
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1907302
인도네시아의 화물 및 물류 : 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Indonesia Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
인도네시아의 화물 및 물류 시장 규모는 2026년 1,393억 5,000만 달러로 평가되었습니다.
이는 2025년 1,312억 달러에서 성장한 수치이며, 2031년에는 1,883억 8,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)은 6.21%로 성장할 전망입니다.
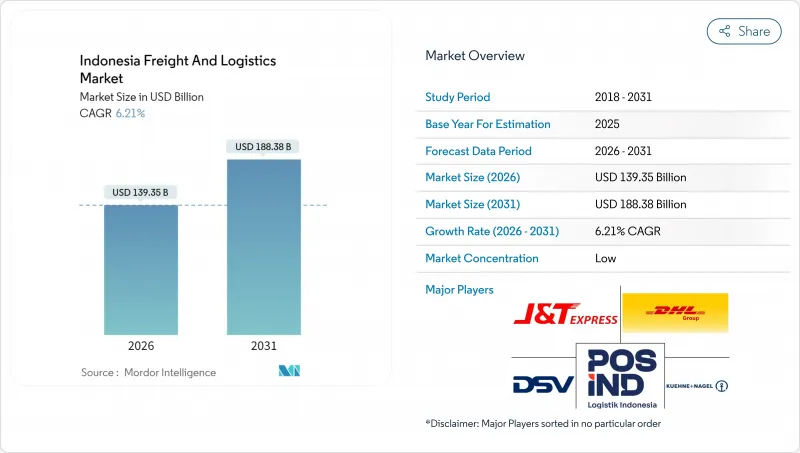
인도네시아의 전자상거래 붐, 2,700km에 달하는 신규 유료도로 개통, 수출 제조업 생산량 증가는 종합적으로 성장을 가속화하는 한편, 인프라 메가프로젝트는 자바 섬을 넘어 지리적 범위를 확대하고 있습니다. 국가 물류 생태계(NLE)와 같은 디지털 플랫폼에 대한 투자는 통관 시간을 단축하고 행정 비용을 낮추어 인도네시아의 화물 및 물류 시장에 구조적 효율성 향상을 가져옵니다. 동시에 콜드체인 시설 확충, 항공 화물 운송 능력 증대, 복합 운송망 업그레이드는 운영사들에게 서비스 차별화를 위한 경로를 제공합니다. 경쟁 역학은 데이터 기반 경로 최적화와 실시간 가시성 도구를 통해 심각한 도시 교통 정체, 변동성 높은 연료 가격, 중복 규제를 헤쳐나갈 수 있는 기술 기반 제공업체에게 유리하게 작용합니다.
인도네시아의 화물 및 물류 시장 동향 및 인사이트
전자상거래 붐과 소포 물량 급증
급속한 디지털화로 2025년까지 온라인 소매 거래가 연간 15% 증가하며, 전례 없는 소형 소포 물량이 라스트마일 네트워크로 유입됩니다. J&T 익스프레스, JNE 등 CEP 전문업체들은 자동화 허브와 픽업 포인트 생태계를 확장해 물류를 효율적으로 처리합니다. 자바의 고밀도 대도시권에서 주문이 집중되지만, 디지털 결제 확산으로 2선 도시에서도 두 자릿수 물량 증가를 기록 중입니다. 자카르타의 혼잡한 도시 간선도로로 인해 평균 배송 속도가 시속 10-15km에 그치면서 소포당 비용이 증가하고, 운영사들은 마이크로 풀필먼트, 이륜차 차량군, AI 기반 경로 계획으로 전환하고 있습니다. 세분화된 주소 데이터베이스와 동적 경로 설정을 보유한 업체들은 비용 우위를 점하는 반면, 전통적인 화물 운송업체들은 소비자 수준 배송을 위해 대량 화물 프로세스를 개조하기 위해 분주하다.
