
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1906877
말레이시아의 화물 및 물류 : 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Malaysia Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
말레이시아의 화물 및 물류 시장은 2025년 297억 달러로 평가되었고, 2026년에 312억 3,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 보입니다. 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 5.14%의 성장이 예상되며, 2031년까지 401억 1,000만 달러에 달할 전망입니다.
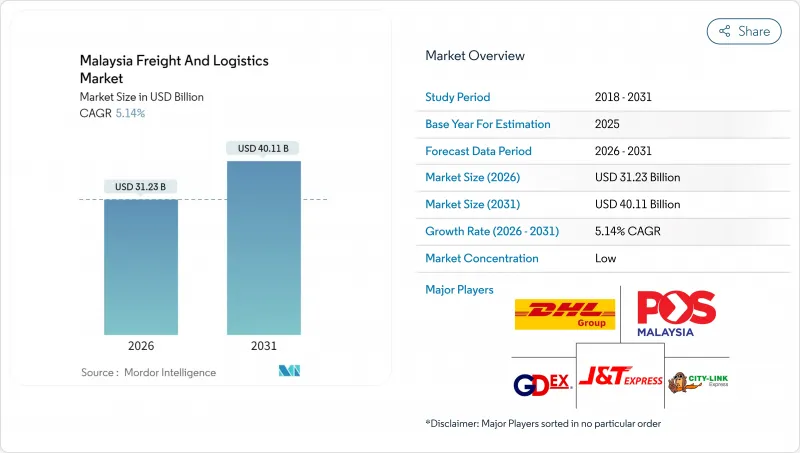
클랑 항이 세계 10위 컨테이너 항구로 부상하고, 철도 및 고속도로 프로젝트에 대한 정부의 대규모 투자, 그리고 지속되는 전자상거래 성장세가 말레이시아 화물 및 물류 시장 전반에 걸쳐 공급망 네트워크, 창고 자동화 우선순위, 운송업체 파트너십을 재편하고 있습니다. 2024년 외국인 직접 투자(FDI)는 3,785억 링깃(823억 달러)에 달해 207,000개의 일자리를 창출했으며, 국경 간 운송, 부가가치 유통, 전문 제조 물류에 대한 수요를 확대했습니다. 소비자들의 당일 배송 선호는 라스트마일 네트워크 밀집화를 가속화하고 있으며, 디젤 보조금 대상 확대 및 간소화된 통관 절차와 같은 규제 조치는 비용 부담과 국경 마찰을 완화하고 있습니다. 글로벌 운송사들은 항공화물 운송량 확보, 해상화물 할당량 확보, 온도 제어 운송 능력 확보를 위해 현지 협력 관계를 강화하며, 아세안 및 광역 아시아태평양 무역 네트워크 내 말레이시아의 허브 역할을 공고히 하고 있습니다.
말레이시아의 화물 및 물류 시장 동향과 전망
폭발적인 B2C 전자상거래 증가가 라스트마일 혁신을 주도
당일 배송은 표준적인 기대치로 자리 잡았으며, 주요 플랫폼들은 주문량의 95%를 24시간 이내에 배송합니다. 인터넷 사용자의 64.8%가 무료 배송을 선호함에 따라 말레이시아 화물 및 물류 시장 공급업체들은 자동 분류 시스템, 마이크로 풀필먼트 센터, 데이터 기반 경로 계획 도입을 강요받고 있습니다. MR DIY와 같은 소매업체들은 로봇 시스템 도입 후 200%의 효율성 향상을 달성하며, 자동화가 이제 경쟁 우위의 기반이 됨을 입증했습니다. UPS-Ninja Van과 같은 파트너십은 글로벌 특송 서비스를 52개 소매점으로 확장하여 수출업체들에게 더 넓은 화물 적재 공간 접근성과 디지털 추적 서비스를 제공하며, 이는 지역 무역에 참여하는 중소기업의 증가 추세와 부합합니다. 이러한 누적된 영향은 용량 탄력성과 서비스 다양성을 더해 말레이시아 화물 및 물류 시장의 단기 성장 궤도를 뒷받침합니다.
