) and PI (PolyImide) are increasingly used for anodes. These water-based binders are particularly suitable for silicon anodes, which utilize water-based solvents as electrolytes. Compared to conventional binders, PAA and PI offer higher tensile strength and stronger adhesion, making them more resistant to the volume expansion of silicon anodes. Additionally, these binders encapsulate the active material, helping to form a stable SEI (Solid Electrolyte Interphase) layer, which enhances electrode stability and cycle performance.
The next-generation cathode binder, PTFE (PolyTetraFluoroEthylene), is a binder for dry electrode processes. As a highly hydrophobic material with excellent chemical and thermal resistance, it is expected to gain attention for use in dry electrode processes and solid-state batteries.
PVDF binders are produced by Kureha (Japan), Solvay (Belgium), and Arkema (France), while SBR binders are manufactured by Zeon (Japan), making them high-cost materials with a high reliance on foreign suppliers.
For cathode binders, Chemtros (South Korea) has successfully localized production, while for anode binders, Hansol Chemical (South Korea) has also achieved domestic production and is supplying to Samsung SDI and SK On. Additionally, LG Chem and Kumho Petrochemical are entering the anode binder supply market.
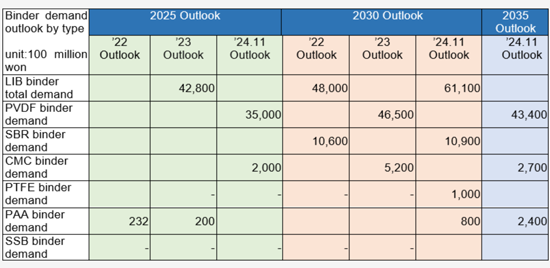
According to SNE Research's global demand forecast for lithium-ion battery binders as of November 2024, the market is expected to grow from 181.2 kton in 2025 to 311.4 kton in 2030. In terms of value, it is projected to increase from KRW 4.4 trillion in 2025 to KRW 6.11 trillion in 2030.
The 2024 edition of the report has been enhanced with a particular focus on solid-state batteries and sodium-ion batteries, which have recently become hot topics. It includes thermal and dispersion properties of binders for these next-generation batteries and provides additional insights into the operational mechanisms and failure mechanisms of binders to improve understanding. Additionally, the report presents a chronological compilation of research on binder design, synthesis, and application in lithium-ion battery electrodes, covering all relevant literature published to date. For those seeking deeper technical details, references to the original papers have been included, allowing for further exploration of the subject.
Based on our lithium-ion battery market outlook, we have projected the demand and market trends for binders. In the appendix, we have included market size estimates and forecasts from external research institutions to help readers gain a comprehensive understanding of the overall market scale. For key binders such as PVDF, SBR, and CMC, the report includes detailed market data from 2021, 2022, and 2023, along with forecasts for 2024, providing a clear view of demand trends over time.
Finally, by compiling the most recent status and key products of binder manufacturers in 2024, this report aims to provide comprehensive insights for researchers and industry professionals. It is expected to contribute significantly to improving battery performance, including energy density, fast-charging capability, and long-term cycle life.
