
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1583179
스마트 팩토리 도입(2024년)Smart Factory Adoption Report 2024 |
||||||
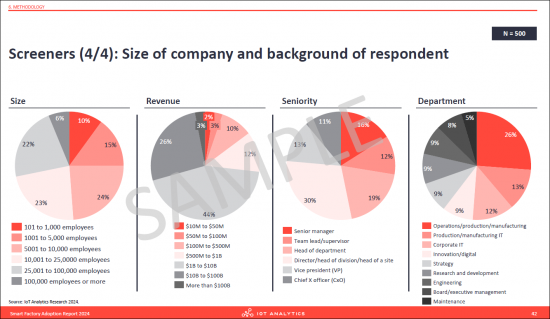
IoT Analytics의 산업용 IoT와 인더스트리 4.0에 관한 지속적 조사의 일부로, 이 보고서에 게재되고 있는 정보는 2024년 2월부터 2024년 3월까지 500사의 제조 업체를 대상으로 한 조사의 결과에 기반하고 있습니다. 이 목적은 제조업체 전체에서 스마트 팩토리의 사용 사례와 기술의 채택 현황에 관한 정보를 참여 기업에게 제공하는 것입니다.
인포그래픽스
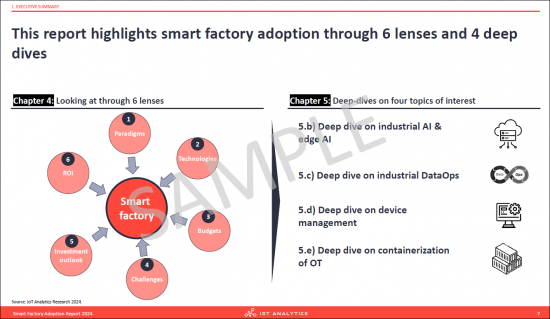
본 리포트는 스마트 팩토리 도입을 아래 6개의 렌즈를 통해 강조합니다.
6개의 렌즈 :
- 1.패러다임
- 2.기술
- 3.예산
- 4.과제
- 5.투자 전망
- 6.ROI
인포그래픽스
4개의 딥 다이브 상세 분석 :
- 1.산업용 AI와 엣지 AI
- 2.산업용 DataOps
- 3.디바이스 관리
- 4.OT의 컨테이너화
인포그래픽스
왜 제조업체는 공장 스마트화를 목표로 하는가?
비용 경쟁력을 유지하기 위해 :
특히 가격 민감도가 높은 산업에서는 원가 경쟁력을 유지하는 것이 생존을 위해 매우 중요합니다. 그 대표적인 예가 독일 태양전지 제조업의 몰락입니다. 한때 세계를 선도하던 독일의 태양광 산업은 2000년대 후반 저렴한 중국산 태양광 모듈이 시장에 출시되면서 SolarWorld와 같은 국내 제조업체들이 몰락했고, 결국 파산에 이르렀습니다. 전기자동차(EV) 산업에서도 비슷한 시나리오가 현재 진행 중일 수 있습니다.
노동력 부족과 기술격차 완화를 위해:
많은 고소득 국가들이 저출산으로 인해 정년퇴직으로 인해 많은 전문 인력을 잃을 위기에 처해 있습니다. 이는 제조업에도 타격을 주고 있습니다. 미국에서만 향후 10년간 190만 개의 제조업 일자리가 사라질 수 있으며, 자동화와 디지털화는 이러한 문제를 완화하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
인포그래픽스
지속가능성과 규제 압력에 대처하기 위해 :
많은 규제 기관은 관련 규제를 도입하여 기후 변화의 도전에 대응하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, EU는 현재 상장된 중소기업뿐만 아니라 대기업에도 탄소 발자국 및 관련 주제의 보고를 의무화하기 시작했습니다. 정확한 추적과 보고는 기술적 기반이 없으면 어렵습니다.
인포그래픽스

보다 높은 유연성과 커스터마이즈성을 실현하기 위해 :
현재 자동차 산업이 전기차로의 전환은 제조 유연성의 중요성을 보여주는 좋은 예입니다. 내연기관 자동차를 위해 구축된 기존 생산 라인은 전기차에 필요한 다양한 부품과 구성에 대응할 수 있는 유연성이 부족한 경우가 많습니다. 또한, 전기차 수요는 크게 변동하기 때문에 현재 수요에 맞추어 생산 체제를 유연하게 조정할 수 있는 자동차 제조업체는 큰 이점을 누릴 수 있습니다. 따라서 고객의 선호도, 제품 디자인, 소재의 변화에 대응하기 위해 보다 적응력과 확장성이 높은 제조 솔루션을 도입하는 것이 향후 핵심이 될 것으로 보입니다.