FDI 주도 제조업 생산 급증이 산업 물류를 변화
2024년 기록적인 3,785억 링깃(823억 달러) 투자 승인으로 반도체 팹, 첨단 자동차 부품, 재생에너지 조립 분야에 자금이 유입되고 있습니다. 반도체 투자는 정전기 방전(ESD) 준수 포장, 보안 로봇, 보세창고 통관 전용 차선에 대한 수요를 촉발하고 있습니다. MKS Instruments와 같은 정밀 공학 기업들은 원자재 유입 흐름의 동기화와 고빈도 출하를 요구하는 '슈퍼 센터'를 구축하고 있습니다. 조호르-싱가포르 특별경제구역 내 국경 간 세제 혜택으로 100개 프로젝트와 2만 개의 숙련 일자리 창출이 예상되며, 이는 말레이시아 화물 및 물류 시장의 새로운 통로를 구축할 전망입니다. ESG 기준이 강화됨에 따라 투자자들은 재생에너지 및 철도 분기점 인근의 복합물류 거점도 우선시하여 장기적인 화물 다각화를 강화하고 있습니다.
인프라 투자에도 불구하고 항만 혼잡이 용량 제약
클랑항에서 선박 평균 대기 시간이 1.3-1.46일에 달하고 야드 가동률이 90%를 초과하면서 일정 신뢰성이 약화되고 있습니다. 2025년 2월 출범한 말레이시아 해상 단일 창구(MSSW)는 서류 처리 주기를 5일에서 단 몇 시간으로 단축했으나, 물리적 부두 확장은 단기 TEU 성장에 여전히 뒤처질 전망입니다. 웨스트포트 홀딩스의 수십 년에 걸친 확장 계획은 총 처리 능력을 현행 한계를 훨씬 뛰어넘도록 추진할 목표이지만, 홍해 우회 항로로 인해 이미 도착 물량 집중과 야적장 포화 현상이 심화되었습니다. 글로벌 해운사들이 컨테이너를 재배치함에 따라 말레이시아 화물 및 물류 시장은 단기적인 용선료 급등과 재고 불균형에 직면하여 처리량 증가로 인한 마진 개선 효과를 잠식당하고 있습니다.
부문 분석
2025년 제조업은 페낭의 4,310억 링깃(937억 달러) 수출 엔진과 셀랑고르의 전자 산업 클러스터에 힘입어 말레이시아 화물 및 물류 시장 점유율의 38.98%를 차지했습니다. 다국적 기업들은 보세 트럭 운송 회랑, ESD 안전 창고, 보안 화물 호송 서비스를 요구하며 서비스 차별화를 주도하고 있습니다. 전기차 부품 및 재생에너지 장비의 성장은 대형 컨테이너 처리 및 특수 리깅 수요를 확대하며 말레이시아 화물·물류 시장 규모를 더욱 확장시키고 있습니다. 도매 및 소매 무역은 절대 금액 기준 규모는 작지만, 가처분 소득 증가와 디지털 결제 확산에 힘입어 2026-2031년 연평균 5.46% 성장률을 기록할 전망입니다. 99 스피드 마트(99 Speed Mart)와 같은 슈퍼마켓 체인은 매장 수를 두 배로 늘릴 계획으로, 소비 집중 지역에 근접한 다중 온도 크로스독 및 마이크로 풀필먼트 센터가 요구됩니다.
농업, 어업, 임업은 중동 수요 시장에 진출하기 위해 인증된 할랄 콜드 체인에 의존하고 있어, 알고리즘 기반 온도 추적 플랫폼의 상업적 매력이 더욱 커지고 있습니다. 건설 물류는 RTS 링크 및 페낭 공항 확장 같은 메가 프로젝트와 직결되어 중량물 크레인, 야간 호송 차량, 동기화된 JIT(적시) 자재 순차 공급을 필요로 합니다. 석유, 가스, 광업은 여전히 주기적이지만 ISO 탱크 컨테이너, 선체 청소 서비스, 파이프라인 유지보수 부품에 대한 꾸준한 수요를 유지하며, 원자재 가격 변동 속에서도 말레이시아 화물 및 물류 산업의 기반을 공고히 합니다.