Strong Points of This Report :
- 1. Comprehensive overview and detailed technical content on binders
- 2. Key design and synthesis considerations derived from binder development case studies
- 3. Analysis of binder development trends and case studies for next-generation batteries, including Li-S batteries, solid-state batteries, and sodium-ion batteries (SIBs), in addition to LIBs
- 4. Binder market outlook based on SNE Research's battery forecasts, along with data on the binder market for LFP batteries
- 5. Detailed information on the latest developments and product status of major binder manufacturers
[PVDF Binder Manufacturers' Shipment Volume and Market Share (M/S)]

[SBR Binder Manufacturers' Shipment Volume and Market Share (M/S)]
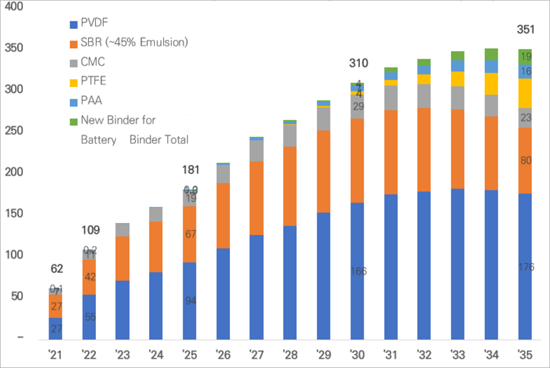
Global LIB Binder(Cathode + Anode) Demand Forecast (kTon)
[Tesla 4680 Battery Binder Cost Analysis]
- Cathode: NCM811, Anode: Si-based
- PVDF cathode binder requirement and cost for 1 GWh battery: around 38 tons
- PAA anode binder requirement and cost for 1 GWh battery: around 24 tons
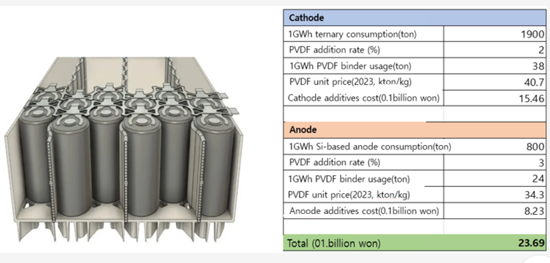
Table of Contents
1. Binder Overview
- 1.1. Introduction
- 1.2. Definition, Role, and Requirements
- 1.2.1. Role and Features
- 1.2.1.1. Mechanical Properties
- 1.2.1.1.1. Improvement of Adhesion and Mechanical Strength
- 1.2.1.1.2. Control of Volume Change
- 1.2.1.2. Mitigation of Interface Performance Degradation
- 1.2.1.3. Electrical Properties
- 1.2.1.3.1. Improvement of Electrical Conductivity
- 1.2.1.3.2. Improvement of Ion Conductivity
- 1.2.1.4. Thermal Properties
- 1.2.1.4.1. Improvement of Thermal Stability and Wide Temperature Operation Range
- 1.2.1.5. Dispersion Properties
- 1.2.1.5.1. Improvement of Electrode Homogeneity
- 1.2.1.1. Mechanical Properties
- 1.2.2. Requirements
- 1.2.1. Role and Features
- 1.3. Categories and Types
- 1.3.1. Types
- 1.4. Operation Mechanism
- 1.5. Binder Failure Mechanisms
- 1.6. Advanced Strategies for Binder Development
- 1.6.1. Improvement of Mechanical Bonding Strength
- 1.6.2. Improvement of Chemical Bonding Strength
- 1.6.3. Design of Multifunctional Integrated Binders
- 1.7. Binder Characterization Techniques
- 1.7.1. Evaluation of Binder Distribution and Composition in Cathode
2. Types of Binders and R&D Practices
- 2.1. Binder for Cathodes
- 2.1.1. Non-Aqueous Binders
- 2.1.2. Industry Status of PVDF Cathode Binders
- 2.1.3. Industry Status of (CMC+SBR) Anode Binders
- 2.1.4. Water-based Binders
- 2.1.5. Other Binders
- 2.1.5.1. Conductive Polymer
- 2.1.5.1.1. Polyacrylonitrile(PAN)
- 2.1.5.1. Conductive Polymer
- 2.2. Binders for Anodes
- 2.2.1. Insertable Anode Binder
- 2.2.1.1. Binders for Graphite Electrodes
- 2.2.1.2. Anode Binder for LTO
- 2.2.2. Alloy Anode Binders
- 2.2.2.1. Linear Polymer Binders
- 2.2.2.2. Crosslinked Polymer Binders
- 2.2.2.3. Branched and Extra-Large Polymer Binders
- 2.2.2.4. Conductive Polymer Binders
- 2.2.1. Insertable Anode Binder
- 2.3. Binder for Next-Generation Batteries (1)
- 2.3.1. Binders for Lithium-Sulfur (Li-S) Batteries