답변된 질문
- 스마트 공장의 현황은?
- 스마트 공장 전략을 시행하는 제조업체에게 가장 중요한 기술은 무엇인가?
- 디지털 기술의 채택에 관하여 '선도적'으로 여겨지는 제조업체는 어디인가?
- 제조업체의 패러다임은 어떻게 변화하고 있는가?
- 제조업체는 어느 AI의 사용 사례를 도입하고 있는가?
- AI 모델의 트레이닝과 추론은 어디에서 시행되고 있는가?
- DataOps 솔루션을 선택할 때 주요 고려사항은?
- 제조업체가 디바이스 관리에 사용하고 있는 소프트웨어의 유형은?
- 엣지에서의 컨테이너화에 사용되는 주요 컨테이너화 툴은?
언급된 기업
|
|
|
"The Smart Factory Adoption Report 2024" is part of IoT Analytics' ongoing coverage of Industrial IoT & Industry 4.0. The information presented in this report is based on the results of a survey of 500 manufacturers between February 2024 to March 2024. The purpose is to inform other market participants about the current state of adoption of smart factory use cases and technology across manufacturers. Survey participants were selected randomly, and their knowledge was verified independently. To ensure complete objectivity, IoT Analytics did not alter or supplement any survey results and did not accept participants who were suggested by third parties (e.g., customers from specific vendors).
INFOGRAPHICS
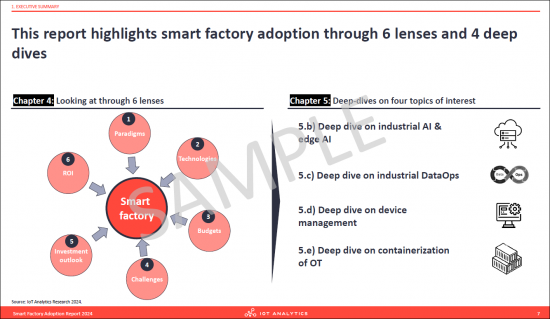
This report highlights smart factory adoption through
6 lenses
- 1. Paradigms
- 2. Technologies
- 3. Budgets
- 4. Challenges
- 5. Investment outlooks
- 6. ROI
INFOGRAPHICS
and 4 deep dives
- 1. Industrial AI & edge AI
- 2. Industrial DataOps
- 3. Device management
- 4. Containerization of OT
INFOGRAPHICS
Why do manufacturers look to make factories smarter?
To stay (cost-)competitive.
Especially in industries where price sensitivity is high, maintaining cost competitiveness is crucial for survival. A stark example is the collapse of the German solar manufacturing industry. Once a global leader, Germany's solar sector struggled when cheaper Chinese solar modules flooded the market in the late 2000s, undercutting domestic producers like SolarWorld, which eventually declared insolvency. A similar scenario may currently be unfolding in the electric vehicle (EV) industry.
To mitigate labor shortages and skill gaps.
Many high-income countries are experiencing declining birth rates and stand on the brink of losing a large chunk of experts as they transition into retirement. This is also harming manufacturing companies. In the US alone, 1.9 million manufacturing jobs could remain unfilled in the next 10 years. Automation and digitalization can help to mitigate these challenges.
INFOGRAPHICS
To address sustainability and regulatory pressures.
Many regulatory bodies have reacted to climate change challenges by introducing related regulations. The European Union, for example, now requires a broad set of large companies, as well as listed SMEs, to start reporting on carbon footprint and related topics. The new rules are first coming into effect in the 2024 financial year, for reports published in 2025. Accurate tracking and reporting will not be difficult without the technological foundation.
INFOGRAPHICS

To achieve greater flexibility and customization.
The automotive industry's current shift towards EVs is a good example of why manufacturing flexibility matters. Traditional production lines built for internal combustion engine vehicles often lack the flexibility to accommodate the variety of components and configurations required for EVs. Additionally, with EV demand highly fluctuating, automotive manufacturers that can flexibly adjust their manufacturing setup to the current demand have massive advantages. That is why implementing more adaptive and scalable manufacturing solutions to handle changes in customer preferences, product design, and materials will be key in the future.
Questions answered:
- What is the current state of smart factories?
- Which technologies are most important for manufacturers who roll out a smart factory strategy?
- Which manufacturers are considered "leading" when it comes to adoption of digital technologies?
- How are the paradigms of manufacturers changing?
- Which AI use cases are manufacturers rolling out?