인프라 메가 프로젝트(유료 도로, 항만, 공항)
국가 전략 프로젝트 프로그램은 4,000억 달러를 도로, 항만, 공항에 투자하여 자바 산업 허브 간 이동 시간을 최대 40% 단축합니다. 2,700km 이상의 신규 유료도로가 내륙 공장과 주요 항만을 연결하며, INAPORTNET 항만 디지털화는 통관 대기 시간을 단축합니다. 마카사르 항의 주요 허브 격상화로 자바 혼잡을 완화하는 동부 수출 통로가 신설됩니다. 연결성 강화로 화물 운송업체는 복합 운송 경로를 재설계하여 재고 완충량을 줄이고 어업 지역으로의 콜드체인 확장을 용이하게 합니다. 지원 철도 지선 및 산업단지가 가동되면서 혜택은 점진적으로 누적되지만, 초기 도입업체들은 이미 개선된 장거리 운송 신뢰성을 바탕으로 창고 규모를 재최적화하고 있습니다.
심각한 도시 지역 정체와 라스트마일의 병목
자카르타의 평균 피크 시간대 속도는 10-15km/h에 머물러 배송비의 50%에 달하는 라스트마일 비용을 부풀립니다. CEP 업체들은 야간 배송, 마이크로 디포, 오토바이 택배를 통해 교통 정체를 우회하지만, 이러한 해결책은 인력 관리 복잡성을 가중시킵니다. 온도에 민감한 상품은 교통 정체 시 방치되면 변질 위험이 있어, 화주들은 프리미엄 시간 보장 서비스로 이동하고 있습니다. 홀짝제 같은 정부 조치는 일정 유연성이 부족한 상업용 트럭에 대한 한계적 완화책에 불과하다. 전자상거래 소포 물량이 증가함에 따라 도시 물류 구역 지정 및 도로 외 하역 규정이 개선되지 않는 한 정체 비용은 더욱 심화될 전망입니다.
부문 분석
2025년 인도네시아의 화물 및 물류 시장 수요의 28.45%는 자동차, 전자제품, 섬유 산업을 중심으로 제조업이 차지했습니다. 높은 수출 지향성은 보세 물류 센터와 항구 및 공항으로의 적시 납품을 요구합니다. 반면 도매 및 소매 무역은 중산층 소비가 확산되면서 2026-2031년 연평균 6.64% 성장률을 기록할 전망이며, 이로 인해 물류 기업들은 다중 노드 유통 구조 설계를 강요받고 있습니다. 농업, 어업 및 임업은 상품 수출과 연계된 안정적인 물량을 유지하는 반면, 건설 물류는 인프라 자본 지출 증가와 함께 상승세를 보입니다.
도매 및 소매 무역 고객들은 전국 주문에 대해 당일 또는 익일 배송을 점점 더 요구하며, 이로 인해 지역별 주문 처리 센터와 강력한 장거리 운송 연계의 필요성이 증가하고 있습니다. 제조업체 화주들은 순환 경제 목표를 채택하여 반품 및 재활용을 위한 역물류 흐름을 추가함으로써 인도네시아의 화물 및 물류 산업 내 서비스 포트폴리오를 더욱 다양화하고 있습니다.
2025년 인도네시아의 화물 및 물류 시장에서 화물 운송이 58.95%의 비중을 차지했습니다. CEP(소형 택배) 부문은 규모는 작지만 B2C 배송 증가에 힘입어 2026-2031년 연평균 7.12% 성장률을 기록하며 다른 기능들을 성장 속도에서 추월했습니다. 특히 산업단지와 수출항을 연결하는 해상-도로 복합 운송망에서 화물 운송 대행은 다모달 협조를 위한 필수 요소로 남아 있습니다. 기업들이 옴니채널 주문 처리 지원을 위해 재고 서비스형 모델을 도입함에 따라 창고 및 보관 수익은 꾸준히 증가하고 있습니다. 관세 중개 및 공급망 컨설팅과 같은 기타 서비스는 규제 복잡성과 무역 디지털화의 혜택을 받고 있습니다.