2025년, 화물 운송은 말레이시아의 화물 및 물류 시장 수익의 55.62%를 차지하며 확고한 제조업 수출과 지역 유통 흐름을 반영했습니다. 택배, 특송, 소포 솔루션과 연계된 말레이시아 화물 및 물류 시장 규모는 전자상거래 업체들이 당일 배송 서비스를 복합 운송사에 아웃소싱함에 따라 2026년부터 2031년까지 연평균 5.86%의 성장률로 더 빠르게 성장하고 있습니다. UPS-닌자 밴의 확장된 클랑 밸리 지점과 같은 자동화 허브는 주소 확인 소프트웨어와 IoT 태그를 활용해 배송 실패율을 줄입니다. 온라인 주문이 트럭 적재 공간을 채우면서 운영사들은 틸트 트레이 분류기로 물류센터를 개조하고 쿠알라룸푸르 인근 정체 지점을 통과하기 위해 전기 밴을 도입하고 있습니다. 이 부문은 국경 간 통관 수수료를 억제하고 라벨링을 통일하는 16개 무역 협정의 혜택도 받으며, 중소기업의 해외 구매자 접근성을 높입니다. 지속적인 소포 밀도 증가는 항공사 화물칸 공급업체와의 협상력을 강화하지만, 생산성 향상보다 디젤 보조금 축소가 더 빠르게 진행될 경우 마진 압박 위험은 지속됩니다.
CEP(일반 택배) 외에도 창고 및 운송 업체들은 소규모 기업이 전체 팔레트 공간 대신 빈 상자만 임대할 수 있는 '사용량 기반 요금제'를 도입 중입니다. 온도 조절 운송은 말레이시아 할랄 인증 기준과 부합하여 수산물, 과자류, 생물학적 제제의 부가가치 통합 운송을 위한 프리미엄 노선을 개척하고 있습니다. 말레이시아 화물·물류 시장에서 화물 운송 비중은 2031년까지 소폭 감소할 전망입니다. 소포 및 계약 물류 활동이 불균형적으로 자본을 흡수하기 때문입니다. 그러나 대형 프로젝트 화물(태양광 패널, 터빈, 정유 탱크 등) 전용 트럭 운송은 여전히 기준 물량을 유지합니다. 기술 준비도, 규제 명확성, 인력 가용성이 기존 업체와 신규 진입자 중 누가 증분 가치를 확보할지 결정할 것입니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 인구통계
- 경제 활동별 GDP 분포
- 경제활동별 GDP 성장률
- 인플레이션
- 경제적 성능과 프로파일
- 전자상거래 업계 동향
- 제조업의 동향
- 운송, 저장 부문의 GDP
- 수출 동향
- 수입 동향
- 연료 가격
- 트럭 운송 운영 비용
- 트럭 운송 차량 규모(유형별)
- 주요 트럭 공급업체
- 물류 성능
- 운송 모드별 점유율
- 해상 운송선대의 적재능력
- 정기선 운송의 접속성
- 기항지와 성능
- 화물운임 동향
- 화물 운송량의 동향
- 인프라
- 규제 프레임워크(도로, 철도)
- 규제 프레임워크(해상, 항공)
- 밸류체인 및 유통채널 분석
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 폭발적인 B2C 전자상거래의 거래량
- 외국 직접투자주도의 제조업 생산 급증
- 정부 메가 프로젝트(ECRL, 범보르네오 고속도로)
- RCEP에 의한 국경을 넘은 무역의 흐름
- 인증 할랄 물류 수요 증가
- 백신 및 생물학적 제제용 콜드체인의 정비
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 항만과 마지막 마일 혼잡
- 만성적인 트럭 운전사 부족
- 국내 카보타지 정책으로 인한 연안 운송 제한
- 강화되는 유로-VI급 배출 규제로 인한 자본 지출 압박
- 시장의 기술 혁신
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 최종 사용자 산업
- 농업, 어업, 임업
- 건설업
- 제조업
- 석유 및 가스, 광업, 채석업
- 도매, 소매업
- 기타
- 물류 기능
- 택배, 익스프레스, 소포(CEP)
- 목적지별
- 국내
- 국제
- 목적지별
- 화물 운송
- 운송 수단별
- 항공
- 해상, 내륙 수로
- 기타
- 운송 수단별
- 화물 운송
- 운송 수단별
- 항공
- 파이프라인
- 철도
- 도로
- 해상, 내륙 수로
- 운송 수단별
- 창고, 보관
- 온도관리별
- 비온도 관리
- 온도 관리
- 온도관리별
- 기타 서비스
- 택배, 익스프레스, 소포(CEP)
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 주요 전략적 움직임