- Where are training and inference of AI models happening?
- What are key considerations when choosing a DataOps solution?
- Which type of software are manufacturers using to manage devices?
- What are the leading containerization tools used for containerization at the edge?
Companies mentioned:
A selection of companies mentioned in the report.
|
|
|
Table of Tables
1. Executive Summary
- 1. Executive summary
- 2. This report highlights smart factory adoption through 6 lenses and 4 deep dives
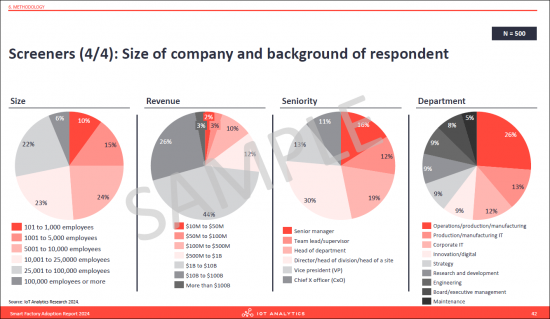
- 3. 500 people participated in this research that represent a variety of different manufacturers
- 4. The Smart Factory Adoption Report 2024 is part of IoT Analytics' ongoing coverage of Industry 4.0 and IIoT
2. Introduction
- 1. Recap: In 2022, manufacturers had or were in the process to develop a smart factory strategy
- 2. Why do manufacturers look to make factories smarter?
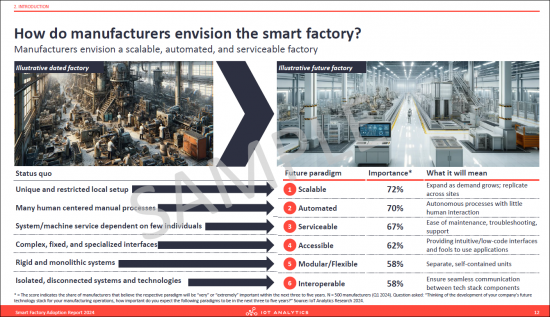
- 3. How do manufacturers envision the smart factory?
- 4. Technology plays a key role for smart factories
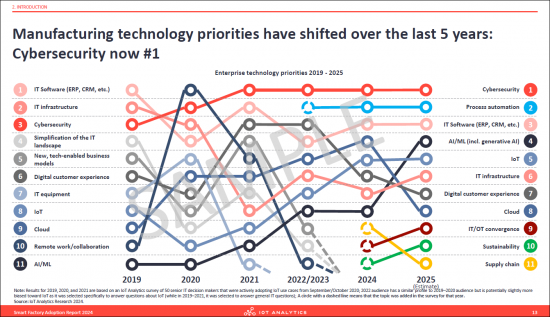