CEP(택배) 부문의 급성장은 연간 15%의 전자상거래 거래 증가율에 기인하며, 이는 고밀도 배송 네트워크와 높은 분류 처리량을 요구합니다. 자동화 허브는 소포당 비용을 절감하고 당일 배송 약속을 가능케 합니다. 화물 운송 사업자들은 소포 보관함 투자 및 차량 공유 업체와의 협력을 통해 경쟁력을 유지하고 있습니다. 한편, 창고 운영사들은 소포 흐름을 위해 크로스독 구역을 개조하며 인도네시아의 화물 및 물류 시장 내 기능적 융합을 부각시키고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 인구통계
- 경제 활동별 GDP 분포
- 경제활동별 GDP 성장률
- 인플레이션
- 경제성과와 개요
- 전자상거래 업계 동향
- 제조업의 동향
- 운송, 보관 부문의 GDP
- 수출 동향
- 수입 동향
- 연료 가격
- 트럭 운송 운영 비용
- 트럭 운송 차량 규모(유형별)
- 주요 트럭 공급업체
- 물류 성과
- 운송 모드별 점유율
- 해상 운송선대의 적재능력
- 정기선 운송의 접속성
- 기항 및 성과
- 화물운임 동향
- 화물 운송량의 동향
- 인프라
- 규제 프레임워크(도로, 철도)
- 규제 프레임워크(해상, 항공)
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 전자상거래의 급성장과 소포 취급량의 급증
- 인프라 메가 프로젝트(유료 도로, 항만, 공항)
- 제조업, 수출 회복(자동차, 전자기기, 섬유제품)
- 국내 소비 증가와 중산계급 지출 확대
- 국가물류 생태계(NLE) 디지털 플랫폼 도입
- 양식업 및 수산물 수출에 의한 콜드체인 수요
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 심각한 도시의 정체와 라스트마일 병목
- 규제의 단편화와 라이선스 중복
- 높은 연료 가격 변동성
- 물류 기술 인력 부족
- 시장의 기술 혁신
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 최종 사용자 산업
- 농업, 어업, 임업
- 건설업
- 제조업
- 석유 및 가스, 광업, 채석업
- 도매, 소매업
- 기타
- 물류 기능
- 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP)
- 목적지별
- 국내
- 국제
- 목적지별
- 화물 운송
- 운송 수단별
- 항공
- 해상, 내륙 수로
- 기타
- 운송 수단별
- 화물 운송
- 운송 수단별
- 항공
- 파이프라인
- 철도
- 도로
- 해상, 내륙 수로
- 운송 수단별
- 창고 보관
- 온도 관리별
- 비온도 관리
- 온도 관리
- 온도 관리별
- 기타 서비스
- 택배, 특송 및 소포(CEP)
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 주요 전략적 움직임
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(Including DB Schenker)
- Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- FedEx
- J&T Express
- Kuehne Nagel
- Linfox Pty Ltd.
- LOGWIN
- Ninja Van(Including Ninja Express)
- NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- Pancaran Group
- PT ABM Investama TBK(including CKB Logistics)
- PT Bina Sinar Amity(BSA Logistics Indonesia)
- PT Cardig International
- PT Citrabati Logistik International
- PT Dunia Express Transindo
- PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir(JNE Express)
- PT Kamadjaja Logistics
- PT Lautan Luas TBK
- PT Pandu Siwi Group(Pandu Logistics)
- PT Perusahaan Perdagangan Indonesia(including BGR Indonesia)
- PT Pos Indonesia(Persero)
- PT Repex Wahana(RPX)
- PT Samudera Indonesia Tangguh
- PT Satria Antaran Prima TBK(SAPX Express)
- PT Siba Surya
- PT Soechi Lines Tbk
- Puninar Logistics
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- Sinotrans, Ltd.
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
HBR 26.02.04The Indonesia freight and logistics market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 139.35 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 131.20 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 188.38 billion, growing at 6.21% CAGR over 2026-2031.
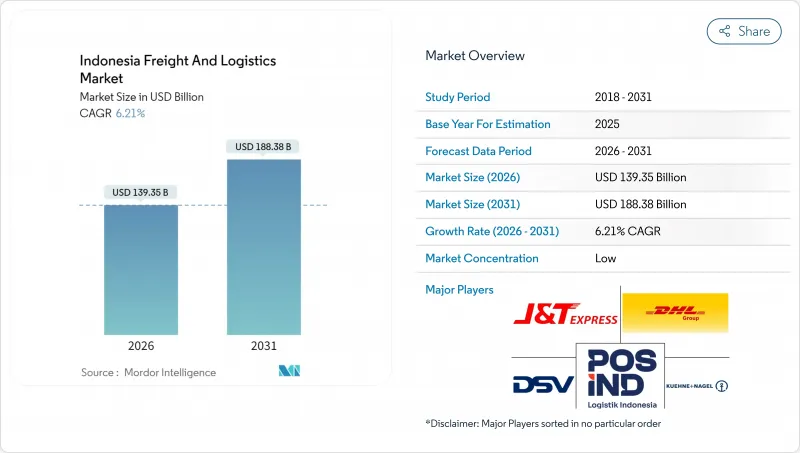
The archipelago's e-commerce boom, the rollout of 2,700 km of new toll roads, and rising export manufacturing output collectively accelerate growth, while infrastructure megaprojects widen geographic coverage beyond Java. Investment in digital platforms such as the National Logistics Ecosystem (NLE) shortens customs clearance times and lowers administrative costs, giving the Indonesia freight and logistics market a structural efficiency lift. Simultaneously, cold-chain facility build-outs, Air freight capacity additions, and multimodal network upgrades provide operators with routes to higher service differentiation. Competitive dynamics favor technology-enabled providers that can navigate severe urban congestion, volatile fuel prices, and overlapping regulations with data-driven route optimization and real-time visibility tools.