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- City-Link Express
- CJ Logistics Corporation
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(Including DB Schenker)
- FedEx
- FM Global Logistics Holdings Bhd
- GDEX Group
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Hextar Technologies Solutions Bhd
- J&T Express
- Keretapi Tanah Melayu Bhd
- Kuehne Nagel
- MMC Corporation Bhd
- NYK(Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- POS Malaysia Bhd
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- SkyNet Worldwide Express, Inc.
- Taipanco Sdn Bhd
- Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings Bhd
- Transocean Holdings Bhd
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
- Xin Hwa Holdings Bhd
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
HBR 26.02.04The Malaysia freight and logistics market is expected to grow from USD 29.70 billion in 2025 to USD 31.23 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 40.11 billion by 2031 at 5.14% CAGR over 2026-2031.
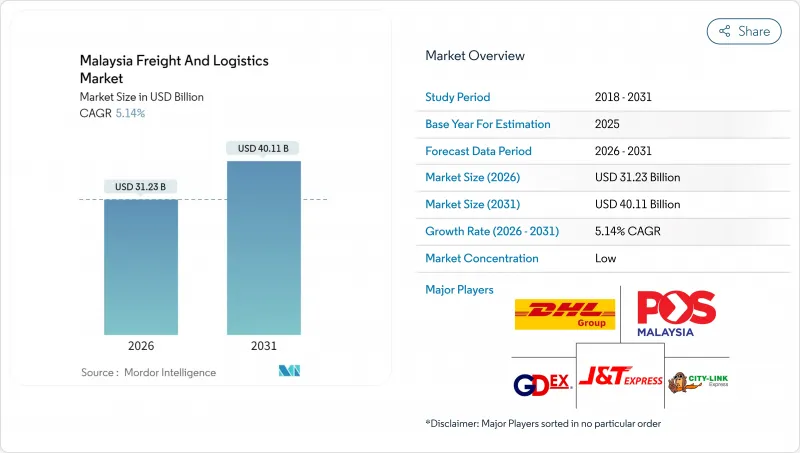
Port Klang's rise to the world's 10th-busiest container port, extensive government funding for rail and highway projects, and sustained e-commerce momentum are reshaping supply-chain networks, warehouse automation priorities, and carrier partnerships across the Malaysia freight and logistics market. Foreign direct investment reached MYR 378.5 billion (USD 82.3 billion) in 2024, creating 207,000 jobs and expanding demand for cross-border forwarding, value-added distribution, and specialized manufacturing logistics. Consumers' preference for same-day delivery is accelerating last-mile network densification, while regulatory moves such as targeted diesel subsidies and simplified customs windows are easing cost pressures and border friction. Global carriers are deepening local ties to secure air-cargo uplift, sea-freight allocations, and temperature-controlled capacity, reinforcing Malaysia's hub role within ASEAN and the broader Asia-Pacific trade lattice.