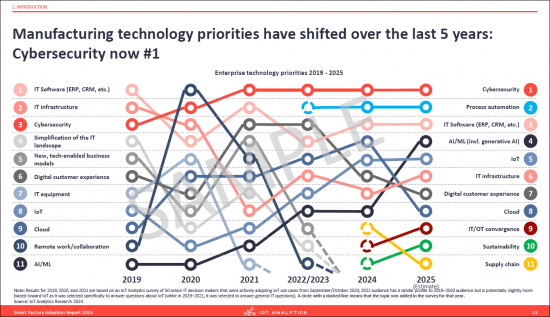
- 5. Manufacturing technology priorities have shifted over the last 5 years
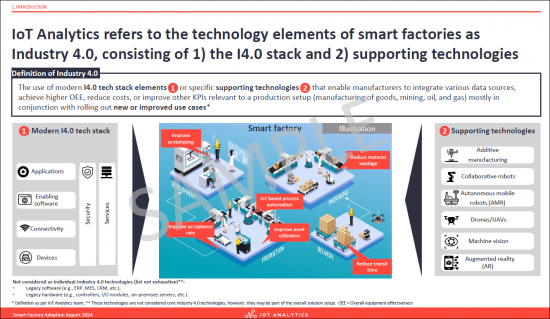
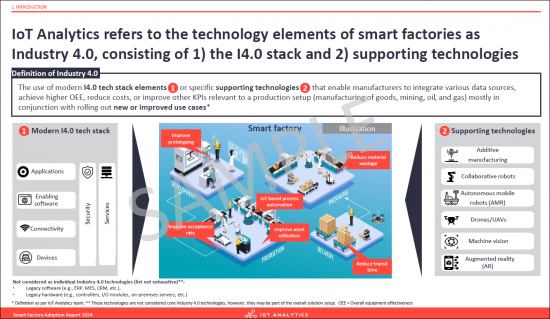
- 6. IoT Analytics refers to the technology elements of smart factories as Industry 4.0
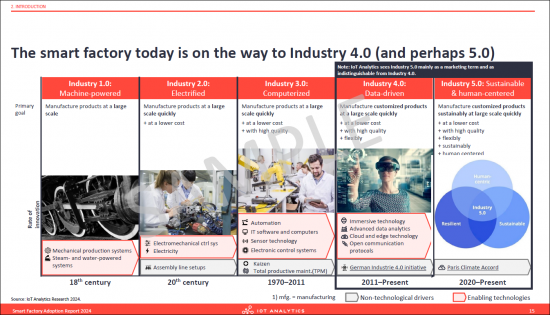
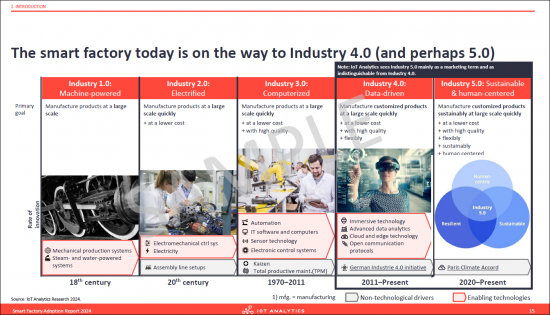
- 7. The smart factory today is on the way to Industry 4.0 (and perhaps 5.0)
- 8. The Industry 4.0 tech stack is forecasted to reach by 2030
- 9. The four deep-dives in chapter 4 have been trending in public search interest in the last 3-4 years
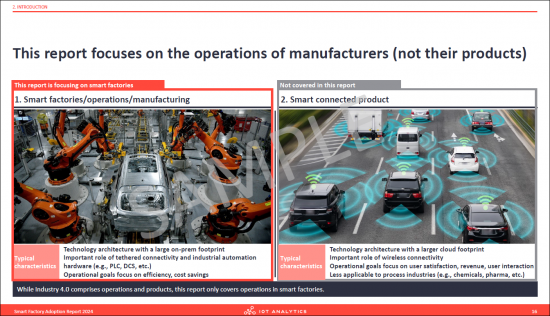
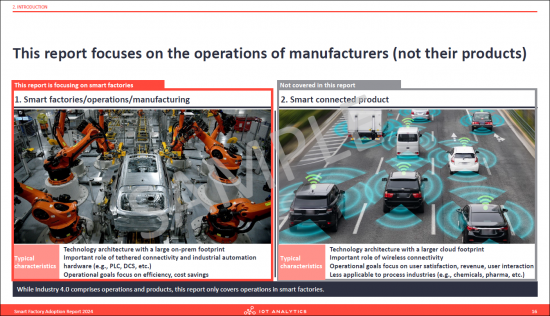
- 10. This report focuses on the operations of manufacturers (not their products)
3. State of smart factories in 2024
- 1. Chapter 3: State of smart factories 2024 - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. State of smart factories 2024: Focus on scalability and security
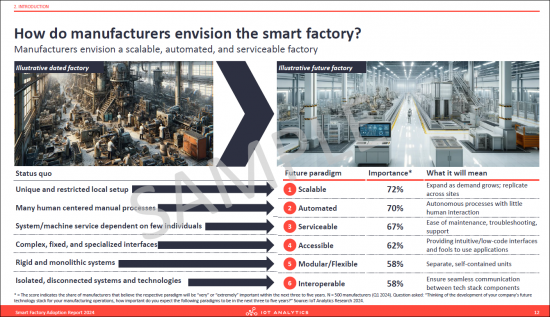
- 3. How do manufacturers envision the smart factory?