Indonesia Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
E-Commerce Boom and Parcel-Volume Surge
Rapid digitization lifts online retail transactions by 15% annually to 2025, funneling unprecedented small-parcel volumes into last-mile networks. CEP specialists such as J&T Express and JNE scale automated hubs and pickup-point ecosystems to handle the flow efficiently. Java's dense conurbations dominate order originations, yet tier-2 cities now post double-digit volume gains as digital payments proliferate. Congested urban arteries in Jakarta limit average delivery speeds to 10-15 km/h, inflating per-package costs and pushing operators toward micro-fulfillment, two-wheeler fleets, and AI-driven route planning. Players with granular address databases and dynamic routing enjoy cost advantages, while traditional freight forwarders scramble to retrofit bulk-cargo processes for consumer-level deliveries.
Infrastructure Megaprojects (Toll Roads, Ports, Airports)
The National Strategic Projects program channels USD 400 billion into roads, ports, and airports, slicing transit times between Java's industrial hubs by as much as 40%. Over 2,700 km of new tollways integrate inland factories with main ports, while INAPORTNET port digitalization shaves customs dwell times. Makassar Port's elevation to major-hub status creates new eastern export corridors that dilute Java congestion. Enhanced connectivity allows freight forwarders to redesign multimodal routes, lowering inventory buffers and facilitating cold-chain expansion into fisheries regions. Benefits accrue gradually as supporting hinterland rail spurs and industrial estates come online, but early adopters already re-optimize warehouse footprints around improved linehaul reliability.
Severe Urban Congestion and Last-Mile Bottlenecks
Jakarta's average peak-hour speed hovers at 10-15 km/h, inflating last-mile fees that can reach 50% of delivery cost. CEP providers deploy night deliveries, micro-depots, and motorcycle couriers to sidestep gridlock, yet these workarounds add labor complexity. Temperature-sensitive goods risk spoilage when idling in traffic, pushing shippers toward premium guaranteed-time services. Government measures such as odd-even license plate schemes offer marginal relief for commercial trucks that lack schedule flexibility. As e-commerce parcel volumes rise, congestion costs are expected to intensify unless city logistics zoning and off-street loading regulations evolve.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Manufacturing-Export Rebound (Autos, Electronics, Textiles)
- Rising Domestic Consumption and Middle-Class Spending
- Fragmented Regulations and Overlapping Licenses
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing generated 28.45% of Indonesia freight and logistics market demand in 2025, driven by automotive, electronics, and textiles. High export orientation demands bonded logistics centers and just-in-time deliveries to ports and airports. Wholesale and Retail Trade, however, expands at a 6.64% CAGR (2026-2031) as middle-class consumption proliferates, forcing logistics firms to design multi-node distribution architectures. Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry maintain steady volumes tied to commodity exports, while Construction logistics climb with infrastructure capex.
Wholesale and Retail Trade clients increasingly stipulate same-day or next-day delivery for nationwide orders, escalating the need for regional fulfillment centers and robust line-haul linkages. Manufacturing shippers adopt circular-economy objectives, adding reverse-logistics flows for returns and recycling, further diversifying service portfolios within the Indonesia freight and logistics industry.
Freight Transport contributed a 58.95% share to the Indonesia freight and logistics market in 2025. CEP, though smaller, posts a 7.12% CAGR (2026-2031) on the back of rising B2C shipments, overtaking other functions in growth velocity. Freight Forwarding remains indispensable for multimodal coordination, especially on sea-road chains linking industrial estates to export ports. Warehousing and Storage revenue scales steadily as firms adopt inventory-as-a-service models to support omnichannel fulfillment. Other Services, such as customs brokerage and supply-chain consulting, benefit from regulatory complexity and trade digitalization.