Malaysia Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
Explosive B2C E-commerce Volumes Drive Last-Mile Innovation
Same-day fulfillment has become a standard expectation, with leading platforms shipping 95% of orders within 24 hours. Free-delivery preferences among 64.8% of internet users are forcing providers in the Malaysia freight and logistics market to adopt automated sortation, micro-fulfillment centers, and data-driven route planning. Retailers such as MR DIY achieved 200% efficiency gains after installing robotic systems, proving that automation now underpins competitive advantage. Partnerships like UPS-Ninja Van extend global express products to 52 retail outlets, offering exporters wider belly-hold access and digital tracking that aligns with rising SME participation in regional trade. The cumulative impact adds capacity resilience and service diversity, supporting the near-term growth trajectory of the Malaysia freight and logistics market.
Surge in FDI-Led Manufacturing Output Transforms Industrial Logistics
Record MYR 378.5 billion (USD 82.3 billion) investment approvals in 2024 are channeling funds toward semiconductor fabs, advanced automotive components, and renewable-energy assemblies. Semiconductor investments are triggering demand for electrostatic-discharge-compliant packaging, secure robotics, and bonded-warehouse clearance lanes. Precision-engineering firms such as MKS Instruments are building "super centers" that require synchronized inbound raw-material flows and high-frequency outbound shipments. Cross-border tax incentives inside the Johor-Singapore Special Economic Zone are expected to add 100 projects and 20,000 skilled jobs, anchoring new corridors for the Malaysia freight and logistics market. As ESG criteria tighten, investors also prioritize multimodal nodes near renewable energy and rail spurs, reinforcing long-term freight diversification.
Port Congestion Constrains Capacity Despite Infrastructure Investment
Average vessel waiting times of 1.3-1.46 days at Port Klang, alongside yard utilization above 90%, undermine schedule dependability. The Malaysia Maritime Single Window, launched in February 2025, has trimmed documentation cycles from five days to mere hours, but physical quay expansions will still lag near-term TEU growth. Westports Holdings' multi-decade expansion blueprint aims to propel total capacity far beyond present limits, yet Red Sea rerouting has already intensified arrival bunching and yard overflow. As global carriers reallocate boxes, the Malaysia freight and logistics market faces short-term charter premium spikes and inventory imbalances that erode margin gains from higher throughput.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Mega-Projects Unlock Regional Connectivity
- RCEP Integration Accelerates Intra-ASEAN Trade Flows
- Chronic Truck-Driver Shortage Threatens Operational Scalability
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing held 38.98% of Malaysia freight and logistics market share in 2025, supported by Penang's MY 431 billion (USD 93.7 billion) export engine and Selangor's electronics clusters. Multinationals require bonded trucking corridors, ESD-safe warehouses, and secure-freight escorts, driving service differentiation. Growth in electric vehicle components and renewable energy equipment further expands the Malaysia freight and logistics market size for oversized container handling and specialized rigging. Wholesale and retail trade, although smaller in absolute dollars, is on pace for a 5.46% CAGR between 2026-2031 as disposable incomes rise and digital payment adoption widens. Supermarket chains like 99 Speed Mart plan to double store counts, demanding multi-temperature cross-docks and micro-fulfillment centers proximate to consumption hotspots.
Agriculture, fishing, and forestry depend on certified halal cold chains to penetrate Middle-East demand pools, giving algorithm-driven temperature traceability platforms greater commercial pull. Construction logistics ties directly to mega-projects such as the RTS Link and Penang Airport expansion, requiring heavy-lift cranes, night-time convoy escorts, and synchronized just-in-time material sequencing. Oil, gas, and mining remain cyclical but sustain steady demand for ISO tank containers, hull-cleaning services, and pipeline maintenance parts, anchoring a baseline for the Malaysia freight and logistics industry amid commodity swings.