- 4. Importance of smart factory paradigms in the next 3-5 years (1/3)
- 5. Importance of smart factory paradigms in the next 3-5 years (2/3) - By region/industry/company size
- 6. Importance of smart factory paradigms in the next 3-5 years (3/3) - By function
- 7. Importance of technologies in the next 3-5 years (1/3) - Overview
- 8. Importance of technologies in the next 3-5 years (2/3) - By type
- 9. Importance of technologies in the next 3-5 years (3/3) - By department
- 10. Severity of challenges (1/3) - Overview
- 11. Severity of challenges (2/3) - By region/industry/company size
- 12. Severity of challenges (3/3) - By department
- 13. Example: Why cybersecurity is so important - 3 recent notable breaches
4. Leading smart factory adopters 2024
- 1. Chapter 4: Leading smart factory adopters 2024 - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Leading smart factory adopters - Top 25
- 3. Why these manufacturers are seen as leading adopters (1/3)
- 4. Example: Tesla Giga Berlin is often regarded as the most advanced Tesla factory
- 5. Why these manufacturers are seen as leading adopters (2/3)
- 6. Why these manufacturers are seen as leading adopters (3/3)
- 7. Extensive list of all companies mentioned by respondents
5. a) Selected deep-dives: Overview
- 1. Chapter 5: Selected deep-dives - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Smart factory technology deep-dives: Overview
- 3. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (1/3): Overview
- 4. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (2/3): By vertical
- 5. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (3/3): By region
- 6. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (in $M) (1/2): Budget by topic
- 7. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (in $M) (2/2): Budget
- 8. Expected budget change between 2024 and 2026 (1/2): Overview
- 9. Expected budget change between 2024 and 2026 (2/2): By company type
- 10. Severity of challenges by type of technology
- 11. Return on investment by type of technology (1/3): Overview
- 12. Return on investment by type of technology (2/3): By company type
- 13. Return on investment by type of technology (3/3): By department
5. b) Selected deep-dives: Industrial AI & edge AI
- 1. Chapter 5b: Deep-dive on Industrial & Edge AI - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Importance of AI use cases (1/3): Overview
- 3. Importance of AI use cases (2/3): By company type
- 4. Importance of AI use cases (3/3): By function
- 5. Training and inferencing of AI use cases 2 years from now (1/2): Overview
- 6. Training and Inferencing of AI use cases 2 years from now (2/2): Deep-dive
- 7. Example: Machine vision training and inference of AI models is happening across the edge-cloud continuum
5. c) Selected deep-dives: Industrial DataOps
- 1. Chapter 5c: Deep-dive on industrial DataOps - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Importance of industrial DataOps themes (1/3): Overview
- 3. Importance of industrial DataOps themes (2/3): By company type
- 4. Importance of industrial DataOps themes (3/3): By function
- 5. Finding: Combined IT/OT data platform is crucial - Example: Vendors react
- 6. How manufacturers implement industrial DataOps (1/3): Overview
- 7. How manufacturers implement industrial DataOps (2/3): Vendors
- 8. How manufacturers implement industrial DataOps (3/3): In-house
- 9. Challenges when adopting industrial DataOps (1/3)
- 10. Challenges when adopting industrial DataOps (2/3): By company type
- 11. Challenges when adopting industrial DataOps (3/3): By department
5. d) Selected deep-dives: Device management
- 1. Chapter 5d: Deep-dive on device management - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. How manufacturers procure device management solutions (1/3): Overview
- 3. How manufacturers procure device management solutions (2/3): Third party
- 4. How manufacturers procure device management solutions (3/3): Device manufacturer
- 5. Importance of aspects in device management (1/3): Overview
- 6. Importance of aspects in device management (2/3): By company type
- 7. Importance of aspects in device management (3/3): By function
- 8. How manufacturers manage and update of devices on the shopfloor
- 9. Management of devices on the shopfloor: By company type
- 10. Update of devices on the shopfloor: By company type
- 11. Most challenging aspects when adopting device management (1/3)
- 12. Most challenging aspects when adopting device management (2/3): By company type
- 13. Most challenging aspects when adopting device management (3/3): By function
5. e) Selected deep-dives: Containerization of OT
- 1. Chapter 5e: Deep-dive on containerization of OT - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Containerization of manufacturing software (next 3 years) (1/3): Overview
- 3. Containerization of manufacturing software (next 3 years) (2/3)
- 4. Containerization of manufacturing software (next 3 years) (3/3)
- 5. Mitigation of challenges by using containerization (1/3): Overview
- 6. Mitigation of challenges by using containerization (2/3): By company type
- 7. Mitigation of challenges by using containerization (3/3): By department
- 8. Usage of container management solutions (1/2): Overview
- 9. Usage of container management solutions (2/2): By company type
- 10. Reasons to use container management tools at the edge (1/3): Overview
- 11. Reasons to use container management tools at the edge (2/3): By company
- 12. Reasons to use container management tools at the edge (3/3): By function
- 13. Usage of containerized workloads today and in the future (1/3): Overview
- 14. Usage of containerized workloads today and in the future (2/3): By company type
- 15. Usage of containerized workloads today and in the future (3/3): By function
- 16. Most challenging aspects when adopting containerization (1/3): Overview
- 17. Most challenging aspects when adopting containerization (2/3): By company type
- 18. Most challenging aspects when adopting containerization (3/3): By function



