- 2.3.2 (4680)Binders for Dry Process
- 2.3.3. Binders for Sodium-Ion Batteries (SIB)
- 2.3.3.1. Development of Binders for SIB
- 2.3.3.2. Conventional Binders
- 2.3.3.2.1. PVDF
- 2.3.3.2.2. PAA
- 2.3.3.2.3. SA(Sodium Alginate)
- 2.3.3.2.4. CMC
- 2.3.3.3. New Binders
- 2.3.3.3.1. Conductive Binders
- 2.3.3.3.2. Cross-linking Binders
- 2.3.3.3.3. Self-healing Binders
- 2.3.3. Binders for Sodium-Ion Batteries (SIB)
- 2.4. Binder for Next-Generation Batteries (2)
- 2.4.1. Binders for Solid Electrolytes
- 2.4.1.1. Overview of All-Solid-State Batteries
- 2.4.1.2. Sulfide-based All-Solid-State Battery Technology
- 2.4.1.3. Manufacturing of All-Solid-State Cells and the Purpose of Binders
- 2.4.1.4. Binder Technology for Cathodes
- 2.4.1.4.1. Binder Technology for Wet Processes
- 2.4.1.4.2. Binder Technology for Dry Processes
- 2.4.1.5. Binder Technology for Electrolyte Layers
- 2.4.1.6. Binder Technology for Anodes
- 2.4.1.6.1. Binder Technology for Graphite-Based Anodes
- 2.4.1.6.2. Next Generation Binder Technology for Anodes
- 2.4.1. Binders for Solid Electrolytes
3. Binder Market
- 3.1. Overall Outlook for the Binders Market(Outlook by Other Researchers)
- 3.2. PVDF Market Outlook for Global LIBs
- 3.2.1. Global Battery Market Demand Outlook
- 3.2.1.1. Global LIB Demand Outlook by Form Factor (GWh, %)
- 3.2.1.2. Global LIB Cathode Material Demand Outlook (GWh, k ton)
- 3.2.1.3. Global LIB Anode Material Demand Outlook (k ton)
- 3.2.2. Global LIB Binder Demand Outlook
- 3.2.3. LIB Binder Price Outlook
- 3.2.4. LIB Binder Market Size Outlook
- 3.2.5. Global Cathode Binder Demand Outlook by Major Battery Companies
- 3.2.6. Global Anode Binder Demand Outlook by Major Battery Companies
- 3.2.7. Market Outlook for Binders for Silicon-based Anodes
- 3.2.8. PAA Binders for Silicon Anode Market Outlook
- 3.2.9. Global LFP Binder Demand Outlook (k ton)(CAGR 12%)
- 3.2.10. Binder cost analysis for 4680 batteries for Tesla
- 3.2.11. Shipments and M/S of LIB Binder Manufacturers
- 3.2.12. Shipments and M/S of PVDF Binder Manufacturers
- 3.2.13. Shipments and M/S of SBR Binder Manufacturers
- 3.2.14. Shipments and M/S of CMC Binder Manufacturers
- 3.2.1. Global Battery Market Demand Outlook
4. Binder Manufacturer Status
- Arkema Group
- BASF SE
- Solvay
- Kureha Corp.
- ZEON Corp.
- JSR Corp.
- Fujian Blue Ocean Co. Ltd (BLUE OCEAN & BLACK STONE)
- Dupont (CMC)
- Ashland Inc.
- MTI Corp.
- TRINSEO
- Xinxiang Jinbang Power Technology Co., Ltd.
- Chongqing Lihong Fine Chemical (CMC Binder Manufacturers)
- Chemtros
- Hansol Chemical
- Kumho Petrochemical
- Daikin Industry
- Nanografi Nano Technology
- Nippon Paper Group
- APV Engineered Coatings LLC
- Sichuan Indigo Materials Science & Technology (INDIGO)
- Guangzhou Songbai Chemical Co (Songbai)
- Nippon A&L Inc.
- Daicel Miraizu Ltd.
- Sinochem Group Co.
- Ube Corp.
- AOT Battery Equipment Technology
- Shanghai Huayi 3F New Materials
- GL Chem
5. Appendix[For reference](Analysis of binder cost for water-based cathodes, etc.)
6. References
(주말 및 공휴일 제외)


