CEP's surge stems from 15% annual e-commerce transaction growth, necessitating dense delivery networks and high sortation throughput. Automated hubs reduce cost-per-package and enable same-day delivery promises. Freight Transport operators invest in parcel lockers and collaboration with ride-hailing fleets to retain relevance. Meanwhile, warehouse operators retrofit cross-dock areas for parcel flow, underscoring functional convergence within the Indonesia freight and logistics market.
The Indonesia Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Others), Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- FedEx
- J&T Express
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Linfox Pty Ltd.
- LOGWIN
- Ninja Van (Including Ninja Express)
- NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- Pancaran Group
- PT ABM Investama TBK (including CKB Logistics)
- PT Bina Sinar Amity (BSA Logistics Indonesia)
- PT Cardig International
- PT Citrabati Logistik International
- PT Dunia Express Transindo
- PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir (JNE Express)
- PT Kamadjaja Logistics
- PT Lautan Luas TBK
- PT Pandu Siwi Group (Pandu Logistics)
- PT Perusahaan Perdagangan Indonesia (including BGR Indonesia)
- PT Pos Indonesia (Persero)
- PT Repex Wahana (RPX)
- PT Samudera Indonesia Tangguh
- PT Satria Antaran Prima TBK (SAPX Express)
- PT Siba Surya
- PT Soechi Lines Tbk
- Puninar Logistics
- SF Express (KEX-SF)
- Sinotrans, Ltd.
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.12 Trucking Fleet Size By Type
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Logistics Performance
- 4.15 Modal Share
- 4.16 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.17 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.18 Port Calls And Performance
- 4.19 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.20 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.21 Infrastructure
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.23 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.24 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.25 Market Drivers
- 4.25.1 E-Commerce Boom and Parcel-Volume Surge
- 4.25.2 Infrastructure Megaprojects (Toll Roads, Ports, Airports)
- 4.25.3 Manufacturing-Export Rebound (Autos, Electronics, Textiles)
- 4.25.4 Rising Domestic Consumption and Middle-Class Spending
- 4.25.5 National Logistics Ecosystem (NLE) Digital Platform Rollout
- 4.25.6 Cold-Chain Demand from Aquaculture and Seafood Exports
- 4.26 Market Restraints
- 4.26.1 Severe Urban Congestion and Last-Mile Bottlenecks
- 4.26.2 Fragmented Regulations and Overlapping Licenses
- 4.26.3 High Fuel-Price Volatility
- 4.26.4 Shortage of Logistics-Tech Talent
- 4.27 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.28 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.28.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.28.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.28.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.28.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.28.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 DHL Group
- 6.4.2 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.3 Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- 6.4.4 FedEx
- 6.4.5 J&T Express
- 6.4.6 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.7 Linfox Pty Ltd.
- 6.4.8 LOGWIN
- 6.4.9 Ninja Van (Including Ninja Express)
- 6.4.10 NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- 6.4.11 Pancaran Group
- 6.4.12 PT ABM Investama TBK (including CKB Logistics)
- 6.4.13 PT Bina Sinar Amity (BSA Logistics Indonesia)
- 6.4.14 PT Cardig International
- 6.4.15 PT Citrabati Logistik International
- 6.4.16 PT Dunia Express Transindo
- 6.4.17 PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir (JNE Express)
- 6.4.18 PT Kamadjaja Logistics
- 6.4.19 PT Lautan Luas TBK
- 6.4.20 PT Pandu Siwi Group (Pandu Logistics)
- 6.4.21 PT Perusahaan Perdagangan Indonesia (including BGR Indonesia)
- 6.4.22 PT Pos Indonesia (Persero)
- 6.4.23 PT Repex Wahana (RPX)
- 6.4.24 PT Samudera Indonesia Tangguh
- 6.4.25 PT Satria Antaran Prima TBK (SAPX Express)
- 6.4.26 PT Siba Surya
- 6.4.27 PT Soechi Lines Tbk
- 6.4.28 Puninar Logistics
- 6.4.29 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.30 Sinotrans, Ltd.
- 6.4.31 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment


