Freight transport generated 55.62% of Malaysia freight and logistics market revenue in 2025, reflecting entrenched manufacturing exports and regional distribution flows. The Malaysia freight and logistics market size linked to courier, express, and parcel solutions is growing faster at a 5.86% CAGR (2026-2031) as e-retailers outsource same-day coverage to multi-modal carriers. Automated hubs, such as UPS-Ninja Van's expanded Klang Valley outlets, harness address-verification software and IoT tags to trim failed-delivery rates. As online orders fill truck bays, operators retrofit depots with tilt-tray sorters and deploy electric vans to navigate congestion nodes near Kuala Lumpur. The segment also benefits from 16 trade pacts that suppress cross-border clearance fees and harmonize labeling, easing SME access to overseas buyers. Continuous parcel-density escalation strengthens bargaining power with airline belly-hold providers, but margin compression remains a risk if diesel subsidies phase down faster than productivity gains materialize.
Beyond CEP, warehousing and forwarding units explore pay-as-you-use charging, allowing micro-enterprises to lease bins rather than full pallet slots. Temperature-controlled shipping aligns with Malaysia's halal-certification standards, opening premium lanes for value-added consolidation of seafood, confectionery, and biologics. The freight transport share of the Malaysia freight and logistics market is expected to decline marginally by 2031 as parcel and contract-logistics activities absorb disproportionate capital. Yet specialized trucking for oversized project cargo-solar panels, turbines, refinery vats-continues to anchor baseline volumes. Technology readiness, regulatory clarity, and workforce availability will largely determine whether incumbents or new entrants capture the incremental value.
The Malaysia Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Others) and by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- City-Link Express
- CJ Logistics Corporation
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- FedEx
- FM Global Logistics Holdings Bhd
- GDEX Group
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Hextar Technologies Solutions Bhd
- J&T Express
- Keretapi Tanah Melayu Bhd
- Kuehne+Nagel
- MMC Corporation Bhd
- NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- POS Malaysia Bhd
- SF Express (KEX-SF)
- SkyNet Worldwide Express, Inc.
- Taipanco Sdn Bhd
- Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings Bhd
- Transocean Holdings Bhd
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- Xin Hwa Holdings Bhd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.12 Trucking Fleet Size by Type
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Logistics Performance
- 4.15 Modal Share
- 4.16 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.17 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.18 Port Calls and Performance
- 4.19 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.20 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.21 Infrastructure
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.23 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.24 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.25 Market Drivers
- 4.25.1 Explosive B2C E-Commerce Volumes
- 4.25.2 Surge in FDI-led Manufacturing Output
- 4.25.3 Government Mega-Projects (ECRL, Pan-Borneo Highway)
- 4.25.4 RCEP-Driven Cross-Border Trade Flows
- 4.25.5 Rising Demand for Certified Halal Logistics
- 4.25.6 Cold-Chain Build-Out for Vaccines and Biologics
- 4.26 Market Restraints
- 4.26.1 Port and Last-Mile Congestion
- 4.26.2 Chronic Truck-Driver Shortage
- 4.26.3 Domestic Cabotage Policy Limits Coastal Shipping
- 4.26.4 Tightening Euro-VI - Like Emission Rules, Capex Squeeze
- 4.27 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.28 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.28.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.28.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.28.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.28.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.28.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 City-Link Express
- 6.4.2 CJ Logistics Corporation
- 6.4.3 DHL Group
- 6.4.4 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.5 FedEx
- 6.4.6 FM Global Logistics Holdings Bhd
- 6.4.7 GDEX Group
- 6.4.8 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- 6.4.9 Hextar Technologies Solutions Bhd
- 6.4.10 J&T Express
- 6.4.11 Keretapi Tanah Melayu Bhd
- 6.4.12 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.13 MMC Corporation Bhd
- 6.4.14 NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- 6.4.15 POS Malaysia Bhd
- 6.4.16 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.17 SkyNet Worldwide Express, Inc.
- 6.4.18 Taipanco Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.19 Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings Bhd
- 6.4.20 Transocean Holdings Bhd
- 6.4.21 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- 6.4.22 Xin Hwa Holdings Bhd
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment


















